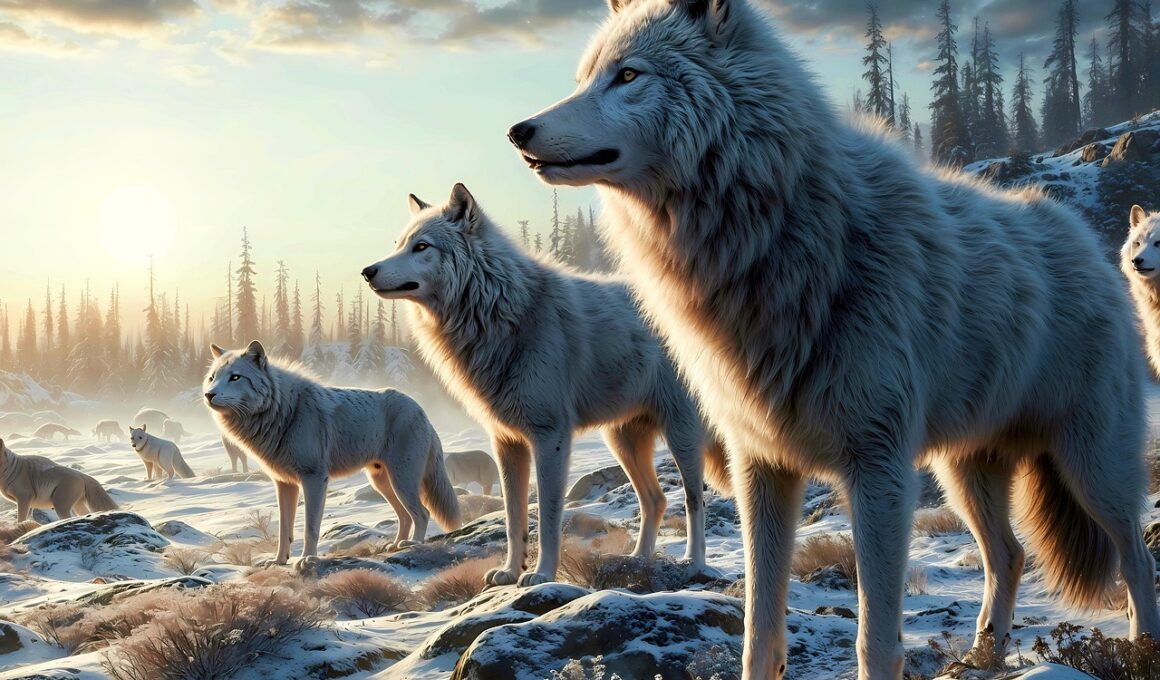
The History and Evolution of Arctic Wolf Packs
The Arctic wolf, a subspecies of the gray wolf, is native to the expansive Arctic regions. These incredible creatures live primarily in small family units called packs, which are essential for their survival in harsh environments. The diet of Arctic wolves typically includes caribou, muskoxen, and Arctic hares, which they hunt together, utilizing teamwork and strategies honed over generations. The evolution of these packs has been influenced significantly by the extreme climate, leading wolves to adapt their hunting techniques. The communal aspect of these packs plays a critical role, not only in sharing responsibilities during hunts but also in caring for young pups. Social structures within these packs vary widely but usually center around familial bonds, enhancing their chances of survival in the unforgiving Arctic tundra. By studying the behavior and hierarchy within these packs, researchers gain insights into social dynamics and adaptive strategies that have shaped these resilient animals over time. Understanding the history of Arctic wolf packs offers a unique window into their evolution, showcasing their adaptability and the importance of social living for survival in extreme conditions.
The Arctic wolf is characterized by its thick white fur, which serves as insulation against harsh Arctic temperatures. As these wolves have evolved over thousands of years, their physical characteristics have adapted to the cold climate. Their smaller body size compared to other wolves allows them to preserve heat more effectively. Additionally, their fur is denser than that of more temperate wolves, providing excellent warmth. Historically, the natural selection pressures in the Arctic led to evolved hunting behaviors that remain today. Some Arctic wolf packs have been observed using specific strategies that involve stalking prey quietly and working together to cut off escape routes. The communal nature of their hunting also fosters strong ties among pack members, which is crucial for the survival of both adults and pups. Family groups exhibit collaborative hunting techniques that allow them to tackle prey much larger than individual wolves could handle alone. These traits ensure that the pack thrives, even in a challenging environment where food can be scarce. The interplay of these physical adaptations and social strategies is what has led Arctic wolves to become one of the apex predators in their ecosystem.
Packs and Their Structure
The structure of Arctic wolf packs often revolves around a dominant breeding pair known as the alpha male and alpha female. These wolves lead the pack, making critical decisions, especially during hunting and territorial disputes. Under their leadership, the rest of the pack, which can consist of both adult wolves and their offspring, works cohesively to maintain their territory against rival packs. The social hierarchy within these packs is essential for order, especially when raising pups. Each member has a role that contributes to the pack’s success; some wolves may be more active hunters, while others may assist in protecting pups. This communal approach to caregiving allows for higher pup survival rates. In order to establish and maintain dominance, alpha wolves display specific behaviors and vocalizations that signal their status to other pack members. These hierarchies and social behaviors are crucial for the welfare of the pack as they navigate the harsh Arctic landscape. Their cohesive social structure differentiates Arctic wolf packs from those of temperate forest wolves, emphasizing the adaptations forged through centuries of evolution.
