Unique Physical Features of Different Lemur Species
Lemurs, the unique primates of Madagascar, exhibit a fascinating array of physical features that distinguish them from other animals. One of the most notable characteristics is their large, expressive eyes, often adapted for nocturnal living. The aye-aye, for instance, has exceptionally large eyes that enhance its night vision. These eyes not only help in foraging, but also play a role in social interactions. Moreover, many lemurs possess elongated limbs and a flexible spine, allowing them to navigate their arboreal habitat efficiently. These adaptations assist in leaping and climbing through tree branches swiftly. Another physical trait found in several species is the presence of whiskers, which enhance their sensory perception and help them detect movement in their surroundings. Coloration also varies significantly; some lemurs have distinct markings or fur patterns that serve various purposes including camouflage and signaling to others. Their tails can be long and bushy, aiding in balance during leaps. Additionally, certain species are known for their unique dental structures that adapt to their diets, further showcasing the diversity among lemur species.
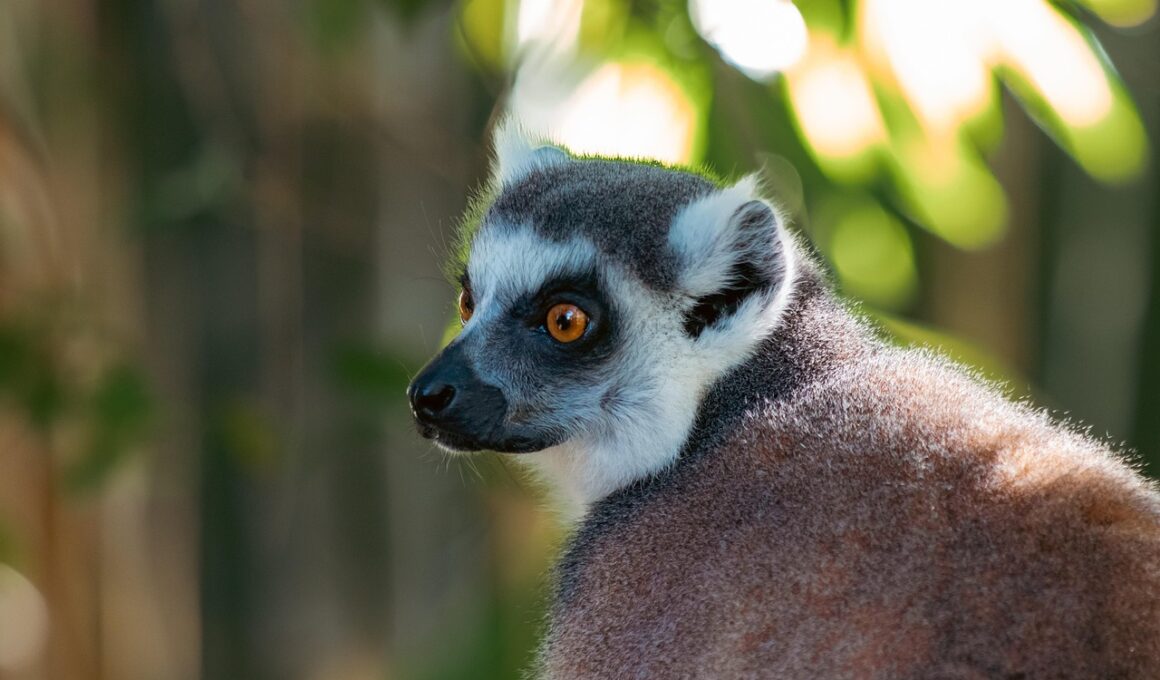
Among the striking features of lemurs, the ring-tailed lemur stands out due to its distinctive black-and-white striped tail. This tail is not only a tool for communication, but also aids in locomotion. The lemur catta uses its tail for balance and display during social interactions, often waving it above its body to ensure visibility to other group members. These social cues are essential as ring-tailed lemurs are known for their complex social structures and behaviors. Their facial structure is also remarkable, with a flat face and a pronounced snout, which is helpful for their omnivorous diets that include fruits, leaves, and insects. Furthermore, ring-tailed lemurs exhibit sexual dimorphism, where males and females display different sizes. Males tend to be larger and have more robust features than females. Their body fur is predominantly gray with white and brown markings, providing effective camouflage within their dry, forest habitat. The combination of their striking tail, facial structure, and social behaviors exemplifies their unique evolutionary adaptations that allow them to thrive in Madagascar’s diverse ecosystems.
