The Conservation of Wetland Habitats in the Serengeti
The Serengeti Plains are renowned for their diverse ecosystems, which include various habitats such as wetlands, grasslands, and forests. Wetlands in particular play a critical role in maintaining ecological balance. These areas also support a variety of wildlife by providing essential resources, such as food, shelter, and breeding grounds. Consequently, conservation efforts are imperative to protect these vital habitats from threats like climate change, pollution, and human encroachment. Efforts to study these ecosystems emphasize the importance of biodiversity and the intricate relationships between various species. Preservation initiatives involve local communities, which allows for sustainable management of resources while also promoting environmental education. Furthermore, global collaboration is essential to tackling the challenges that wetlands face, ensuring that policies protect both wildlife and the ecosystems within the Serengeti. Failure to conserve these habitats may lead to dire consequences, such as loss of species and disruption of regional ecological processes. Therefore, a multi-faceted approach combining scientific research, community involvement, and governmental support is crucial for effective conservation. Protecting the Serengeti’s wetlands is not just important for wildlife but for humanity as well.
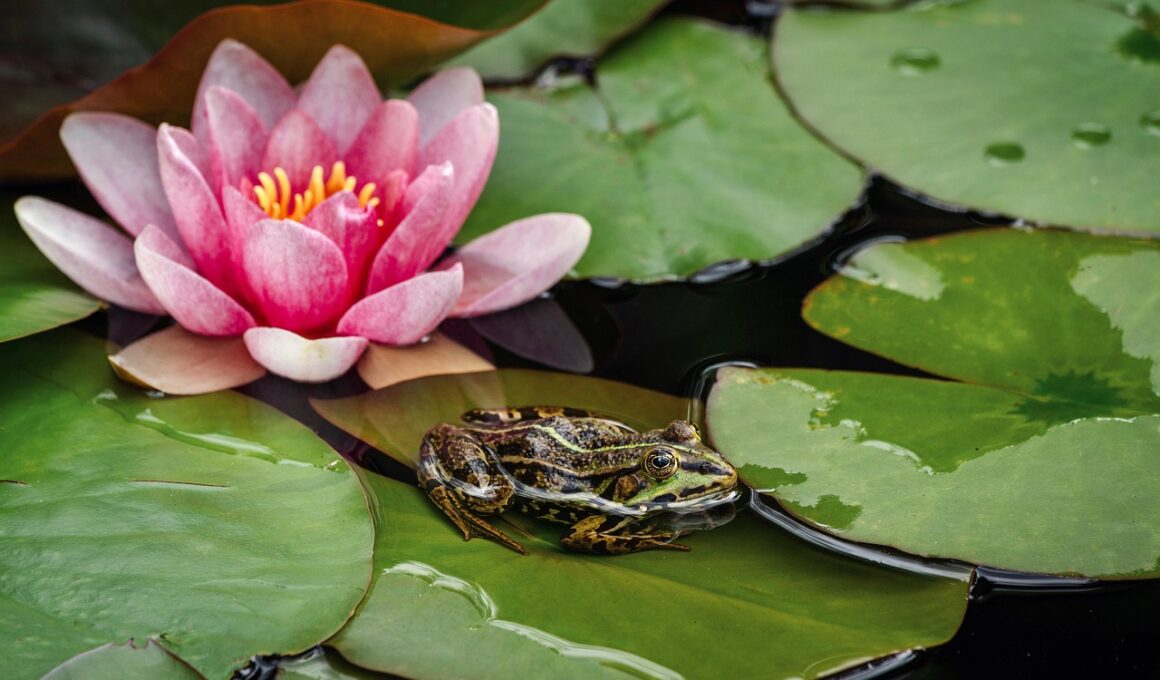
Wetlands in the Serengeti are complex ecosystems that support a multitude of plant and animal species. Here, you find unique flora and fauna adapted to wet conditions. This biodiversity helps maintain ecological stability, which is essential for the health of the entire region. Among the many species that thrive in these wetlands, some are exclusive to this specific habitat. Conservation efforts focus on preserving these unique aquatic zones, ensuring that species like the endangered African marsh owl and various amphibians remain protected. Moreover, wetlands act as natural water filters, improving water quality in the surrounding areas. This function is essential for both wildlife and local communities who depend on clean water sources. Inevitably, degradation of these habitats can lead to increased flooding and decreased water quality, affecting not only wildlife but also human populations living nearby. Wetland protection goes hand in hand with sustainable practices like responsible agriculture and eco-tourism. Collaboration between local stakeholders, governments, and conservation organizations is vital for creating comprehensive management plans. Citizens should also be informed and involved in these conservation efforts to ensure long-term benefits for both people and the environment.
Importance of Biodiversity in Wetland Habitats
Biodiversity within wetland habitats of the Serengeti is crucial for ecosystem resilience. The interdependence of species forms a complex web that supports the entire habitat. When one species thrives, others benefit, demonstrating the intricate balance necessary for a healthy ecosystem. Protecting this biodiversity is paramount, as each species plays a unique role in nutrient cycling and food web integrity. For example, aquatic plants like reeds and sedges provide vital cover for many fish and insect species. Additionally, these plants help stabilize the soil, preventing erosion and maintaining water quality. Furthermore, the decline of specific species can significantly impact their ecological niche, leading to unforeseen consequences. Conservation programs aim to monitor species populations and restore habitats essential to maintaining biodiversity. This can involve rehabilitating degraded wetlands and reinstating native plants to facilitate the return of wildlife. Public awareness campaigns play a vital role in educating communities about the value of local biodiversity, promoting stewardship, and encouraging conservation participation. Every single effort contributes to sustaining the natural beauty and ecological harmony within the Serengeti’s vital wetland habitats, making them a priority for conservationists globally.
