Effects of Human Interaction on Feline Social Behavior
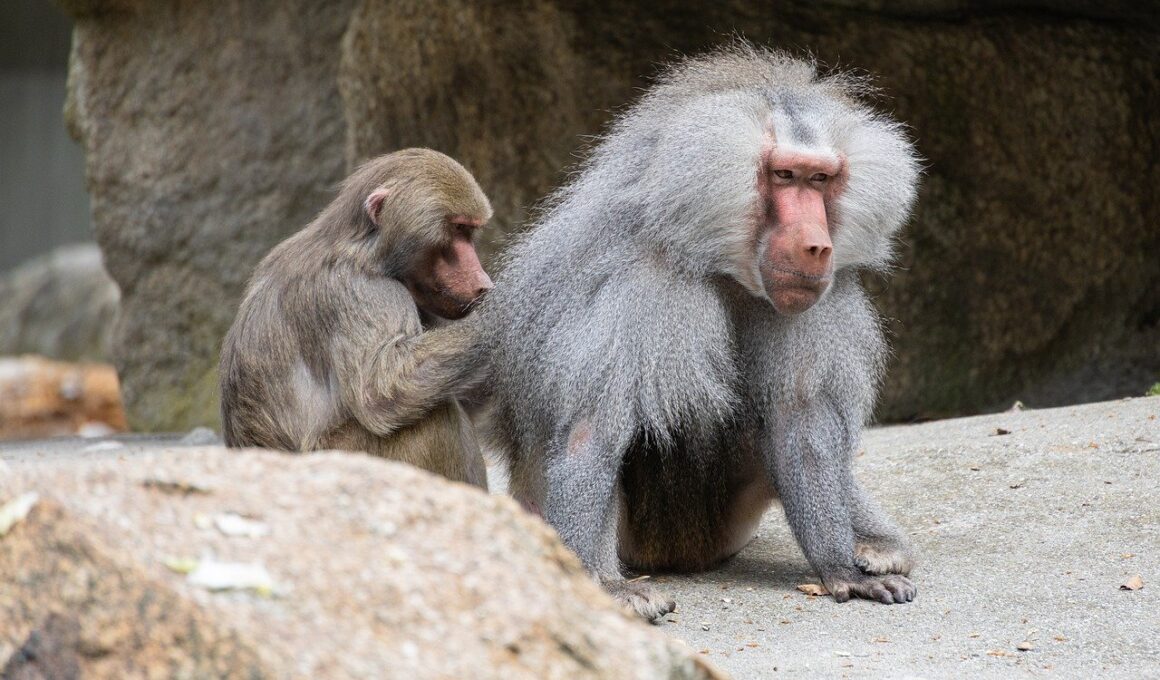
Feline social behavior is profoundly influenced by various aspects of human interaction. It can shape, modify, or even completely alter the way cats interact with one another. Cats are known for being solitary hunters, yet they also demonstrate complex social structures in certain environments, especially when they have consistent interactions with humans. The degree to which they socialize is often contingent upon their upbringing, such as whether they were raised in a feral setting or in a household. This dynamic interplay between isolation and interaction can significantly affect how felines perceive social bonding, territory acquisition, and resource distribution. Furthermore, human behavior towards felines can establish specific norms within their social hierarchy. For example, feeding routines, affection, and play can create behavioral changes indicative of tameness and reliance on humans. This reliance can lead to fascinating social adaptations, where cats might become more social among themselves in environments rich in human companionship. Understanding these effects is crucial, as it opens avenues for more effective feline care, addressing behaviors that arise from human influence, and optimizing the environment to better suit their inherent social needs.
Cats, unlike many canines, exhibit unique social structures influenced by their natural instincts and experiences. In multi-cat households, the presence of humans often alters traditional feline hierarchies. This social structure can include bonding behaviors that facilitate peaceful coexistence. Factors, such as the number of cats available, their sex, and whether they are neutered, play critical roles in forming social bonds. Human interaction can nurture relationships between cats by providing mental stimulation and opportunities for social play. Disruptive human behaviors, such as frequent changes in routines or introductions of new pets, can create stress, leading to competitive or aggressive behaviors. Furthermore, providing positive reinforcement during human-cat interactions can help cats develop a more cohesive social structure. Engagement in play, for instance, can mimic hunting behaviors and promote camaraderie. Humans can further influence these social bonds by being attentive to each cat’s personal space. Observing how cats interact in response to human presence can teach us valuable lessons on their social development. As such, fostering environments that prioritize these interactions can optimize feline social behavior significantly, leading to happier and healthier feline companions.
