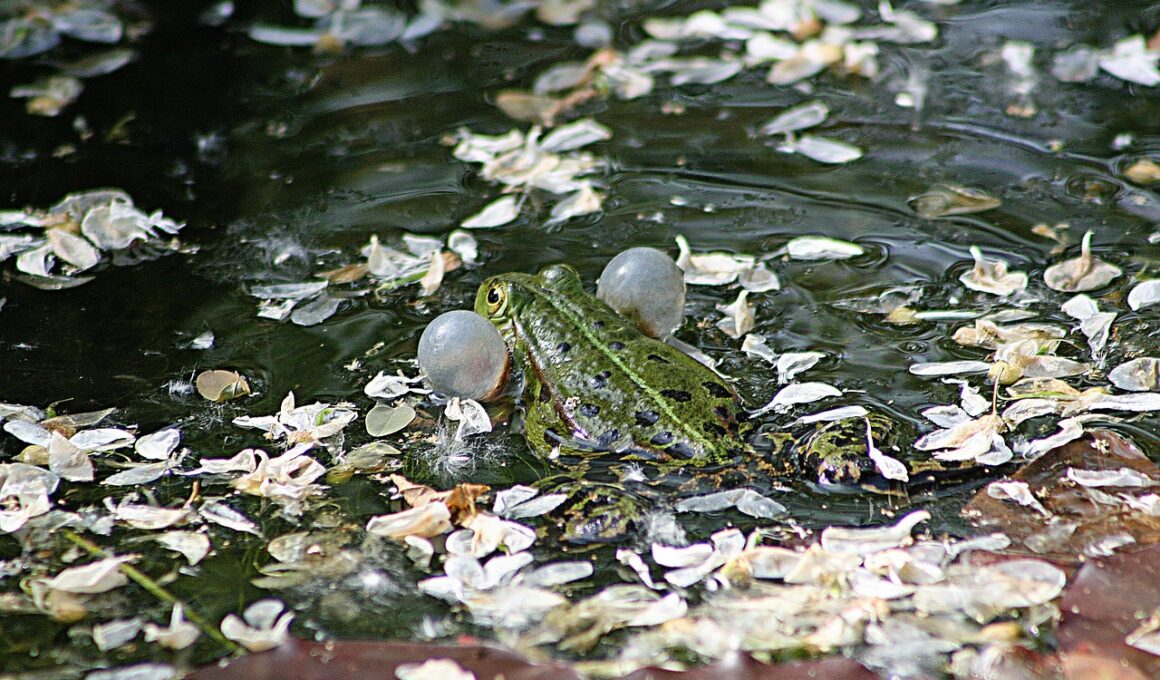
Water Quality Requirements for Ranidae Frog Habitats
The Ranidae family, commonly known as true frogs, plays a vital role in ecological balance. Understanding water quality is essential for their habitat sustainability. Factors such as pH, temperature, and dissolved oxygen are crucial for breeding and growth. These amphibians thrive in freshwater environments, necessitating clear and clean waters. Various pollutants can disrupt their lifecycles leading to populations declining rapidly. Monitoring water quality helps to ensure that these frogs can reproduce successfully. In addition, the habitats must be rich in vegetation to provide not only cover but also food sources. Frogs often require shallow waters for breeding; thus, it’s relevant to maintain proper depth. Introduced species may outcompete them for resources, further emphasizing the need for clean ecosystems. Conservation efforts, including banning harmful chemicals, are critical for safeguarding their environments. Also, clean water bodies protect frogs from diseases that thrive in unhealthy conditions. Stakeholders should engage in regular water testing to assess any risks the species may face. In summary, water quality is a cornerstone of successful Ranidae sustainability.
Proper Pest Management in Frog Habitats
Frog habitats often face threats from invasive pests that can disrupt ecological balance. To maintain healthy populations of Ranidae, integrated pest management (IPM) strategies are essential. IPM involves using various methods to control pest populations effectively while minimizing harm to non-target species. It includes biological, mechanical, and chemical practices tailored to each unique habitat. By focusing on natural predators and environmentally safe chemicals, populations of harmful insects can be managed sustainably. Additionally, habitat restoration plays a significant role in pest management. Providing adequate cover and diverse vegetation increases resilience against pest infestations. Encouraging local community involvement in maintaining natural habitats can enhance IPM success. Regular monitoring of pest populations allows for timely intervention, ensuring that habitats remain healthy. Furthermore, educating communities about the importance of preserving native species helps bolster local frog populations. Sustainable farming practices near water sources can also benefit frog habitats. Adopting organic methods minimizes chemical runoff, thus protecting vital water quality. Stakeholders should work closely with local authorities to develop pest management regulations that are friendlier to local wildlife and their habitats.
The Role of Vegetation in Water Quality
Vegetation plays a critical role in maintaining water quality in Ranidae habitats. Aquatic plants absorb nutrients and filter pollutants, which is vital for the health of water bodies. Dense vegetation provides shelter not only for frogs but also for species that contribute to the food web. This vegetation acts as a natural barrier, reducing soil erosion and sedimentation, thus improving water clarity. Moreover, plants can influence pH levels, making environments more suitable for frog survival. In addition, the shade provided by larger plants can help regulate water temperatures, which is important for amphibians’ metabolic rates. A diverse plant community supports various insects, thereby supplying essential food sources for Ranidae frogs. Consequently, maintaining a robust plant community is crucial for sustaining not just frogs but the overall biodiversity of aquatic ecosystems. Hydrophytic species, or plants that thrive in wet conditions, are particularly beneficial for these environments. Such plants assist in nutrient cycling, adding organic matter to the soil and water. Stakeholders should prioritize conservation efforts aimed at preserving vegetation around water bodies to safeguard Ranidae frog habitats.
