Camouflage and Survival Techniques of Tropical Hummingbirds
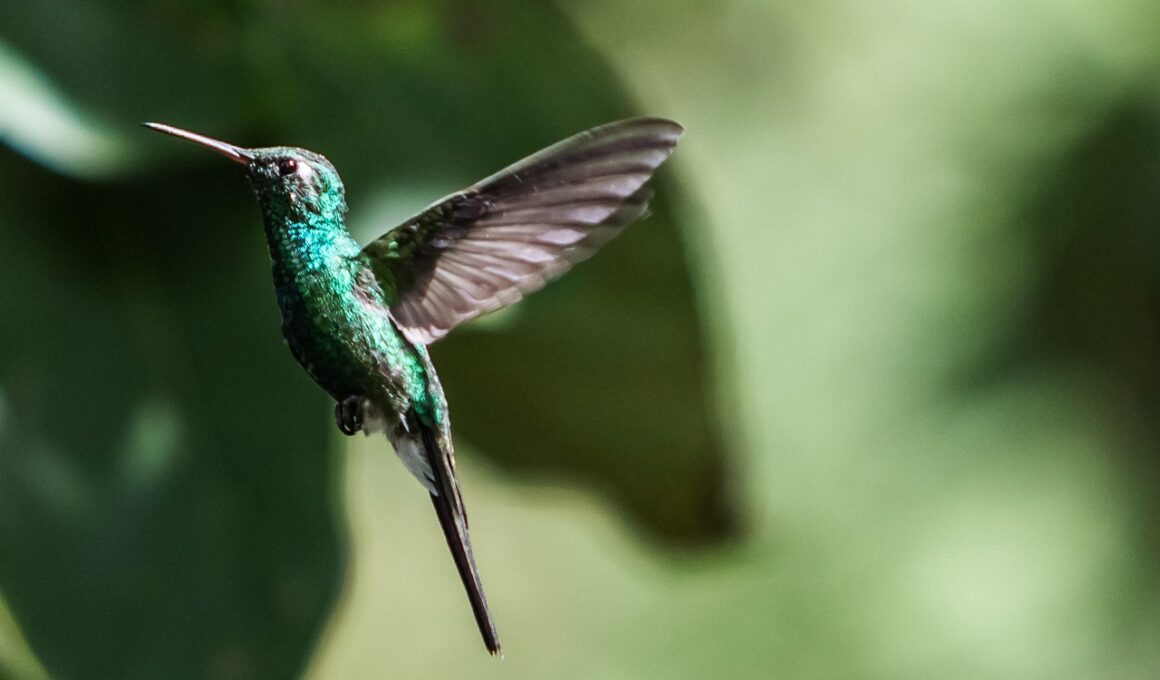
Tropical hummingbirds are remarkable creatures, known for their iridescent feathers and agility. Their survival strategies are intricate and fascinating, primarily relying on camouflage and behavioral adaptations. One notable tactic involves their coloration, which helps them blend effortlessly with the surrounding flora. For instance, many species exhibit vibrant colors that mimic the flowers they frequent. This not only helps them evade predators but also attracts mates. Research shows that their bright plumage can vary based on their habitat and the specific environmental cues. Additionally, their ability to hover allows them to remain concealed while foraging for nectar, enhancing their chances of survival. Further, during the breeding season, some species display altered feathers to further enhance camouflage. In this crucial period, it is vital for them to avoid detection by both predators and competing males. Observations indicate that females, particularly during nesting, choose locations rich in foliage to obscure their nests from sight. These strategies are essential for maintaining their population in the wilderness, where every advantage counts in ensuring their survival against predator threats.
Another fascinating aspect of tropical hummingbird survival includes their remarkable agility and speed. These birds can perform incredible aerial maneuvers, allowing them to dart quickly from flower to flower in search of nectar. This ability not only facilitates feeding but also aids in avoiding potential threats. Their flight requires a high level of energy, encouraged by their specialized diet of nectar and insects. To fuel their energetic lifestyles, hummingbirds consume around twice their body weight in sugar daily. Additionally, some species utilize specific flower types that provide a reliable and energy-rich food source. Their remarkable memory plays a key role in survival; studies reveal that these birds can remember the locations of individual flowers, which are often highly localized. With seasonal migrations, tropical hummingbirds showcase their adaptability to varying environments, using memory to navigate through their habitats. In addition to their feeding techniques, the use of specific perches helps them survey their surroundings, enhancing their detection capabilities for potential dangers. Each feature of their anatomy and behavior is finely tuned to enrich their survival prospects in the complex ecosystems where they thrive.
Coping with Predators
Predators are a significant concern for tropical hummingbirds, and they have developed several strategies to cope with these threats. Camouflage plays a crucial role, where specific colors and patterns help them blend in with their environment. For example, their feathers can mimic the leaves or flowers of their habitat, making it difficult for predators to spot them. Furthermore, these birds utilize their speed and maneuverability to escape from danger swiftly. When threatened, hummingbirds can perform rapid changes in direction, which often confuses predators. Another survival strategy includes their vigilant behavior; these birds are always on alert, constantly scanning their surroundings for movement. They also engage in strategic perches to monitor their feeding areas and identify potential threats. In social settings, group behavior might serve as a defense mechanism. When a flock is present, individual hummingbirds can benefit from the enhanced vigilance of their companions. This collective awareness increases the chances of detecting predators early, granting them vital extra seconds to react and flee. Overall, combining visual camouflage with behavioral adaptations allows tropical hummingbirds to thrive despite the dangers posed by predation.
