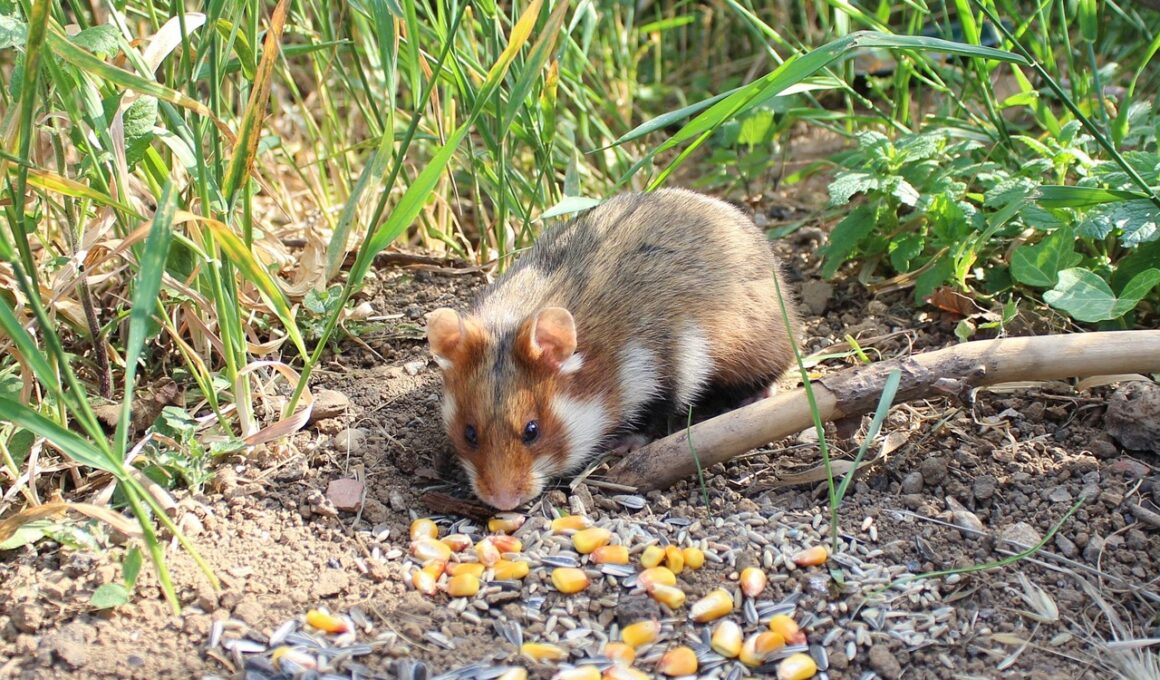
Exploring Hamster Habitats in the Wild
Hamsters are small mammals belonging to the family Cricetidae, native to various regions around the world. Their habitats typically range from arid deserts to grasslands, demonstrating an adaptability to different environments. Wild hamsters are primarily found in areas with adequate burrowing opportunities. For instance, regions like Eurasia and the Middle East provide dry, sandy soil suitable for their living habits. Common species include the Golden hamster and the Syrian hamster, both recognized for their portability as pets. They often dig intricate tunnel systems to evade predators and store food. These burrows feature multiple chambers, which serve various purposes such as nesting and food storage. Hamsters naturally forage for seeds, roots, and grains, contributing to the local ecosystem’s balance. In the wild, their diets are diverse, allowing them to thrive in different terrains. Seasonal changes also impact their behavior, as hamsters tend to store excess food during fall for winter months. Observing these creatures in their wild habitats showcases their amazing adaptations. Furthermore, understanding their environment helps promote responsible pet ownership by replicating these conditions as much as possible.
In addition to their burrows, understanding humidity and temperature is crucial for hamsters. The right climate influences their health, activity level, and overall well-being. Wild hamsters prefer moderate temperatures, avoiding extremes that could lead to stress or hibernation. During severe weather, they stay underground, where it remains relatively stable. This leads to a significant area of interest when it comes to pet care. Hamster owners must replicate these conditions within their cages to keep them healthy. A suitable habitat should include bedding that provides warmth, such as paper-based materials or aspen shavings, which accommodate their burrowing instincts. Moreover, maintaining appropriate humidity levels and avoiding drafts are essential to preventing respiratory issues. Providing essential enrichment through toys and tunnels also mimics their natural behavior. These activities engage their natural exploration instincts, preventing boredom and stress, which may lead to health decline. Understanding their wild habitats emphasizes the importance of a well-structured living environment for pet hamsters. As we appreciate their charm as pets, a close examination reveals how much they resemble their wild counterparts, making it vital for owners to prioritize their health and happiness.
