Tracking and Studying Rainforest Carnivore Populations
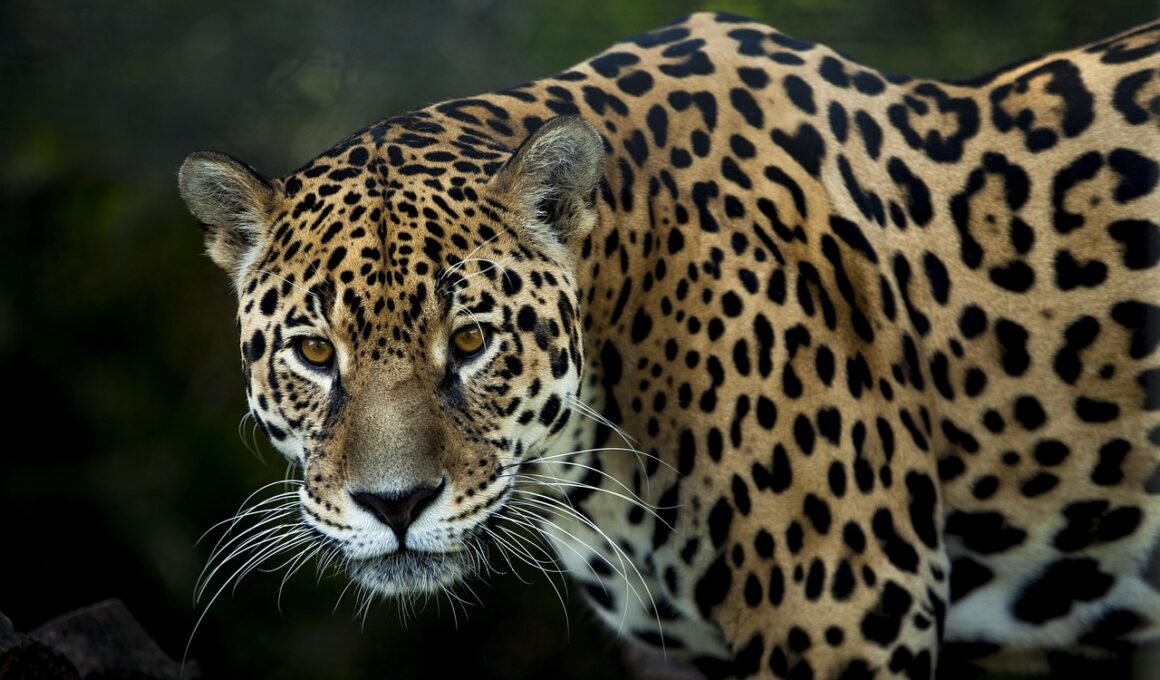
Rainforests are home to a diverse array of carnivorous animals, each playing a crucial role in the ecosystem. Among the most notable rainforest carnivores are jaguars, ocelots, and various species of snakes. These animals have adapted to their dense, humid surroundings, utilizing their skills to hunt prey and maintain balance in their habitat. Understanding and monitoring these populations is critical for biodiversity conservation efforts. Through scientific research, biologists can identify trends in carnivore populations, assess the impact of habitat loss, and understand predation pressures on herbivores. Tracking techniques such as camera traps, radio collars, and field surveys provide valuable data on animal behavior, territory sizes, and breeding patterns. Rainforest carnivores often face threats from deforestation, poaching, and climate change, making their study essential. Conservationists are developing strategies to mitigate these risks and support sustainable coexistence between humans and wildlife. By fostering community engagement and awareness, we can protect the vital roles that these carnivores play in maintaining ecological balance and contribute significantly to the health of rainforest habitats.
Monitoring these formidable creatures requires a multi-faceted approach that combines technology and local knowledge. GPS telemetry and drones facilitate the collection of comprehensive data on movement patterns and habitat use. By engaging with local communities, researchers can gather insights into animal sightings and ecological changes. Local populations often have valuable information about wildlife interactions that mainstream science might overlook. Participatory research fosters an inclusive environment where communities become proactive participants in conservation initiatives. One beneficial approach is establishing wildlife corridors that connect fragmented habitats, allowing carnivores to thrive and move freely between regions. These corridors are essential for genetic diversity, which enhances population resilience. Further, effective partnerships between conservation organizations and indigenous groups contribute to the sustainable management of rainforest resources. Engaging in education and capacity-building empowers communities to take ownership of their natural resources. As such, collaborative efforts hold immense potential to safeguard rainforest carnivores and their habitats. The intertwining of local knowledge and modern technology not only helps in tracking populations but also promotes greater sensitivity toward conservation.
The Role of Apex Predators in Ecosystem Health
Apex predators like jaguars and large snakes play a critical role in maintaining the ecological balance of rainforest ecosystems. They regulate prey populations, preventing overgrazing, and promoting species diversity across various trophic levels. By controlling herbivore numbers, carnivores indirectly support plant health and regeneration. Additionally, apex predators influence the distribution of other species within the ecosystem. Their hunting behaviors create opportunities for scavengers and smaller carnivores, fostering a vibrant food web. The loss of such predators can result in ecological imbalances, leading to increases in herbivore populations and subsequent habitat degradation. Research shows that preserving apex carnivores contributes to the resilience of rainforest environments in the face of climate change and human encroachment. Effective management strategies involve setting aside protected reserves and establishing no-hunting zones. Awareness campaigns highlighting the importance of these predators can galvanize public support for conservation measures. Furthermore, collaborative efforts involving governmental and non-governmental agencies enhance the efficacy of these initiatives. Understanding the multifaceted role of apex predators in rainforest ecosystems underlines their importance in conservation strategies.