Impacts of Climate Change on Frog Habitats
Climate change poses severe threats to many wildlife species, including Ranidae frogs. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can drastically alter their habitats. For instance, temperature increases can lead to altered breeding seasons, affecting population dynamics. Similarly, reduced rainfall can lower water levels in ponds and streams, crucial for their reproduction. Amphibians are especially sensitive to environmental changes, making them early indicators of ecosystem health. Pollutant concentrations may increase due to climate change, adversely impacting water quality and food availability. As a result, declines in frog populations can signal broader ecological issues. Furthermore, climate-related shifts can lead to habitat fragmentation. This essentially isolates populations, reducing genetic diversity and increasing vulnerability to diseases. Conservation measures must adapt by implementing strategies that consider climate change impacts. Hence, engaging in habitat restoration and protection is essential for sustainable frog populations. Working together with scientists, policymakers, and local communities can enhance resilience to climate changes. It is imperative to develop adaptive management practices that can support biodiversity, especially for vulnerable species like Ranidae frogs. Overall, addressing climate change is critical to safeguarding their future.
Human Activities and Their Consequences
Human activities significantly impact the water quality and habitats of the Ranidae family. Urbanization leads to habitat destruction and increased pollution runoff, adversely affecting water ecosystems. Construction and industrial activities contribute further pollutants, diminishing frog populations and biodiversity. Agricultural practices, particularly the use of pesticides and fertilizers, can contaminate nearby water sources, posing health risks to local wildlife. Runoff from these chemicals not only affects water quality but also disrupts natural food webs. In addition, recreational activities can lead to physical disturbances in habitats. Foot traffic, pollution from litter, and boating activities can damage sensitive ecosystems. Efforts to educate communities about sustainable practices can help mitigate these impacts. Conservation groups are essential in promoting responsible land use and protecting existing habitats. Effective legislation to regulate pollutants entering water bodies is necessary for preserving Ranidae populations. Furthermore, restoration projects to rehabilitate damaged ecosystems can improve water quality for these frogs. All stakeholders, including governments and individuals, should participate in initiatives aimed at conserving amphibian habitats. In summary, our collective actions play a crucial role in ensuring the survival of the Ranidae family.
Community Involvement in Habitat Conservation
Community involvement is vital in maintaining and improving water quality for Ranidae frog habitats. Engaging local communities fosters awareness of environmental issues, encouraging people to take action. Educational programs can enlighten individuals about the role frogs play in ecosystems, promoting species conservation. Volunteer opportunities for habitat restoration lead to better awareness and hands-on experience in protecting local species. Communities can participate in clean-up efforts along water bodies to ensure that trash and pollutants are removed effectively. This helps safeguard vital habitats and maintains water quality. Additionally, establishing community-led monitoring programs can help collect data on water conditions and species populations. Local knowledge can contribute significantly to conservation strategies and practices. Collaborating with schools can inspire the younger generation to appreciate biodiversity. Workshops focusing on sustainable practices can empower individuals to maintain healthy ecosystems. Working alongside conservation organizations can provide resources and technical support for local initiatives. Ultimately, building strong community connections enhances ecological stewardship that benefits the Ranidae family. Community-driven conservation efforts can enhance local habitats, ensuring long-term sustainability for these essential amphibians.
Future Directions for Conservation Efforts
The future of Ranidae frog conservation depends on innovative approaches and collaboration. Conservationists must assess and adapt to new environmental challenges. Research plays a fundamental role in understanding the needs of different frog species. Studies evaluating habitat requirements and population dynamics help inform effective conservation strategies. As threats evolve, adapting conservation methodologies will be essential. Technological advances can facilitate more efficient monitoring, enabling data collection through remote sensing tools and citizen science. This could lead to broader engagement and commitment to conservation from diverse sectors of society. Furthermore, creating protected areas dedicated to Ranidae habitats can ensure their survival against external pressures. Coordinated efforts among biologists, policymakers, and local organizations are crucial for successful conservation actions. Public engagement campaigns can enhance awareness and support for frog conservation initiatives. By increasing understanding of ecological roles, communities can advocate for protection efforts. Collaborating globally to share best practices and resources ensures that local conservation efforts are informed and effective. Optimistically, combined strategies can lead to healthier environments for the Ranidae family. Achieving lasting results in conservation efforts requires ongoing commitment and innovation.
Conclusion: The Importance of Water Quality for Frogs
In conclusion, maintaining water quality is paramount for the sustainability of Ranidae frogs. Environmental factors such as temperature, vegetation, and pollution levels significantly influence their habitats. Communities, conservationists, and stakeholders must work together to combat the threats these amphibians face every day. Effective management strategies focused on maintaining clean, healthy water bodies can promote thriving populations. Additionally, understanding the relationship between frogs and their ecosystems emphasizes the importance of biodiversity. Protecting these wetlands and freshwater systems is essential for the overall health of the environment. Citizens must remain vigilant and committed to preserving natural habitats that support local wildlife. Investing in education and community involvement fosters greater awareness and support for conservation efforts. Implementing sustainable practices locally can yield significant benefits globally. Moving forward, it is crucial to recognize the importance of every aspect of habitat health. By prioritizing water quality, we can enhance the chances of survival for the Ranidae family. Ultimately, a collaborative approach to conservation can ensure that future generations recognize the significance of these remarkable amphibians.