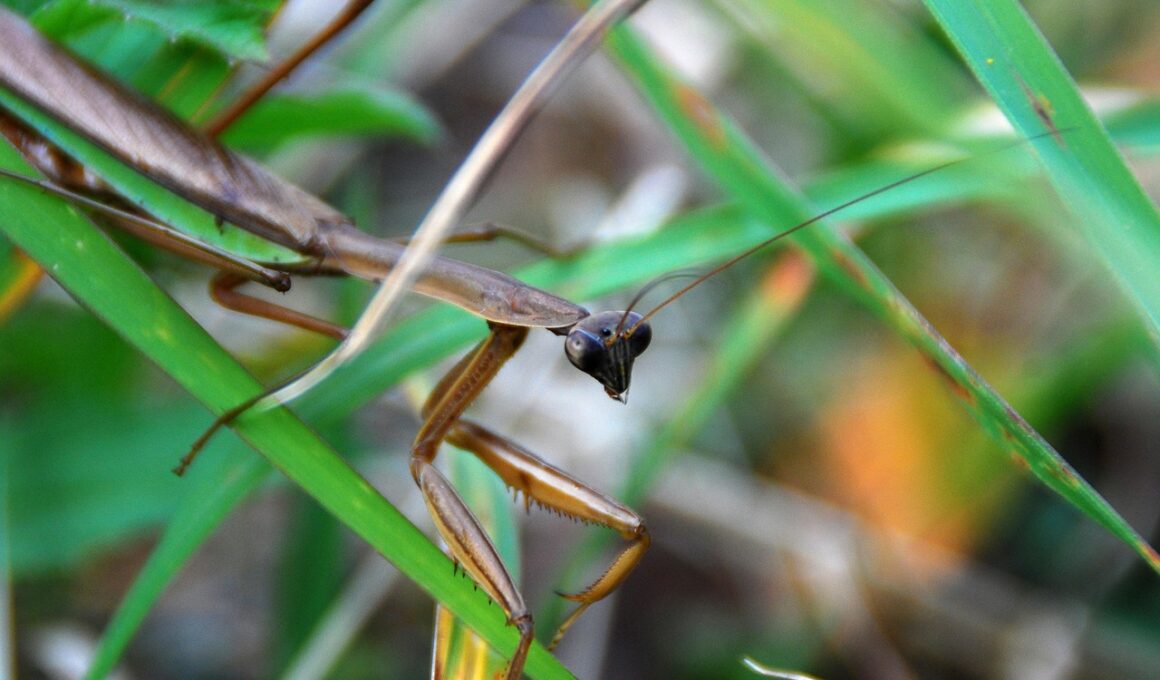
The Role of Invertebrate Carnivores in Controlling Pest Populations
Invertebrate carnivores play a vital role in the ecosystem by controlling pest populations that threaten plant and animal health. Various invertebrate species, including predatory insects like ladybugs and mantises, serve as natural pest controllers. Their presence in agricultural settings can significantly reduce the need for chemical pesticides, promoting healthier food production. These carnivorous invertebrates feed on a wide array of pests, including aphids, caterpillars, and beetles, contributing to maintaining ecological balance. Farmers can harness the power of these creatures to enhance crop yields and reduce the likelihood of pest outbreaks. Sustainable agriculture relies heavily on biodiversity, where invertebrate carnivores act as key players in pest management systems. Encouraging habitats that foster these beneficial species will not only help in pest control but also lead to healthier ecosystems. Integrating invertebrate carnivores into pest management strategies can result in a more resilient agricultural system, making it essential for farmers and land managers to understand their importance. Through practices that balance nature and agriculture, we can ensure high yields without harming the environment.
Invertebrate carnivores serve as both indicators and regulators of ecosystem health due to their significant roles in food webs. These creatures typically occupy higher trophic levels, predating on herbivores and other pests detrimental to crops. Their decline can lead to unchecked pest populations, emphasizing the need to sustain their populations through habitat conservation. Invertebrate consumers contribute to nutrient cycling, which enhances soil quality and overall fertility, thereby facilitating crop growth. A diverse range of invertebrates, including spiders, centipedes, and predatory beetles, helps ensure the vitality of agricultural systems. Additionally, the presence of these predator species indicates a balanced ecosystem, suggesting that farmers can trust their natural pest management solutions. To support these vital species, land management practices should focus on preserving natural habitats and minimizing chemical inputs. By promoting invertebrate diversity, we increase the chances of maintaining sustainable pest control without reliance on synthetic pesticides. Sustainable farming practices that support invertebrate carnivores will ultimately lead to healthier ecosystems and more productive agricultural landscapes.
Types of Invertebrate Carnivores
Among the many types of invertebrate carnivores, predatory insects like ladybugs and lacewings are particularly noteworthy for their pest control capabilities. These insects are known for their voracious appetites, especially for soft-bodied pests, which they consume in large quantities. Additionally, spiders are exceptional carnivores that prey on various insects, effectively controlling pest populations within gardens and fields. Other beneficial invertebrates, such as predatory beetles and certain wasps, also contribute significantly to ecological balance. These various groups exhibit diverse hunting strategies and life cycles, influencing how they affect pest populations in different environments. Recognizing the types of invertebrate carnivores present in a given area can help in designing effective pest management plans. For instance, encouraging the presence of spiders in agricultural settings can dramatically decrease insect pest populations without harming beneficial organisms. Farmers can promote these carnivorous species by implementing strategies like planting native flora, creating suitable habitats, and minimizing pesticide use. Incorporating multiple strategies to encourage invertebrate carnivores can lead to more effective and sustainable pest control outcomes.
