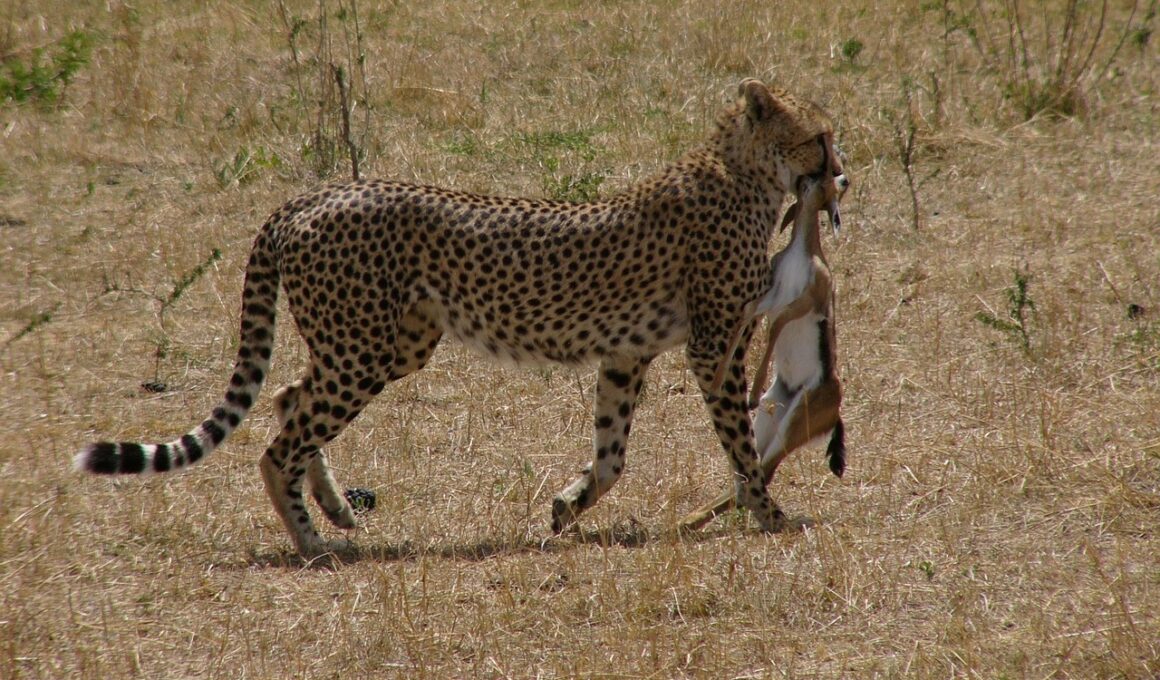
Top 10 Prey Species of Cheetahs in the Wild
Cheetahs thrive in various habitats across sub-Saharan Africa, skillfully hunting diverse prey species. Their diet primarily consists of smaller ungulates, which offer them a high-energy return for the energy expended in hunting. A prime prey species for cheetahs is the Thomson’s Gazelle. These swift and agile animals, known for their incredible speed, are often targeted by cheetahs due to their abundance in open plains. Another preferred choice is the Grant’s Gazelle, which grows larger than the Thomson’s but shares similar habitats. Their endurance makes them constant prey for predators like cheetahs. Furthermore, small to medium-sized mammals also play significant roles in a cheetah’s diet. Animals like impalas are an accessible and frequent target due to their common landscape presence. In dry seasons, opportunities arise when food is scarce and the cheetah must adapt, targeting other species for survival. In such circumstances, they may turn to young wildebeest, which are generally less agile and easier to catch, particularly in a group setting. This adaptability is vital for the success of cheetahs in the wild, making them formidable hunters.
Another crucial prey species for cheetahs is the smaller antelope known as the steenbok. The steenbok is highly adept at hiding, which presents a unique challenge for the cheetah. Their innate ability to remain still and remain undetected allows them to dodge the keen eyesight of their predators. Although their size is considerably smaller than a gazelle, their stealthy nature means they are often hunted when the opportunity arises. Cheetahs also target young and vulnerable members of larger prey species, like the wildebeest calves. This is especially true during calving seasons, when herds become sedentary, making them easy targets. Cheetah mothers are known to selectively hunt these young calves, contributing to the maintenance of ecological balance within their habitats. Another species that falls within the cheetah’s hunting repertoire is the duiker. These small antelopes are notoriously cautious and adept at fleeing; however, when they become careless, they become prey. Cheetahs capitalize on the element of surprise, rapidly accelerating to catch these animals with unusual intensity. This dynamism and adaptability in hunting strategies significantly enhance their success rate. They possess remarkable agility while chasing their chosen prey.
Cheetahs and Their Hunting Techniques
To enhance their hunting capabilities, cheetahs rely on a combination of speed and strategy. Utilizing their keen eyesight to spot potential prey from a distance, cheetahs typically stalk their targets with calculated precision. When in close proximity, they initiate their sprint, achieving remarkable bursts of speed, which can sometimes reach up to seventy miles per hour. This unparalleled acceleration is pivotal while chasing swift prey such as gazelles, where each moment counts. There’s a significant reliance on terrain during the hunt; flat, open areas are the preferred landscapes, where they can effectively exploit their incredible speed. As they close in, silence is paramount. A successful hunt depends not only on physical capability but also on the skillful use of stealth. Natural camouflage from their spotted coats allows them to blend against the savannah grasses. Once they engage, they must rely on short, explosive bursts, indicating the necessity for the hunt’s rapid conclusion, as cheetahs tire quickly. This chasing technique defines their hunting persona, offering insight into their remarkable adaptations for survival in a competitive ecosystem. Each successful hunt strengthens their role as apex predators.