The hunting tactics employed by Arctic wolf packs are compelling and highlight their intelligence. Wolves rely heavily on teamwork and strategy, showcasing their advanced skill sets. Unlike solitary hunters, Arctic wolves often initiate and execute hunts collectively, capitalizing on group dynamics. When stalking their quarry, they communicate through a combination of body language and vocalizations, ensuring synchronization among members. In winter, when snow covers the terrain thickly, pack behavior becomes even more critical as resources dwindle. The smaller pack sizes, typically ranging from 5 to 10 wolves, allow for stealthier approaches as they hunt caribou or other large prey. Furthermore, this cooperation significantly increases their hunting success rate compared to lone wolves. Despite working as a cohesive unit, these wolves also exhibit variation in roles during hunts—some may flush out prey while others ambush from concealed positions. By mastering these collaborative tactics, Arctic wolf packs have remained successful in their attempts to secure adequate food sources in unforgiving habitats. Their hunting prowess, combined with social cooperation, demonstrates a remarkable evolutionary success within their challenging environment.
Adaptations to Climate
The Arctic environment presents unique challenges that have significantly influenced the evolution of wolf packs. The extreme cold and seasonal scarcity of food resources prompt these wolves to adapt their social behaviors. For instance, during harsh winters, pack cohesion becomes paramount; they often rely on each other for warmth, lying close together during resting periods. Behavioral adaptations also extend to their hunting strategies, altering according to the availability of prey. In times of food scarcity, packs may expand their territories, exploring new hunting grounds in search of caribou or other available food sources. This adaptability ensures the survival of wolves throughout the varying seasons of the Arctic. The dynamics of social interactions within the pack further play a vital role in sustainability. By strengthening their familial bonds through social grooming and play, Arctic wolves enhance social cohesion, which ultimately improves the pack’s ability to endure and thrive in this challenging habitat. Thus, understanding how Arctic wolf packs have adapted to their environment unveils profound insights into not only their survival but also the intricate balances that exist in nature.
Throughout history, the plight of Arctic wolves has been influenced by climate change, impacting their habitat and food sources. As global temperatures rise and Arctic ice diminishes, the landscape that has shaped their evolution is drastically altered. Consequently, the availability of prey species such as caribou is also changing, forcing wolves to adapt continually to shifting ecological conditions. Some experts believe that these pressures may lead to significant changes in pack behavior; for example, wolves may need to travel further distances to locate food. Increased human contact, whether through tourism or resource extraction, presents another layer of challenge. This interplay emphasizes the importance of studying Arctic wolf packs and their adaptive behaviors in the face of change. Conservation efforts targeting these wolves must consider the impact of environmental changes on their social structures and hunting strategies. Researching how these wolves respond to new ecological challenges will provide critical insights into wider ecological dynamics in the Arctic. Monitoring and preserving these majestic animals in their native environment is vital to maintaining the integrity of Arctic ecosystems.
Conservation and Future Outlook
As we look to the future, the conservation of Arctic wolf packs becomes imperative as ecological factors become increasingly unpredictable. Organizations and researchers are working tirelessly to protect their natural habitats and mitigate the impacts of climate change. Efforts include habitat restoration, monitoring populations, and educating the public about the vital role these wolves play in maintaining ecological balance. Engaging local communities is essential in ensuring that wolves are respected and their habitats preserved. By fostering a deeper understanding of wolf behavior and their requirements, communities can develop sustainable practices that benefit both wolves and humans. Furthermore, scientific research continues to uncover the complexities of pack behavior, revealing the intricate social networks that facilitate their survival. This knowledge is crucial for developing effective management strategies aimed at population sustainability. As we navigate unprecedented changes in the Arctic environment, it is vital to support conservation initiatives that prioritize the health and longevity of Arctic wolf populations. Conservation efforts must address both the wolves’ immediate needs and the broader ecological challenges they face in a warming world.
In conclusion, Arctic wolf packs epitomize resilience and adaptation in one of the planet’s most challenging climates. Their evolution is shaped by a combination of physical adaptations, social structures, and intricate hunting strategies that allow them to thrive. As conditions in the Arctic continue to change, understanding their history and the threats they face becomes increasingly important. Collaborative efforts through research and community engagement will be vital for securing a future where Arctic wolves can continue to flourish. Recognizing the ecological importance of these wolves not only enriches our understanding of Arctic ecosystems but also highlights the interconnectedness of all species within these systems. The story of Arctic wolf packs serves as a reminder of nature’s complex web, urging us to respect and protect these magnificent creatures. In our pursuit to conserve their habitats and ensure their survival, we safeguard not just the wolves but the entire Arctic ecosystem. The ongoing efforts to study and maintain the Arctic wolf population will not only benefit the wolves themselves but also contribute to the broader goal of biodiversity preservation as we face a rapidly changing world.