Madagascar Indri: A Unique Physique
Indris, the largest living lemurs, boast unique adaptations that highlight their physical characteristics. They possess a stocky body covered in thick fur, primarily black and white, which helps them blend into Madagascar’s forests. The indri’s notably short tail contributes to its distinctive look, as it relies on its strong forelimbs rather than a tail for balance. These primates are known for their exceptional vocalizations. Indris communicate with long, complex calls that resonate through the forest, showcasing their social nature. Their hands are adapted for an arboreal lifestyle, featuring flexible digits that enable them to grip tree branches securely. The strength in their limbs allows them to leap up to 10 meters between trees, a crucial adaptation for their survival. Their keen eyesight plays a vital role in navigating the canopies while searching for food, primarily consisting of leaves and fruits. This unique combination of size, strength, and ecological adaptations illustrates how the indri has evolved to thrive in its specific environmental niche, making it a remarkable representative of Madagascar’s unique primate diversity.
Sifakas are another fascinating group of lemurs, recognized for their distinctive locomotion, known as vertical clinging and leaping. They have elongated limbs that allow them to leap gracefully between trees, making them one of the most acrobatic primates in the animal kingdom. Sifakas have a unique body structure with large, muscular hind limbs designed for powerful leaps, and their forelimbs are adapted for grasping and stabilizing. Their fur is often creamy white or light brown, coupled with a contrasting facial fur pattern that enhances their visual appeal. Notably, sifakas also possess a unique tail that aids in maintaining balance during their leaps. Their vertical posture while leaping gives them an impressive appearance among the trees. In addition to physical traits, their social behavior involves complex family structures with strong bonding among group members. Sifakas communicate through a series of vocalizations and physical displays, emphasizing not only their physical attributes but also their social complexities. These adaptations and interactions illustrate how sifakas exemplify the rich diversity found within Madagascar’s lemur species.
The Unique Dental Adaptations of Lemurs
Lemurs also show remarkable diversity in their dental structures, which have evolved based on their varied diets. Dental characteristics play a crucial role in how different species adapt to their environments. For instance, the propithecus species, known as sifakas, have specialized incisors that enable them to effectively scrape bark and access soft inner wood. This adaptive feature is essential for their survival in Madagascar’s ecosystems where food sources can be scarce. Meanwhile, frugivorous species, like the brown lemur, are equipped with broader molars suitable for grinding fruit and leaves. Their unique dental formula helps them exploit available food resources efficiently. Additionally, some lemurs have developed a multitasking dentition that allows them to consume varied diets, including insects and plant material. These adaptations showcase not only the evolutionary processes at work but also the ecological niches occupied by lemurs in Madagascar. As these primates continue to thrive, their unique dental features reveal the interplay between their physical attributes and dietary needs.
Moreover, lemurs possess unique adaptations in their sensory systems, which play an integral role in their survival. Many species have a keen sense of smell, thanks to their large olfactory bulbs. The ring-tailed lemur particularly relies on scent marking for social communication and territorial claims. Their ability to detect pheromones and other chemical signals aids them in identifying potential mates and rivals. Such adaptations are crucial in a dense forest environment where visibility is limited. Additionally, lemurs have highly developed hearing capacities, allowing them to detect predators easily. Species like the sportive lemur exhibit specialized adaptations that enable acute hearing, essential for avoiding danger. Furthermore, the combination of sharp vision helps them spot food and potential threats in the treetops. These sensory adaptations reflect their evolutionary path in Madagascar’s diverse habitats. As they adapt to their environments, these unique physical features not only enhance their survival but also contribute to the rich tapestry of Madagascar’s ecosystems. The diversity among lemur species underscores the importance of conservation efforts to protect these unique primates.
Conclusion on Lemur’s Physical Diversity
In conclusion, the unique physical features of different lemur species highlight their adaptations that allow them to thrive in diverse habitats. From the striking tail of the ring-tailed lemur to the specialized dental structures of the sifaka and indri, these traits are essential for their survival. These adaptations reflect the ecological challenges they face in Madagascar, such as habitat loss and food scarcity. The complex social behaviors, stunning physical appearances, and remarkable adaptations of lemurs exemplify the beauty of evolution in action. As explorers of the treetops, lemurs contribute to the ecological balance in their environment. Conservation efforts are vital to ensure their continued existence; preserving their natural habitats is essential for maintaining biodiversity. By understanding their unique adaptations and the roles they play in their ecosystems, we can advocate for their protection. The diversity within lemurs serves as a reminder of the importance of conserving unique species and their habitats. Protecting these primates from extinction ensures their survival for future generations to appreciate.