The Role of Urban Gardens in Supporting Amphibian Life
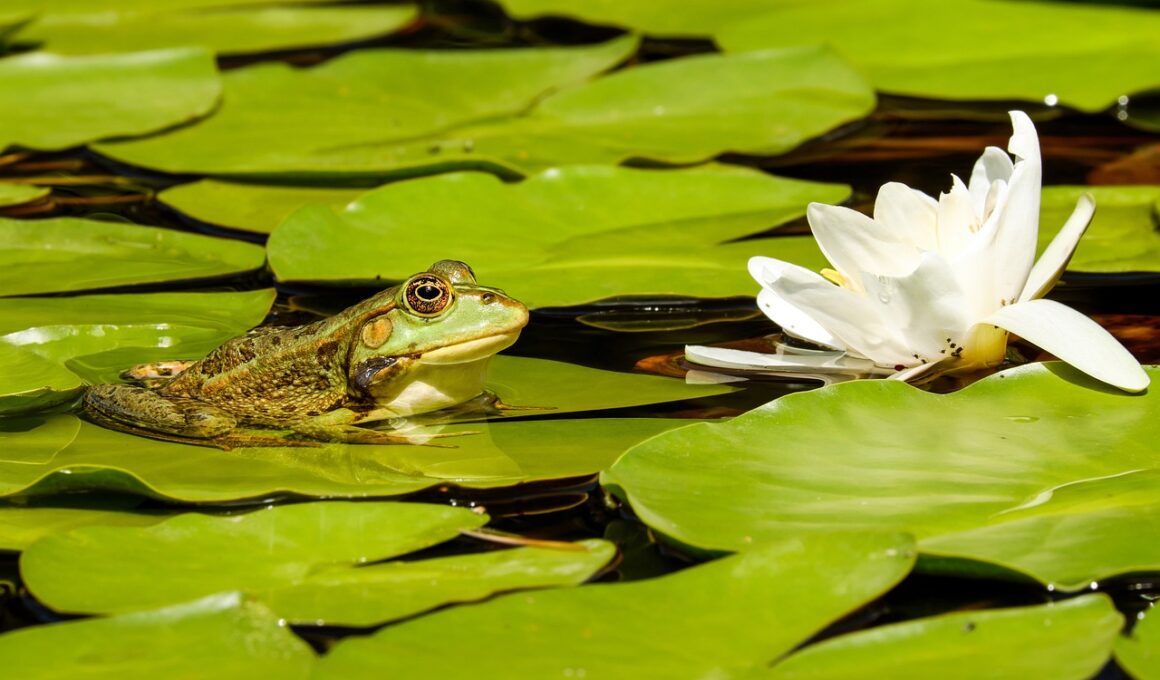
Urbanization has transformed landscapes and ecosystems, making it challenging for amphibians to thrive. However, urban gardens provide essential habitats that restore some ecological balance. These gardens come in various forms including community gardens, private backyards, and green rooftops. Each of these spaces can play a crucial role in creating microhabitats that benefit amphibians, offering food, shelter, and breeding sites. Urban gardens foster biodiversity by providing food sources for various insects, which serve as critical prey items for amphibians. Moreover, they can feature native vegetation that supports local wildlife. To maximize benefits for these creatures, urban gardeners can prioritize native plant species that can thrive locally. Moreover, gardens that incorporate water features, such as ponds or water basins, contribute significantly to amphibian populations by providing necessary moisture. The careful design of these gardens, with a focus on organic gardening practices, can also minimize harmful chemicals that negatively impact amphibian health. Creating awareness and community involvement in urban gardening will ultimately encourage the conservation of these vital species in urban environments.
Urban gardens not only provide sustenance for humans but also create crucial habitats for urban amphibians. These green spaces function to mitigate the negative effects of urbanization, providing food sources and refuges. Additionally, they support essential ecological functions such as water filtration and climate regulation. By integrating elements such as compost bins and rain gardens within urban gardening practices, residents can improve the biodiversity of urban settings. Furthermore, urban gardens allow for essential breeding sites for amphibians, which often require specific environments for successful reproduction. Amphibians are susceptible to climate change; thus, these gardens can serve as climate refuges in urban landscapes. Educational programs that engage local communities can help raise awareness of the importance of amphibians and their conservation in urban settings. Gardeners can be encouraged to plant a variety of flora that appeals to different amphibian species, from frogs to salamanders. In this way, urban gardens are more than just aesthetic enhancements; they are pivotal in preserving biodiversity and improving ecological health in city ecosystems. A continued focus on sustainable practices will ensure long-term benefits for both gardeners and local amphibian populations.
Climate Change and Urban Amphibians
The impact of climate change on amphibians has become increasingly concerning, especially in urban areas where habitats are fragmented. Urban gardens, however, provide a refuge for these vulnerable species. As global temperatures rise, amphibians face threats from habitat loss, altered breeding cycles, and disease outbreaks. Urban gardens can help by creating microclimates that buffer some of these effects, offering cooler, moist areas where amphibians can survive. Furthermore, these gardens can act as corridors connecting patches of green space, allowing for increased movement and gene flow among amphibian populations. Awareness programs can educate gardeners on the importance of maintaining these habitats. Urban gardeners can also help monitor amphibian populations, contributing valuable data to scientists studying climate impacts. Utilizing sustainable gardening practices, such as integrated pest management and organic fertilization, further reduces the negative impacts on local amphibians. Community involvement and citizen science initiatives can enhance the ecological value of urban gardens while benefiting amphibian populations. By fostering a culture focused on biodiversity and sustainable practices, urban areas can mitigate the effects of climate change on their amphibian inhabitants.
