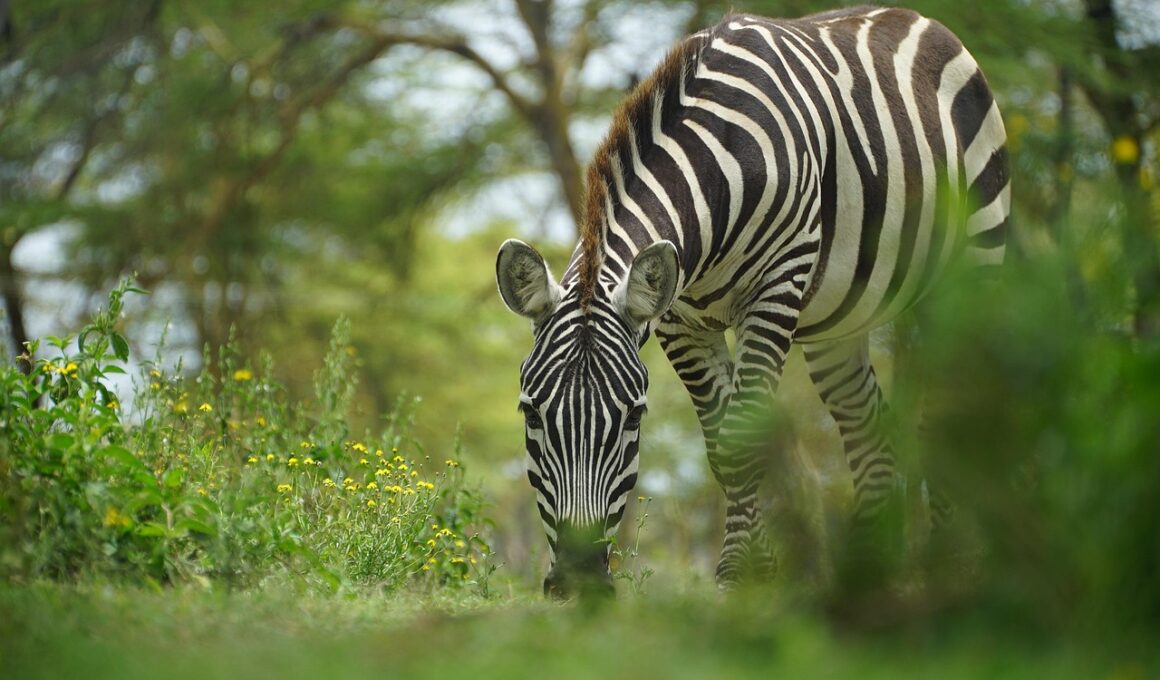
Zebra Prey Behavior During Different Times of Day
Zebras exhibit distinct behaviors throughout various times of the day, largely influenced by their need for food, safety, and social interactions. During the early morning hours, zebras actively graze in groups, often moving to higher ground. This behavior helps them to keep an eye on any potential predators, such as lions or hyenas lurking nearby. At this time, zebras rely on their acute senses, particularly their vision and smell, to detect threats in the environment. Grazing in groups allows them to be alert and provides safety in numbers. Their social structure plays a significant role, as they communicate with each other through sounds and body language. The early light facilitates these interactions, making foraging more efficient. Additionally, they tend to stick to open areas where visibility is enhanced during the day. These behaviors are crucial for both their survival and sustenance. In the morning light, other animals, including herbivores, can also be spotted in similar feeding behaviors, as the grass is still dewy and tender. Understanding these patterns helps conservationists better protect and manage zebra populations.
As the sun reaches its peak, zebras undergo changes in their behavior that reflect the hotter temperatures and increased predator activity. Midday marks a shift from foraging to seeking shade and conserving energy. Zebras often find refuge under trees or in thickets where they can cool off from the intense heat. This behavior illustrates their adaptability to environmental conditions, as they utilize available natural resources. While resting, they are also vigilant; their acute hearing helps them sense approaching predators even in a calmer state. The midday heat may cause some zebras to become more sedentary, while others remain alert, monitoring their surroundings. Social interactions may also diminish during this period, with groups becoming more dispersed. The shading behavior can be vital for survival as overheating can pose risks. Additionally, it is during this time that zebras may engage in mutual grooming, thereby strengthening social bonds. The interactions help in the maintenance of their skin and coal black coats. Overall, midday presents a strategic time for rest and socialization while ensuring they remain aware of their environment.
Evening Grazing Rituals
As dusk approaches, zebras exhibit a distinct increase in activity, preparing for their evening grazing rituals. When the sun sets, temperatures drop, making it more comfortable for zebras to venture out in search of food. The early evening hours are critical as this is when many predators are also active. Zebras resume grazing in open grasslands, taking advantage of the cooler temperatures. Their herding instincts become more pronounced, allowing them to come together and graze as a unified group. The low light conditions at dusk give them a tactical advantage, as they can often see better in shaded areas and use their own movements to confuse predators. During this time, they tend to graze on the most nutritious grasses, replenishing energy stores after a long day. Social behaviors, such as vocalizations, increase as they communicate their needs and alert each other to dangers. Additionally, zebras are highly aware of their surroundings, often watching out for threats. This evening period allows for both sustenance and safety, ensuring that zebras can survive in the wild.
