Classifying Desert Animals Based on Metabolic Adaptations
Desert environments are challenging, yet a variety of animals have evolved to thrive in such conditions. These unique habitats experience extreme temperatures and limited water resources. To survive, desert animals exhibit diverse metabolic adaptations. Understanding these adaptations reveals insights into their survival strategies. This classification includes animals that have specific physiological traits developed to cope with minimal water availability and high evaporation rates. Metabolic strategies, such as water conservation, energy efficiency, and temperature regulation, categorize these species. For instance, some animals have adapted to reduce their metabolic rate during the hottest part of the day. This allows them to endure heat stress more effectively. Others, such as camels, store fat in their humps, which can be converted into water during metabolism. Such adaptations enable these creatures to minimize dehydration risks. Additionally, behavioral adaptations, such as nocturnal lifestyles, further assist in conserving water and avoiding midday heat. Studying these classifications enhances our knowledge of survival in extreme environments. Ultimately, recognizing these adaptations underscores the resilience of life in deserts.
Water Conservation Strategies
One of the most critical adaptations of desert animals is their ability to conserve water. Animals like the kangaroo rat can survive without direct water sources, extracting moisture from their food. This is achieved through specialized kidneys that excrete highly concentrated urine, thus minimizing water loss. Their ability to metabolize seeds and other plants contributes to their hydration level. Many desert reptiles, such as the desert tortoise, can withstand long periods without water by entering a state of dormancy during dry spells. They emerge only when it rains, taking advantage of temporary water availability. This survival strategy highlights the importance of biological adaptations in desert environments. Additionally, some animals exhibit behaviors that enhance water conservation, like burrowing into the ground to escape heat and retain moisture. This underground lifestyle significantly reduces evaporative loss. Besides these adaptations, nocturnal activity patterns also help mitigate hydration loss during the day. Many mammals, including foxes and rodents, are primarily active during the cool nights, which aids in maintaining their water balance. Observing and understanding these water conservation strategies offers insights into the resilience of desert species.
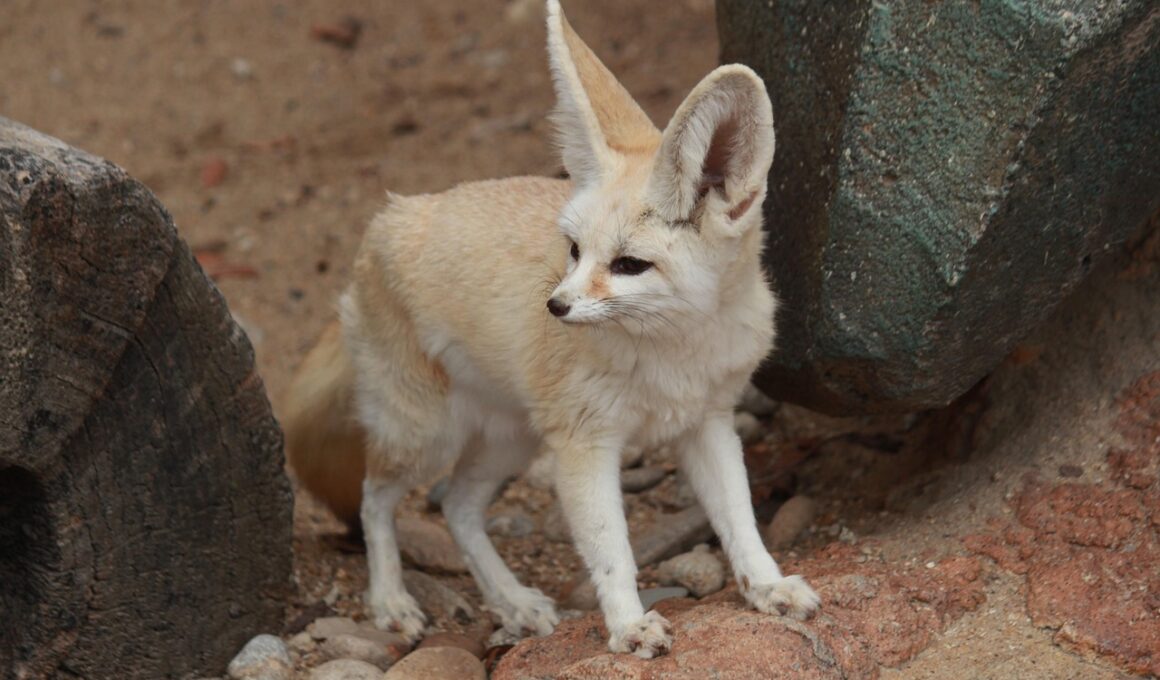
Thermoregulation is another essential metabolic adaptation of desert animals and plays a crucial role in their survival. Animals in extreme heat face the risk of overheating, making effective temperature regulation critical. Camels, often called ‘ships of the desert,’ possess remarkable capabilities to tolerate high body temperatures. They can allow their body temperatures to rise significantly before sweating. This adaptation enables them to conserve water during periods of extreme heat. Furthermore, these animals have a specialized cooling mechanism through their saliva and perspiration. Reptilian species, such as the sidewinder snake, utilize behavioral adaptations for thermoregulation, such as moving sideways across hot sands to limit direct contact with the ground. They also have the ability to change shade during the day, periodically seeking coolness beneath shrubs. Another example of thermoregulation is seen in desert foxes, which exhibit larger ears that enhance heat dissipation. Fat storage also plays an essential role, as animals can convert this to energy during scarce times. By studying these thermoregulatory adaptations, researchers can further appreciate the ingenuity of life in extreme environments.