Social interactions among tropical hummingbirds also play a vital role in their survival strategies. Many species display complex behaviors, engaging in various social interactions that ultimately enhance their chances of survival. For instance, during feeding, they may establish territories, leading to competition with other individuals. Aggressive displays and vocalizations often accompany these territorial disputes, signaling dominance without physical confrontations. Such behaviors not only reinforce social hierarchies but also help maintain a balance in resource access among peers. Furthermore, witnessing another individual’s actions can provide crucial information about potential dangers, allowing them to make informed decisions. When a fellow hummingbird detects a predator or danger, its alarm calls can alert others nearby. Additionally, communal roosting is another behavior that enhances protection during the night. By huddling together, hummingbirds can share warmth and increase their safety from nocturnal predators. The social dynamics within groups assist each member in navigating threats and resource competition more effectively. Research into these dynamics continues to provide fascinating insights into the adaptive behaviors of tropical hummingbirds, shedding light on their complex world driven by survival.
Nesting Strategies
Nesting strategies among tropical hummingbirds are diverse and meticulously crafted to enhance offspring survival. The selection of nesting sites is crucial; many species prefer to construct nests in dense vegetation that offers natural cover from predators. Often, females build their nests using materials such as spider silk, plant fibers, and feathers, creating a secure and insulated environment for their eggs. The choice of location also considers factors like proximity to feeding sites, ensuring easy access to nectar sources during the demanding feeding period. Some species even select locations that provide a view of potential threats, enabling them to respond quickly if needed. Additionally, behavior during the early stages is critical; females often take turns incubating eggs while remaining vigilant against intruders. The design and placement of nests may also help in camouflage, making them less noticeable in the surrounding foliage. After fledging, juvenile hummingbirds continue to rely on the mother’s guidance for survival, learning feeding techniques and predator evasion strategies. Constant adaptation to changing environments is essential, with successful nesting playing a significant role in maintaining their populations within tropical ecosystems.
Adaptations in physical features also enhance the survival of tropical hummingbirds. Their unique beak shapes vary significantly depending on their feeding preferences and ecological niches. Some species possess long, slender bills optimized for probing deep into flowers, while others have broader beaks suited for accessing nectar more efficiently. These variations allow them to exploit different floral resources, reducing competition. Moreover, their dynamic wing structure grants incredible maneuverability, enabling rapid ascents and descents. This ability proves advantageous while navigating through crowded environments, enabling them to evade predators more effectively. Furthermore, their high metabolic rates necessitate frequent feeding, pushing hummingbirds to maintain robust feeding territories. Adaptation extends to feather structure; iridescent feathers are not merely for attraction but also serve in camouflage. Depending on the light conditions, these feathers can appear to change color, making it challenging for predators to pinpoint their location. Moreover, some species exhibit color variations that adjust with age and season, enhancing their survival strategies. Continuous evolution allows these birds to thrive in their respective niches within the tropical landscapes they inhabit, ensuring their continued existence and ecological role.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the survival of tropical hummingbirds hinges on their myriad coping techniques, which blend camouflage, social interaction, and physical adaptations. Their vibrant yet strategic coloration allows them to navigate complicated relationships with their environments while evading predators. The agility of these birds, combined with their keen observational skills and memory, ensures continued success in their ecosystems. In nesting, their choices reflect profound adaptations to enhance their offspring’s safety. Furthermore, social dynamics enrich their chances of survival, supporting individual success through awareness and vigilance. As researchers continue to explore these fascinating behavioral patterns, the complexity of hummingbirds’ survival strategies becomes increasingly evident. The adaptations illustrate a remarkable evolutionary process that highlights intricate relationships within tropical environments. Each strategy — from foraging techniques to nesting behavior — contributes to the resilience required for survival in ever-changing landscapes. Understanding these dynamics underscores the need for habitat conservation, ensuring that future generations of tropical hummingbirds can flourish. Protecting their ecosystems strengthens not only their species but the delicate balance within which they reside, emphasizing the vital importance of ecological preservation.
Tropical hummingbirds are remarkable creatures, known for their iridescent feathers and agility. Their survival strategies are intricate and fascinating, primarily relying on camouflage and behavioral adaptations. One notable tactic involves their coloration, which helps them blend effortlessly with the surrounding flora. For instance, many species exhibit vibrant colors that mimic the flowers they frequent. This not only helps them evade predators but also attracts mates. Research shows that their bright plumage can vary based on their habitat and the specific environmental cues. Additionally, their ability to hover allows them to remain concealed while foraging for nectar, enhancing their chances of survival. Further, during the breeding season, some species display altered feathers to further enhance camouflage. In this crucial period, it is vital for them to avoid detection by both predators and competing males. Observations indicate that females, particularly during nesting, choose locations rich in foliage to obscure their nests from sight. These strategies are essential for maintaining their population in the wilderness, where every advantage counts in ensuring their survival against predator threats.