Nighttime brings a different dynamic to zebra behavior; they become more vigilant and cautious due to the increased risk of predator encounters. Predators such as lions are most active during the night. Zebras’ night vision enhances their ability to detect threats, allowing them to remain alert and prepared to flee at a moment’s notice. While some zebras might graze quietly during the night hours, others remain on high alert, constantly scanning their environments. The darkness, while posing a danger, also allows them to camouflage better. Their striped coats can confuse predators, especially in low-light conditions, adding a layer of protection. Nighttime is also a time for social bonding; zebras will often congregate tightly, utilizing group safety as they find respite from hunger. Communication may still occur, albeit in quieter forms than during the light of day. Research on zebra behavior at night has shown that their social structures profoundly influence their survival tactics. These strategies not only help zebras stay alive but also maintain their herds. Understanding nighttime behaviors provides insights into their survival and adaptation strategies.
The Role of Water Sources
Water sources play a critical role in zebra behavior, influencing their daily movement patterns and interactions. Zebras need to drink water regularly, making proximity to water vital for their survival. During hot days, they often travel toward waterholes, where they gather to hydrate, relax, and socialize. The vigor and energy of the animals can be seen at water sources as they drink and engage with other animals. This behavior is not only essential for hydration but also serves as a social meeting point for herds. When water becomes scarce, zebras may have to travel longer distances, multiplying the risk of predation. Their ability to adapt to changing water availability showcases their resilience as a species. Ensuring access to water also means that zebras may be more vulnerable to predators that lie in wait near these resources. As such, they tend to be more alert when approaching water. This multifaceted approach to their environment demonstrates the importance of water in zebra ecosystems, influencing not just individual behaviors but overall herd dynamics.
Understanding the significance of time and the Zebra’s interactions provides key insights into their social structures and survival strategies. Each segment of the day represents a different set of behaviors that help zebras cope with environmental pressures. By analyzing their activities across these times, researchers can gather valuable data on how they respond to predators and changes in their habitat. The morning grazing rituals show their foraging strategies, while midday resting patterns reflect their adaptability. Evening activities reveal their group dynamics, and nighttime vigilance emphasizes their need for survival. Water sources integrate into their daily lives and enhance group interactions; thus, it becomes vital for conservation efforts. Studying these behaviors aids conservation professionals in developing targeted strategies that promote the safety of zebras in their natural habitats. There are numerous nuances within these behaviors that illustrate the complexity of zebra life. As zebras interact with their environment, each behavior is a reflection of evolutionary adaptations meant to enhance their survival in the wild. Research into these patterns contributes significantly to our understanding of wildlife management and ecological balance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, zebras’ prey behavior is profoundly affected by different times of day, reflecting their adaptive strategies for survival. As they navigate through mornings, afternoons, evenings, and nights, their actions are dictated by environmental cues and threats from predators. Each time period presents unique opportunities and challenges, illustrating the importance of being aware of their surroundings. Understanding these patterns not only offers insights into their daily lives but also highlights the need for effective conservation methods. Since zebras are such critical players in their ecosystems, their behaviors and interactions with other species must be preserved for future generations. Protecting their habitats and maintaining water sources are essential to supporting their populations. Enhanced research and observation can lead to improved strategies for managing zebra populations in the wild. The more we learn about these magnificent creatures, the better we can ensure their survival. Therefore, recognizing the intricate relationships zebras have with their environment will significantly contribute to their conservation. Our responsibility as stewards of the planet is to ensure that we maintain biodiversity and protect these iconic animals.
In summary, a greater understanding of zebra prey behavior through different times of day will not only enrich our knowledge about these fascinating animals but can also inspire future conservation efforts. By paying close attention to how zebras interact with their habitat throughout the day, researchers can gather valuable insights into their social structures and survival strategies. Proper management and protection of natural habitats must be prioritized. Awareness of their patterns contributes to effective conservation programs that ensure the survival of zebra populations within the ecosystem they inhabit. As we delve deeper into the intricacies of zebra life, we can also draw connections to broader ecological health. The upcoming generations will benefit from our efforts to safeguard their existence. Furthermore, fostering an appreciation for wildlife attracts interest and resources to conservation initiatives. As constituents of the animal kingdom, zebras represent a critical piece of the ecological puzzle. Their well-being mirrors the health of their environments, prompting us to actively engage in their preservation. Addressing challenges and threats to their existence must be of utmost importance, as such actions will contribute to the overall balance of nature.