Understanding Socialization in Felines
The social behavior of felines is an intriguing topic that reveals their adaptability to human environments. Felines, specifically domestic cats, often navigate their social structures through signals and cues. For example, body language is vital in how they communicate with humans and each other. Tail position, ear orientation, and vocalizations play essential roles in expressing their emotions. Socialization with humans can enhance these behaviors, leading to a more robust understanding of feline communication. The way felines behave around people can also affect their interactions with other cats, prompting behaviors like grooming or nuzzling that are seen as bonding actions. Conversely, a lack of human interaction can result in shy or aggressive behaviors among felines, indicating their discomfort with social situations. Enrichment activities, such as interactive toys or group play sessions, can stimulate social bonding not only among cats but also between cats and their owners. A well-socialized feline often exhibits confidence, reducing markings and territorial disputes. Thus, understanding these social cues is essential for enhancing a pet feline’s behavioral health and creating a harmonious living situation.
Human social behaviors can inadvertently affect feline social structures by creating environments that encourage or discourage socialization. For instance, inconsistent handling can cause confusion and distress among cats, leading to social complications. This is particularly evident in multi-cat households, where dominant and submissive roles often emerge based on human interactions and reactive responses. Additionally, the availability of resources, such as food and litter boxes, determines how cats distribute themselves in a space. If humans fail to provide adequate resources or neglect territoriality, feline social dynamics can shift, prompting competition or aggression. By recognizing how humans influence these dynamics, pet owners can establish clear norms that encourage cooperative behaviors. Implementing routine feeding times or creating designated rest areas can eliminate competition. Moreover, fostering social interaction through designated playtimes or communal activities can enhance their social behaviors. Positive experiences associated with humans can encourage cats to exhibit more friendly and playful attitudes toward one another. Thus, nurturing an environment that is attentive to these needs can result in healthier feline social structures and reduce anxiety and conflicts.
Feline Social Structures in Different Environments
The environment plays a critical role in shaping feline social behavior. Stray cat colonies, for example, exhibit different social dynamics compared to house cats. Within a colony, cats may form coalitions for hunting, sharing food, and childcare responsibilities. This cooperation is influenced by resource availability, allowing cats to thrive in shared spaces. Research has shown that friendly interactions within these colonies often lead to the establishment of strong social bonds. In contrast, cats raised in isolation often exhibit more aggressive or fearful behaviors, making it essential for them to experiences a mix of both human and feline interactions. Homes that lack social enrichment may lead to increased territorial disputes and stress-induced issues. Alternatively, environments where cats have ample opportunity for social play can create a supportive atmosphere. Providing vertical spaces, such as cat trees or shelves, encourages exploration and communication among cats. Adequate space within the home allows each cat to establish their territories while fostering positive social interactions. By enriching the living environment, cats can develop healthier and more stable social bonds with both humans and other felines.
Role of Play in Feline Social Structures
Play is an essential aspect of feline social behavior, offering a unique platform for interaction. Felines often engage in playful activities to develop their social skills, bond with one another, and learn communication cues. Without the element of play, cats can miss out on crucial developmental experiences, leading to awkward social interactions later in life. Positive play experiences with humans can increase overall harmony in multi-cat households. It fosters cooperation as cats interact naturally, mimicking hunting behaviors that strengthen their social ties. Regular play sessions also help reduce aggression and rivalry, creating a more welcoming environment for cats of all temperaments. Moreover, introducing interactive toys can simulate competition while fostering teamwork. This shared experience allows felines to engage positively with each other and humans. But it’s vital to monitor their play to ensure that it remains healthy and inclusive. By understanding and facilitating healthy play behaviors, caregivers can enhance the overall well-being of their cats. Thus, recognizing the role of play in shaping social interactions among felines serves as a keystone in promoting healthier, happier relationships.
Conclusion: Enhancing Feline Socialization
In conclusion, the effects of human interaction on feline social behavior are vast and significant. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for fostering optimal feline social structures in both domestic and colony settings. Today’s feline owners must recognize that their interactions can enhance or hinder behavioral development. By creating enriched environments that promote healthy social interactions, it becomes possible to see improvements in feline well-being. Providing proper resources, rewarding positive behaviors, and understanding the natural social signals of cats are fundamental steps. Additionally, offering opportunities for both independent play and social engagement can create a more fulfilling life for cats. Observing feline interactions can help owners better understand their pets’ needs, leading to more informed decisions about their social environments. Encouraging interaction through play, proper care, and humane treatment helps maintain the social structure within feline communities. This approach benefits overall feline health, minimizing stress-related issues or aggression. In summary, prioritizing socialization will lead to happier, healthier felines who thrive in their human-influenced communities.