Dietary Needs and Foraging Behavior
Dietary habits of hamsters in the wild are notably diverse, affecting their health and development. In their natural habitats, they consume seeds, grains, and occasional insects, showcasing their omnivorous nature. This variety allows them to meet their nutritional needs efficiently. Foraging behavior involves a keen sense of smell and hunting skills, essential for locating food sources. Hamsters typically search for food during twilight hours, staying hidden to avoid predators. This behavior is mirrored in captivity, where balanced diets should replicate wild meals. Selecting high-quality pellet mixes or specially formulated diets ensures pets receive necessary nutrients. Incorporating fresh fruits and veggies further enhances their diet, but it must be done cautiously to avoid digestive upset. Additionally, hamsters naturally hoard food in their burrows, which reflects their instinctual behavior. Owners can encourage similar behaviors by providing hiding places in cages filled with treats. These enrichment activities create a more enjoyable living experience, reducing stress levels. Moreover, creating a balance between wild-inspired diets and safety ensures pet hamsters can thrive. Observing how they forage hones awareness for both hamster lovers and pet owners to promote healthier lifestyles for these fascinating creatures.
Social interactions amongst hamsters in the wild vary significantly based on species. Generally, wild hamsters are solitary creatures, often establishing territorial boundaries to avoid confrontations. This behavior remains consistent when they are domesticated. Different species exhibit distinct social dynamics, giving insights into how hamsters interact with their environment and fellow members, if they exist. Syrian hamsters, for example, are highly territorial and prefer isolation, making them less suitable for communal living situations. Conversely, Roborovski hamsters can exhibit more social behaviors, allowing potential housing in pairs or small groups. Understanding their social structures aids owners in providing appropriate housing arrangements, reducing stress during enclosure. However, cohabitation needs careful observation; aggressive behaviors may arise. Providing vast living spaces, multiple hides, and various resources can alleviate tensions. Note also that environmental factors influence interactions; overcrowded spaces lead to competition and conflict. Thus, recreating a natural habitat as closely as possible fosters a more relaxed environment. Acknowledging these social behaviors enriches the understanding of hamsters in the wild—leading to better care practices and ultimately a happier life for domesticated hamsters.
Environmental Challenges and Survival
Environmental challenges pose a constant threat to wild hamsters, drastically affecting survival. Changes like habitat loss, climate change, and increased predation lead to a decline in populations. Urban development significantly reduces their natural habitats, which forces hamsters into smaller and less hospitable environments. The depletion of food sources due to agricultural practices also greatly impacts their ability to thrive. Thus, maintaining a sustainable approach in land use is imperative for the survival of these creatures. Climate-induced factors such as droughts have been known to alter activity patterns and reproduction. In locations experiencing extreme weather conditions, hamsters may have to relocate or adapt their behaviors to survive. This adaptive behavior is essential for their continued existence. Additionally, predators such as birds of prey, snakes, and weasels contribute to the natural challenges they face. The ability to navigate their environment while staying aware of predators showcases their survival instincts. Awareness of such challenges emphasizes the importance of conservation efforts aimed at protecting wild hamster habitats. Understanding these challenges encourages hamster enthusiasts to prioritize ethical practices, whether in preserving wild populations or treating domesticated ones with dignity.
Breeding habits of hamsters in their natural habitats are influenced by environmental factors, which vary by location and species. Typically, mating seasons coincide with favorable climate conditions, often occurring in spring or early summer. This leads to healthier litters as food sources are abundant, enhancing offspring survival rates. Female hamsters exhibit nesting behavior, creating burrows lined with soft materials from their surroundings. However, breeding can present challenges; high competition for mates or limited resources can impact reproductive success. Maintaining a balance regarding their breeding habits is crucial to ensure that populations do not grow excessively, which may degrade their habitat. Additionally, stress from predation or environmental changes can lead to a synchronized breeding cycle that results in overcrowding. As such, conservation efforts must recognize these issues to support healthy breeding behaviors. Captive breeding practices can benefit from these insights, allowing pet owners to emulate natural conditions that foster well-being. Responsible breeding can positively affect the domestic diversity within hamster species. Learning from wild reproductive cycles sheds light on how best to nurture these creatures. Enhancing awareness of breeding and it’s interconnection with their ecology ensures a thorough understanding of hamster care.
Concluding Thoughts on Hamster Habitats
In conclusion, exploring hamster habitats in the wild reveals the remarkable adaptations and behaviors these creatures possess. Their journey provides insights into their needs, offering valuable lessons for pet ownership and conservation efforts. 🐹 Understanding the intricacies of wild habitats emphasizes the importance of replicating these conditions for domesticated hamsters. A habitat that reflects their natural environment promotes healthier, happier lives. Providing appropriate diets, social structures, and environmental stimulation fosters well-being and thrives as they would in the wild. Moreover, engaging with their natural behaviors allows pet owners to strengthen their bond with these charming creatures. As we learn more about these adaptations and behaviors, fostering an appreciation for their ecological role becomes essential. Ultimately, creating awareness around hamster habitats encourages ethical practices both in pet care and conservation. Thus, ensuring future generations can also enjoy the companionship of these fascinating animals. Emphasizing sustainable practices aids in preserving wild habitats, protecting both the species and their homes. Take the lessons from wild hamsters, adapt them for care, and promote their well-being for a better understanding of these delightful animals.
Observing wild hamsters in their natural habitats further enhances appreciation and respect for our furry friends. Engaging in gentle observation allows individuals to understand their behaviors without causing disturbance. It’s essential to remember how crucial wild habitats are to their survival, thus necessitating a commitment to responsible pet ownership and wildlife conservation efforts that reflect this knowledge.