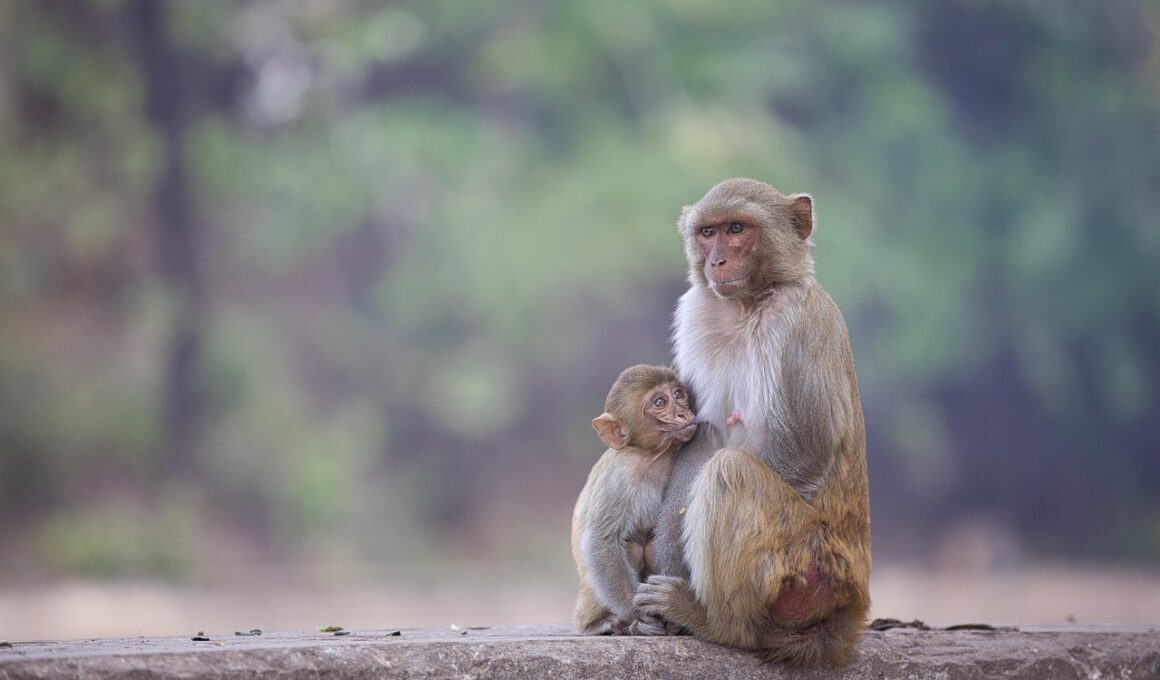
Mental Acuity in Desert-Dwelling Primates
Desert animals have adapted in various ways to survive in harsh environments, yet their cognitive abilities remain less studied compared to those in lush ecosystems. Among these unique beings, desert-dwelling primates stand out for their remarkable mental acuity. Adaptations of these primates demonstrate not only physical survival strategies but also remarkable intelligence that aids their resourcefulness. Their ability to find food in a sparse environment exemplifies their cognitive skills through strategies that involve memory, learning, and problem-solving. Often, these primates exhibit complex social behaviors that emphasize their intelligence. Research suggests that desert-dwelling primates, such as the ring-tailed lemur, exhibit advanced social structures and communication methods for survival. These factors contribute to their adaptation in extreme climates where resources are limited. Understanding the intelligence of desert animals provides insights into cognitive evolution in challenging environments, as these primates exhibit behaviors suggesting an understanding of their surroundings. Their resourcefulness helps them navigate their territory and find food, which reveals their impressive mental faculties beyond mere instinctual survival.
Intelligence in desert-dwelling primates encompasses not just solitary survival tactics, but also cooperative strategies among group members. Social learning plays a significant role in how these primates share knowledge about foraging and predator evasion. Young primates observe their parents and peers, mimicking behaviors that enhance their survival chances. This form of observational learning is vital in desert habitats, where the transmission of skills from one generation to another can make a substantial difference. For instance, when harrowing temperatures cause plants to wilt, primates with social learning can quickly adopt alternative food sources. Such adaptability indicates that cognitive capabilities extend beyond individual grasp to community resilience. Moreover, studies reveal that desert primates can exhibit problem-solving skills. They can navigate mazes and remember the location of water sources learned through experience. Their adaptability symbolizes a high level of intelligence that allows them to utilize resources effectively. Overall, the intelligence of these primates mirrors the complexities involved in surviving in demanding environments while fostering social bonds that enhance communal survival strategies.
Foraging Strategies of Desert Primates
Foraging strategies exemplified by desert-dwelling primates further illuminate their cognitive prowess. They often demonstrate sophisticated techniques for locating and acquiring food in arid environments characterized by limited resources. One prevalent behavior observed is their ability to remember the location of diverse food sources. These primates utilize both spatial and temporal memory, tracking when and where specific food items are available. With the scarcity of vegetation in the desert, primates like the African green monkey will engage with various types of plant life, often adjusting their foraging techniques based on seasonal changes. Furthermore, they have mastered the art of using tools, such as stones to crack open hard-shelled fruits and seeds. This innovative behavior not only showcases their intelligence but also their ability to manipulate their environment effectively. Even sharing discovered food reinforces social interactions among primates, which enhances their survival. As they learn new foraging habits, they also share information across generations, ensuring community survival. Through such adaptations, desert-dwelling primates exemplify the remarkable fusion of intelligence and survival instinct in their arid habitats.