In addition to the smaller ungulates, cheetahs also prey on larger mammals when necessary. Wildebeest, particularly calves, can occasionally become victims of their speedy prowess. During migration seasons, herds become predictable, offering an opportunity for keen-eyed cheetahs to target defenseless younglings. Young ones are often separated from their parents, making them vulnerable to swift cheetah attacks. In particular, females with cubs tend to be more cautious, often allowing cheetahs to pursue a more opportunistic hunting approach. Though larger prey generally poses a challenge due to combined defense strategies within herds, cheetahs have devised alternative techniques. Often, they employ teamwork when hunting in small groups, increasing their chances of securing and ambushing larger prey more effectively. Social collaboration allows accurate targeting and ultimate success when delicately planned. This ingenuity demonstrates their ability to adapt hunting strategies when facing larger mammals. Cheetahs continually refine their skills through practice and experience, learning to make split-second decisions during the heat of the chase. Individual preferences and learning experiences shape their hunting trends. In this unpredictable world, the cheetah’s ability to adjust ensures their prime position among the wild.
Success Rates and Adaptations
Success rates in cheetah hunts vary, typically averaging only about 50% when targeting large prey like wildebeests. Yet, smaller prey increases their chances significantly due to the agility and speed associated with catching them. Adapting to environmental changes is crucial for achieving favorable hunting outcomes. For instance, during droughts, cheetahs may shift focus toward more abundant lesser-known prey species, illustrating their flexibility in dietary habits. This adaptability also includes switching hunting times, transitioning towards dusk and dawn for optimal ambush opportunities. While cheetahs often face competition from lions or hyenas, they still retain a solid hunting record against their competitors. The cheetah’s finer hunting style contrasts starkly with lions, who predominantly hunt in packs and prefer larger prey. Moreover, the social structures within predator groups play a significant role in food availability, prompting cheetahs to refine their solitary hunting tactics to thrive in competitive settings. Each encounter educates cheetahs, helping them develop strategic insights based on past experiences. This keen awareness aids in ensuring survival over generations, fortifying their stake as effective hunters. As the ecosystem continues to shift, these adaptations prove vital for cheetah populations.
Additionally, the African wild has seen a rise in interspecies competition as populations fluctuate. With such changes, cheetahs are required to alter their hunting habits based on the resulting population dynamics. For example, they may choose to hunt during specific lunar phases to align their hunting schedules with the movements of potential prey species. By keenly observing behavioral changes, they establish various methods for maximizing hunting success. In competitive landscapes, young animals become fragiles between the populations of apex predators. Knowledge of local species plays a crucial role in informing an effective hunting strategy. All these elements become strategies that ensure their ongoing occupancy in ecosystems. Moreover, changing climates and human encroachment often lead to habitat fragmentation. This adaptation to hunting tactics becomes imperative when navigating these challenges. Cheetah mothers frequently educate their cubs on the basic principles of hunting, ensuring that subsequent generations inherit crucial survival tactics. By instilling particular techniques at pivotal developmental moments, they enhance the chance of survival for their offspring. This manner of proactive teaching showcases cheetahs’ intricate social behaviors and ensures their lineage remains capable of adapting through changing circumstances.
Conclusion on Cheetah Prey Dynamics
Ultimately, the diverse prey species of cheetahs reflect their adaptability and resilience as hunters. Relying chiefly on small ungulates fills an essential role within their ecological dynamics. By targeting specific prey based on various factors, including habitat, competition, and seasonal changes, cheetahs ensure sustainable populations among prey species. Prey choice also offers insight into broader ecological balance, highlighting the predator-prey relationships that define the African plains. With fierce competition from larger carnivores, cheetahs must continuously refine their hunting tactics to ensure their survival. Ensure the species can endure in the face of environmental change and human impact is crucial for their future. Beautifully adapted to swift hunting in open areas, these cats remain one of nature’s most spectacular predators. Observing their hunting prowess offers a unique glimpse into the rhythms of the wildlife kingdoms. Educational efforts aimed at conserving habitats and safeguarding the ecosystems are paramount, ultimately supporting the intricate web of life that interlinks various species. Cheetahs’ plight as apex predators brings to light the importance of preserving their habitats, ensuring continued survival of these magnificent cats.
Cheetahs also face various challenges within their ecosystems. By establishing a thorough understanding of their prey dynamics, conservation efforts become more robust and viable. Targeted initiatives aimed at reducing habitat loss and preserving biodiversity help cheetah populations thrive. Organizations dedicated to wildlife conservation frequently raise awareness about habitat preservation’s significance, highlighting the need to protect regions vital for prey species. Supporting local communities has proved beneficial. Initiatives that empower local populations while promoting coexistence may help reduce human-wildlife conflict. Creating buffer zones around national parks can mitigate encounters. Engaging in eco-tourism also promotes awareness while providing economic benefits to local communities. By participating in conservation efforts, we can protect the delicate balance cheetahs require for survival, ensuring that future generations will continue to marvel at their incredible hunting abilities. Maintaining ecological integrity is imperative for fostering healthy predator-prey relationships. Conservationists ongoingly engage in educational programs that raise awareness from a young age about the crucial role of top predators within ecosystems. This goal leads to a sustainable future for various species, where cheetahs play a critical role in maintaining ecological balance, showcasing the beautifully intricate web of life they inhabit.