Energy Efficiency
In the harsh desert landscape, energy efficiency is paramount for survival. Many species have adapted their behaviors and metabolic processes to make the most of their limited food resources. For instance, animals like the desert hare have developed a slower metabolism that allows them to thrive on less food. They often consume fibrous plants that provide minimal energy, yet are abundant in their environment. This evolutionary adaptation enables them to toggle between hunger and minimal energy expenditure successfully. Additionally, some animals can lower their metabolic rates during periods of scarce food availability, thus conserving energy. This strategy is not only critical for survival but also facilitates reproduction during seasonal abundance. Predators, such as the desert fox, have adapted hunting techniques to maximize energy gains while minimizing energy expenditure. They often rely on stealth and patience, stalking their prey to ensure successful hunts. Understanding energy efficiency adaptations provides valuable insights into the survival strategies employed by desert animals. Researchers emphasize that energy conservation and utilization are critical elements that allow these species to thrive despite harsh environmental challenges. Further studies may reveal even more extraordinary adaptations in the future.
Desert animal classification based on metabolic adaptations also considers their reproductive strategies. Many desert species display unique reproductive behaviors that align with environmental conditions. For instance, oviparous species, like certain reptiles, lay eggs that can withstand the desert’s harsh climate. These eggs are often buried in sand, providing insulation and moisture until they hatch. During the rainy season, most animals engage in breeding activities, synchronized with food availability. Polyandrous mating systems are observed in some species, increasing genetic diversity while ensuring better resource utilization. Mammals, such as the desert kangaroo, give birth to underdeveloped young. Initially, these young rely heavily on their mother’s milk, which is rich in nutrients and helps reduce energy expenditure. Moreover, some animals can delay reproduction until conditions are favorable, ensuring successful offspring survival. This strategy is crucial for maintaining population stability in challenging environments. Understanding these reproductive strategies sheds light on the complexities of life in deserts. Studying reproductive adaptations allows researchers to support conservation efforts, ensuring these species continue to thrive despite an ever-changing habitat.
Behavioral Adaptations
Behavioral adaptations are integral in understanding how desert animals cope with their environments. Many desert species exhibit unique behavioral traits that enable them to successfully navigate harsh conditions. Nocturnal activity is common; by being active at night, animals reduce heat exposure and conserve water more efficiently. For example, the desert fox predominantly hunts during cooler night hours. Furthermore, many species avoid surface activity during the hottest part of the day. Some animals, such as the mejican mouse, display specific foraging behaviors that optimize resource acquisition. Burrowing is also prevalent among desert-dwelling creatures, providing protection from heat and predators. These burrows create microclimates that offer relief from extreme temperatures. Additionally, specific social behaviors can enhance survival through group living, allowing sharing of resources and alertness to predators. Observing improvements in foraging and mating behaviors can provide insights into the evolution of desert species. Understanding these behavioral adaptations contributes significantly to the broader context of ecological resilience in desert environments. Such behavioral strategies underscore the importance of adaptability to climate extremes and inform future conservation efforts for these unique species.
In conclusion, classifying desert animals based on their metabolic adaptations reveals the remarkable ingenuity of life surviving in extreme environments. Various adaptations including water conservation strategies, thermoregulation, energy efficiency, and behavioral responses highlight how these creatures have evolved to cope with the challenges posed by desert habitats. Each adaptation serves as a vital component in their survival toolkit, allowing them to manage scarce resources effectively. Understanding these classifications not only fills knowledge gaps about biodiversity but also underscores the importance of these species in maintaining ecological balances. Furthermore, studying these metabolic adaptations can inform conservation efforts aimed at protecting desert ecosystems. These environments are increasingly threatened by climate change and human encroachment, making it crucial to safeguard the unique adaptations that allow these animals to thrive. By prioritizing the preservation of desert habitats and understanding the intricacies of life within them, future generations can appreciate the resilience of these remarkable species. Ultimately, classifying desert animals emphasizes the interdependence of life and environment, highlighting the need for continued research and conservation.
In summary, classifying desert animals based on their metabolic adaptations provides valuable insights into survival strategies in harsh environments. Recognizing the significance of each adaptation allows for a deeper understanding of how these creatures navigate their challenging habitats. The complex interplay of physiological, behavioral, and reproductive adaptations showcases the resilience and diversity of life in deserts. Whether through conserving water, regulating body temperature, or optimizing energy use, desert animals demonstrate remarkable adaptations that ensure their survival. Understanding these classifications also enhances conservation efforts, promoting the protection of vulnerable species. As research continues, new discoveries about desert adaptations can emerge. This knowledge can augment efforts to mitigate the impact of environmental change. Ultimately, preserving desert ecosystems is vital for maintaining biodiversity and ensuring the continued survival of these remarkable animals. By exploring the richness of desert life and the stunning adaptations that facilitate survival, we uncover the extraordinary creativity of nature. So, let us delve deeper into the world of desert animals and appreciate their adaptations with newfound respect and curiosity. The marvels of life in the desert inspire a greater connection to nature and its complexities.