Water management plays a fundamental role in preserving the wetlands within the Serengeti. Ensuring adequate water levels is essential for maintaining the health of these ecosystems. Changes in precipitation patterns due to climate change significantly impact water availability, affecting both wildlife and human populations. Therefore, effective water management strategies must be implemented to mitigate these impacts. This can involve monitoring water quality and launching initiatives to prevent pollution from agricultural runoff. The introduction of sustainable agricultural practices is vital to reduce water contamination and enhance habitat integrity. Furthermore, creating buffer zones around wetlands can minimize human pollution while supporting agricultural productivity. Engaging local communities in these initiatives fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility towards their environment. Successful water management requires a collaborative approach, where governmental bodies, conservation organizations, and local communities can work together. Applying integrated water resource management principles ensures that the needs of both the ecosystem and the human population are met. This collaborative effort can yield positive outcomes, protecting the delicate balance necessary for the sustainability of the wetlands. Ultimately, preserving water resources is non-negotiable for sustaining the rich biodiversity found within the Serengeti.
Challenges and Threats
Wetland habitats in the Serengeti face numerous challenges that threaten their integrity and the species that inhabit them. One significant issue is climate change, which alters rainfall patterns and affects the availability of water vital for these ecosystems. Increasing temperatures can lead to evaporation, reducing wetland areas and, consequently, the homes of many species. Another threat is human encroachment through agriculture, settlements, and infrastructure development. As communities expand, wetlands may be drained or polluted, resulting in habitat loss and reduced biodiversity. Furthermore, invasive species pose a significant threat to native populations, as they can outcompete indigenous plants and animals for resources. Conservation professionals working in the Serengeti must navigate these compound challenges to effectively restore and conserve wetland habitats. Strategies often include the establishment of protected areas to safeguard biodiversity and reduce human impact. Education initiatives also empower local communities to engage in conservation efforts actively. By addressing these multi-layered threats, conservationists can develop sustainable solutions that consider ecological, social, and economic needs, promoting a balance between human activities and environmental preservation in the Serengeti.
Community involvement and education are keys to successful conservation efforts in the Serengeti’s wetland habitats. Engaging local populations in environmental stewardship fosters a deeper understanding and appreciation for these precious ecosystems. Programs that educate residents about the ecological importance of wetlands can inspire sustainable practices that reduce harm to the environment. Moreover, training local communities in eco-friendly tourism can create economic opportunities while promoting conservation. For instance, responsible wildlife viewing can generate income while minimizing habitat disruption. The involvement of local voices also establishes a sense of responsibility toward preserving natural resources. Collaborative initiatives that include community and conservation groups can lead to the development of management practices that benefit both people and wildlife. Additionally, schools and local organizations can conduct workshops and activities that promote environmental awareness. Creating forums for sharing knowledge and experiences helps unify the shared goal of wetland preservation. Empowering communities through education not only helps protect wildlife but fosters a more resilient population capable of adapting to environmental changes. Supporting community-driven conservation efforts can greatly enhance the success of wetland protection in the Serengeti.
Future Directions for Wetland Conservation
Looking ahead, the future of wetland conservation in the Serengeti requires innovative solutions to emerging challenges. Advances in technology and research offer critical insights into monitoring and evaluating wetland health more effectively. For instance, satellite imaging allows conservationists to track changes in land use and detect areas at risk of degradation. Additionally, utilizing drones can provide real-time data on wildlife populations and habitat conditions, facilitating timely intervention when necessary. Stakeholder collaboration remains essential to craft comprehensive conservation plans that integrate scientific knowledge with local practices. Moreover, ongoing funding and investment in conservation initiatives are vital to ensure sustained efforts. Engaging local, regional, and global partnerships can leverage resources to address various challenges facing wetlands. Policymakers must prioritize wetland conservation within broader environmental strategies, advocating for policies that protect these ecosystems. The development of adaptive management practices will also play a crucial role, allowing for flexibility in responding to changing conditions and new threats. Ultimately, ensuring the success of wetland conservation efforts in the Serengeti will rely on holistic and adaptive approaches that incorporate scientific research, community engagement, and effective policy frameworks.
In conclusion, the preservation of wetland habitats in the Serengeti is imperative for environmental sustainability and the well-being of local communities. The complex interactions of diverse species within these ecosystems contribute significantly to overall biodiversity. Ongoing conservation efforts, including community involvement and sound water management practices, are crucial to combat threats like climate change and pollution. Implementing effective educational programs will inform and empower residents, fostering a sense of shared responsibility. Future conservation strategies will benefit from technological advancements and collaborative partnerships that enhance monitoring and adaptive management. Each of these efforts contributes to the long-term sustainability of these vital habitats, ensuring that they continue to thrive. Furthermore, preserving wetlands benefits not only the flora and fauna but also the human populations that rely upon the ecosystem services they provide. As we face growing environmental challenges, collective action in conserving the Serengeti’s wetlands will ultimately benefit all species, including us. The interconnectedness of life thrives within these rich habitats, encapsulating the essence of nature’s balance. Promoting awareness and proactive measures is essential to maintaining the health of the Serengeti’s wetland ecosystems for generations to come.