Effective population monitoring also informs conservation actions and policy-making. Regular assessments help to identify population declines or shifts, allowing conservationists to adapt strategies promptly. Collaborations with local universities and research institutions strengthen the scientific foundation behind management practices. Such collaborations facilitate knowledge exchange, leveraging both traditional ecological knowledge and contemporary scientific studies. Rainforest carnivores often serve as indicators of ecological health, meaning their populations reflect the overall state of the environment. For instance, a decline in jaguar populations can signify broader ecological issues. Implementing adaptive management practices based on monitoring data ensures that conservation efforts can evolve in response to changing environmental conditions. This iterative process fosters resilience in conservation programs, allowing stakeholders to respond effectively to challenges. Additionally, promoting sustainable land-use practices helps mitigate human impacts on these animals. Tools like land-use zoning, conservation easements, and restoration projects can reduce habitat fragmentation. Engaging local communities in decision-making reinforces the importance of these carnivores while fostering a collective commitment to their conservation. In conclusion, consistent monitoring underpins effective conservation strategies.
Community Involvement in Conservation Efforts
Community involvement is essential in tracking and conserving rainforest carnivores. Local residents possess acute knowledge about their environment and wildlife, which is invaluable for data collection. By training community members as citizen scientists, researchers can broaden their monitoring capabilities significantly. Citizen science programs encourage volunteers to enter data, document animal sightings, and assist in field studies. This participatory approach enhances local stewardship and fosters advocacy for wildlife conservation. Moreover, community-based conservation initiatives help address human-wildlife conflicts, as local individuals can develop strategies to mitigate potential issues. For instance, educating communities about carnivore behavior can reduce fear and misconceptions. As a result, effective conservation strategies often rely on the establishment of trust and collaboration. Support from local stakeholders provides vital resources for long-term projects. Workshops and information sessions can empower communities, ensuring their direct involvement in shaping conservation policies. This inclusive model nurtures a sense of ownership over local wildlife and promotes sustainable practices that benefit both carnivores and people. Ultimately, fostering community involvement strengthens the effectiveness and durability of rainforest conservation endeavors.
Innovative technologies play a crucial role in enhancing our understanding of rainforest carnivores. Remote sensing, environmental DNA sampling, and acoustic monitoring are just a few advancements contributing to wildlife research. These technologies facilitate the collection of data over vast areas, providing insights into elusive species. For example, acoustic monitoring allows researchers to detect carnivore vocalizations, aiding in species identification and distribution mapping. Moreover, environmental DNA analysis can reveal the presence of species through genetic material collected from the environment, such as soil or water samples. Such non-invasive methodologies minimize stress on wild populations and enable consistent data gathering. Additionally, machine learning and artificial intelligence are increasingly utilized to analyze monitoring data efficiently. By identifying patterns related to carnivore movement and behavior, researchers can tailor conservation efforts effectively. The integration of technology in wildlife monitoring can enhance traditional methods, yielding more comprehensive datasets. Furthermore, collaborations between tech companies and conservationists create innovative solutions for tracking wildlife. Sharing knowledge and resources is essential to advancing our understanding of these ecosystems. In doing so, we can develop more effective conservation strategies grounded in accurate, data-driven science. This synergy between technology and ecology is vital.
The Future of Rainforest Carnivore Conservation
Looking towards the future, the conservation of rainforest carnivores faces numerous challenges. Climate change poses a significant threat, altering habitats and impacting prey availability. As the effects of climate change escalate, adaptive management strategies become critical. These strategies encompass habitat restoration, corridor creation, and connectivity enhancement to ensure the survival of carnivores in shifting environments. Additionally, engaging with global initiatives can amplify local conservation efforts. International collaborations often bring resources, research expertise, and funding to local projects. Such partnerships ensure comprehensive strategies are developed to address complex ecological dynamics. Furthermore, public awareness campaigns are essential for fostering global understanding and support for rainforest conservation. By highlighting the significance of carnivores in maintaining ecosystems, advocates can galvanize action. These efforts can include educational programs, community outreach, and social media engagement. Implementing sustainable practices at local, national, and international levels is imperative for preserving rainforest biodiversity. Finally, ongoing monitoring and evaluation are necessary to measure the effectiveness of conservation efforts continually. Balancing human interests with wildlife needs is an ongoing priority in ensuring a harmonious future for rainforest carnivores.
Collaboration among different sectors enhances the success of rainforest carnivore conservation, leading to innovative solutions. Government agencies, non-profits, local communities, and academic institutions can work hand-in-hand to shape effective conservation strategies. Interdisciplinary approaches not only allow for diverse perspectives but also address multiple facets of conservation, from ecological research to policy implementation. Such partnerships can foster funding opportunities and resource sharing that might otherwise be inaccessible. Moreover, nurturing a culture of conservation at various levels of society can build momentum toward protecting rainforest ecosystems. Public and private sectors, alongside civil society, play critical roles in advocacy and awareness-raising efforts. By promoting eco-tourism and sustainable land practices, stakeholders can contribute positively to local economies, while benefitting rainforest fauna. Additionally, fostering resilience in local communities to adapt to environmental changes is crucial. Conservation strategies that account for socio-economic factors can increase the likelihood of sustainable outcomes. This holistic approach ensures that everyone has a stake in the preservation of these biodiverse ecosystems. As we advance in our understanding of rainforest carnivores, maintaining a sense of global responsibility for protecting their habitats will remain paramount.