The role of invertebrate carnivores in maintaining pest control cannot be overstated, especially in organic farming practices. Organic farmers prioritize the use of natural pest control methods, relying heavily on these invertebrate predators to manage pest populations effectively. By fostering environments that support these carnivores, organic farms can reduce their reliance on chemical pesticides while enhancing overall biodiversity. Strategies include planting diverse crops, maintaining natural vegetation borders, and practicing crop rotation. These practices help establish habitats that encourage predators to thrive and reproduce. Additionally, creating shelters and places for predators to hide can further support their populations. The presence of invertebrate carnivores leads to better pest management and healthier ecosystems surrounding the agricultural lands. Furthermore, sustainable pest control methods help preserve soil health and protect water sources from chemical runoff, reinforcing organic practices’ ecological benefits. Incorporating invertebrate predators is an effective way to develop resilient farming practices, benefiting farmers and the environment alike. Ultimately, integrating these natural pest controllers into organic farming systems is essential for long-term agricultural sustainability.
Challenges Facing Invertebrate Carnivores
Despite their benefits, invertebrate carnivores face numerous challenges that threaten their populations and, consequently, pest control abilities. Habitat loss is one of the principal factors contributing to declining invertebrate numbers, as urbanization and intensive agricultural practices diminish their living environments. Additionally, the widespread use of pesticides, even in controlled amounts, endangers these beneficial species, inadvertently harming the very organisms that farmers rely on for pest management. Monoculture farming practices further exacerbate these issues, creating less diverse ecosystems where invertebrate carnivores struggle to survive. To combat these challenges, it is crucial to focus on restoring natural habitats and promoting biodiversity within agricultural systems. Insecticide alternatives are essential in supporting invertebrate populations while managing pest issues effectively. Small changes in agricultural practices can significantly impact the recovery and sustainability of these predator species. By prioritizing ecological balance, farmers can nurture pest control capabilities and minimize reliance on chemical treatments. Ultimately, protecting invertebrate carnivores is vital for maintaining resilient and sustainable ecosystems that yield productive agriculture.
Awareness and education about the importance of invertebrate carnivores are paramount in promoting sustainable agriculture. Farmers, land managers, and consumers alike must recognize the benefits these creatures provide in controlling pest populations. Awareness programs can highlight proactive strategies for fostering invertebrate habitats, such as cover cropping and reduced tillage practices. By informing diverse agricultural stakeholders, we can encourage practices that enhance invertebrate populations and biodiversity. Educational resources can equip farmers with tools and knowledge to implement sustainable pest management effectively. Encouraging community initiatives that focus on biodiversity will support both environmental and agricultural health. In addition, collaboration among researchers, farmers, and policymakers can lead to innovative solutions to enhance invertebrate habitat and protect these essential species. By prioritizing these ecosystems, we not only achieve pest control but also bolster the entire agricultural system’s resilience. Growing public interest in sustainability presents an opportunity to champion the cause of invertebrate carnivores and promote integrated pest management programs across multiple sectors. Through education and collective action, we can positively affect agricultural landscapes and ecological health.
Conclusion: The Future of Pest Control
The future of pest control in agriculture is closely tied to the presence and health of invertebrate carnivores. As effective natural pest managers, these creatures demonstrate the benefit of embracing ecological principles in farming. Moving forward, integrating invertebrate protection and support strategies will be essential for sustainability. Increased awareness and education surrounding these species can lead to more widespread adoption of practices that enhance their populations. Future research plays a vital role in understanding the dynamics of invertebrate predators and their impact on pest control. Innovations in pest management that incorporate these natural allies will contribute to healthier agricultural ecosystems. By shifting our focus from synthetic to biological pest control methods, we create a more sustainable agricultural future rooted in biodiversity and ecological health. Advocating for initiatives that support invertebrate life is crucial in forging connections between agricultural practices and ecosystem conservation. In doing so, we unlock the potential for a more sustainable and efficient approach to pest management that benefits farmers, consumers, and the environment. As we advance, invertebrate carnivores will remain a cornerstone of effective pest control strategies.
To summarize, invertebrate carnivores are indispensable allies in the effort to manage pest populations sustainably. By emphasizing their critical role in agriculture, we underscore the importance of biodiversity in achieving ecological balance. Recognizing their contributions enables farmers to harness the benefits of natural pest control, thereby reducing the need for harmful chemicals. Practices that encourage the proliferation of these predators can enhance agricultural productivity and promote ecosystem health. The future of pest control lies in the strategies we choose to implement to sustain these remarkable creatures. By collaborating to protect invertebrate carnivores, we pave the way for a more resilient, effective, and environmentally-friendly agricultural system for years to come. It is essential to champion the cause of these remarkable animals and create awareness of their invaluable contributions to pest management. As we navigate agricultural challenges, the solutions will emerge from understanding and integrating natural pest control methods. The journeys towards sustainability must include invertebrate carnivores as partners in our quest for effective pest management. Together, we can build a thriving agricultural landscape that harmonizes with nature for the benefit of all.