Another crucial aspect of urban gardens is their role in community engagement and education. Schools and local organizations can collaborate to create educational gardens, emphasizing the importance of amphibian conservation. Workshops on native planting, habitat restoration, and composting can empower community members to participate actively in these efforts. Additionally, engaging children and young adults in gardening fosters a strong connection to nature, encouraging them to appreciate and protect local wildlife. Urban gardens can also be sites for research projects about local amphibian species, bridging the gap between education and real-world conservation. Gardening clubs can be formed to meet regularly and share knowledge while improving local biodiversity. Local governments can support these efforts through funding and resources, further promoting environmental sustainability in urban areas. By focusing on amphibian education, urban gardens can function as vital learning hubs that foster responsible stewardship. Additionally, engaging local parks and recreation departments can reinforce the importance of maintaining green spaces. Ultimately, these efforts contribute to better informed communities who understand the intrinsic value of amphibians and the importance of preserving their habitats.
Encouraging Sustainable Practices in Urban Gardens
Implementing and promoting sustainable practices within urban gardens serves to enhance habitats for amphibians and other wildlife. Homeowners and community gardeners can reduce their ecological footprint by minimizing pesticide use and embracing organic gardening methods. Moreover, adopting simple water conservation techniques, such as drip irrigation or rainwater harvesting, can promote healthier gardens that attract amphibians. Planting diverse species also encourages a wider range of insects, providing ample food sources for amphibians. Well-planned landscape design, with thoughtful placements of flora and water features, aids in maintaining humidity and temperature levels favorable to amphibian survival. Additionally, educating community members about the importance of native plants helps preserve local ecosystems. A commitment to habitat protection is crucial; thus, gardeners should be mindful of their environmental practices. Planting native plants—such as shrubs or herbaceous perennials—represents an effective strategy for attracting and supporting amphibians. Community initiatives aimed at removing invasive species are equally necessary for maintaining the health of urban environments. This collaboration not only benefits urban ecosystems but fosters a niche for various amphibian species to flourish among humans.
In conclusion, the role of urban gardens in supporting amphibian life cannot be overstated. They serve as invaluable resources amidst urbanization, providing crucial habitats and promoting biodiversity. The involvement of local communities enhances the effectiveness of these gardens, creating a culture that values conservation. As urban areas continue to grow, the importance of amplifying awareness about the benefits of gardening for amphibians becomes even more pronounced. By transforming urban gardens into wildlife-friendly spaces, we can significantly impact amphibian survival. Urban planners should prioritize integrating green spaces in their designs, not only for aesthetics but also for supporting local wildlife. Collaborative efforts among community members, local authorities, and conservation organizations are essential in this initiative. Promotion of sustainable gardening practices will foster urban ecosystems that thrive while simultaneously preserving amphibian populations. Advocacy efforts focused on AMD or amphibian-friendly design will attract interest and participation among citizens. The integration of science into community-based conservation will magnify these efforts significantly. Ultimately, these strategies contribute significantly to amphibian conservation, ensuring that these vital species continue to exist within urban environments.
Amphibians are integral components of healthy ecosystems, and their presence in urban gardens signals ecological health. The ability to support diverse amphibian populations in urban settings hinges on active community participation and sustainable gardening practices. By designing gardens that integrate water features, native plants, and spaces for conservation, residents can significantly influence local biodiversity. Collectively, urban gardens represent a pivotal opportunity to restore ecological balance in fragmented landscapes. Cities can flourish, not just as human habitats, but as vibrant ecosystems that foster wildlife. Moreover, policies that support urban greening initiatives are vital for unlocking the potential of these gardens. Community investment focuses on cooperation between local groups, educational institutions, and policymakers. This collective responsibility showcases how urban dwellers can directly contribute to conserving biodiversity. As urban habitats evolve, the support for amphibian populations hinges on creating varied landscapes. Urban gardeners should see themselves as stewards of biodiversity, providing suitable environments for amphibians to thrive. The importance of promoting these principles cannot be understated, as it ensures continued ecological balance and sustains species crucial for maintaining healthy environments. The future of urban biodiversity depends on the active participation of the community.
Ultimately, the future of urban gardens as supportive environments for amphibians rests in the hands of urban dwellers. To foster these relationships between human beings and wildlife, passionate advocates must champion sustainable gardening practices. Innovative approaches, such as integrating technology with gardening, can enhance the awareness and engagement of various demographics. Establishing designated garden spaces in schools and community centers serves to bridge intergenerational gaps concerning both gardening and amphibian conservation. Furthermore, sharing success stories that highlight positive impacts on urban wildlife can inspire others to join these initiatives. Urban areas worldwide can benefit from implementing such models of community-centered conservation, promoting healthy ecosystems for future generations. Every individual’s contribution, even through small gardening efforts, can collectively create significant ecological benefits. By embracing an active role in conservation, urban gardeners not only contribute to the landscape’s vibrancy but also actively engage in preserving local wildlife. Encouraging partnerships between diverse organizations, schools, and government can bolster these efforts. The connections cultivated between urban gardens and amphibians represent an unprecedented opportunity to reshape urban wildlife interactions. Through deliberate action and awareness, we can ensure a harmonious coexistence with these vital species.