Communication in desert-dwelling primates is another facet that highlights their intelligence, facilitating social interactions essential for survival. Through vocalizations, body language, and facial expressions, these primates convey vital information about their environment and social status. Alarm calls serve as warnings against potential predators, illustrating their awareness and group cohesion patterns. Additionally, these non-verbal cues can express emotions, reinforce social hierarchies, or initiate cooperative behaviors, all of which are critical for their social structures. For example, when a troop of desert primates encounters danger, their coordinated vocalizations can deter threats or facilitate collective movement away from hazards. Researchers have identified patterns in their communication, indicating a level of complexity rivaling that found in more socialized species. Their ability to adapt their communication strategies based on particular situations is indicative of an advanced cognitive process guiding their interactions. Enhanced communication capability provides an evolutionary advantage, promoting cooperation and unity among members during foraging and nurturing. By fostering relationships and conserving energy, the social intelligence of these desert primates emphasizes their need for collective survival. Such dynamics underscore the significant role of communication in their overall intelligence and adaptability.
Problem Solving and Learning in Desert Primates
Desert-dwelling primates have also demonstrated impressive problem-solving skills, showcasing adaptability in ever-changing environments. Problem-solving experiments reveal their cognitive abilities, allowing these creatures to navigate obstacles effectively. Studies illustrate that with training, many primates can complete tasks requiring innovative methods. They often rely on trial-and-error strategies, learning how to manipulate their environment efficiently. For instance, certain primates can solve puzzles to retrieve hidden food, illustrating their cognitive dexterity. Memory plays a crucial role throughout these learning processes, acting as a cognitive tool that aids in retention and recall. Real-life scenarios within their habitats often mimic experimental conditions, where they engage in similar problem-solving tasks to find resources. Moreover, social learning contributes significantly, as younger primates observe and imitate the successful strategies employed by older, more experienced group members. This acts as a crucial knowledge transfer mechanism that enhances group survival. With the harsh conditions in their environments, the evolution of problem-solving skills among desert primates epitomizes their adaptability and resilience. Indications that these skills could evolve further highlight their significant place in the broader ecosystem and cognitive study of primates.
The relationship between intelligence and survival strategies among desert animals often intrigues researchers. Desert primates have evolved unique behaviors that not only ensure survival but also reflect their intellectual abilities. Their communal living structures allow for the pooling of wisdom, facilitating informed choices in harsh surroundings. Factors such as seasonal variation and resource availability shape their survival strategies, demonstrating their cognitive flexibility. The adaptability inherent in such strategies confirms that intelligence alone can cultivate unique techniques to navigate nightmare environments. Additionally, climate change poses growing threats, prompting these beings to shift their survival behaviors. As their habitats evolve, desert-dwelling primates will need to explore new methods for gathering resources and coping with alterations in their environment. Such resilience indicates an evolving intelligence that continues to adapt and thrive amidst odds. Importantly, studies on behavioral plasticity will elevate understanding of mental acuity in desert ecosystems. Seeing these primates adjust their cognitive strategies provides insight into the ecological constraints that refine intelligence in collective groups. Survival behaviors adaptively interlinked with knowledge underscores the complexities of evolution in these fascinating desert primates.
The Future of Desert Primates’ Intelligence
The future of desert-dwelling primates and their intelligence raises important questions about their adaptation in light of rising environmental challenges. With climate change accelerating, foreseeing how these primates will modify their behaviors becomes essential for conservation efforts. Will their cognitive abilities enable them to develop innovative survival strategies as their habitat conditions alter? Current studies hint that these primates possess a degree of resilience and flexibility in adapting to new challenges. However, human encroachment and habitat degradation remain major threats that could compromise their survival and intelligence. Ensuring the preservation of their natural habitat is vital for maintaining the cognitive skills evolved over time. Furthermore, understanding how these primates can continue to thrive in changing environments is paramount for ecological balance. Continued research into their intelligence not only enriches our understanding of cognitive evolution but also assists in developing effective conservation strategies. Collaborative initiatives focused on protecting these environments and the species inhabiting them should be prioritized. Investing in education and awareness of desert ecosystems guarantees the survival of these unique inhabitants, allowing future generations to admire their cognitive capabilities.
In summary, desert-dwelling primates exemplify remarkable intelligence shaped by the demanding nature of their environments. Their mental acuity manifests in various aspects, including foraging strategies, communication, learning abilities, and problem-solving. Research continues to showcase their adaptability and cognitive capabilities, paving the way for a deeper understanding of their relevance in ecology. As desert ecosystems face numerous threats, preserving these primate populations becomes paramount. With their unique adaptations and intelligence, they provide invaluable insights into cognitive evolution and species survival. Prioritizing conservation efforts and promoting awareness of desert habitats will ensure these remarkable beings continue to thrive while enriching the biodiversity around them. In doing so, the future of these desert animals and their exceptional mental acuity can be preserved for generations to come. Their story serves as a reminder of the complexities of life in Earth’s most vulnerable ecosystems, wherein intelligence plays a crucial role in survival. The collective intelligence of these primates reflects their adaptability while providing hope for conservationists committed to protect the delicate balance of life. Ultimately, recognizing and valuing the unique intelligence of desert-dwelling primates is essential for both ecological sustainability and ethical responsibility.