The Role of Animal Body Cavities in Organ Protection
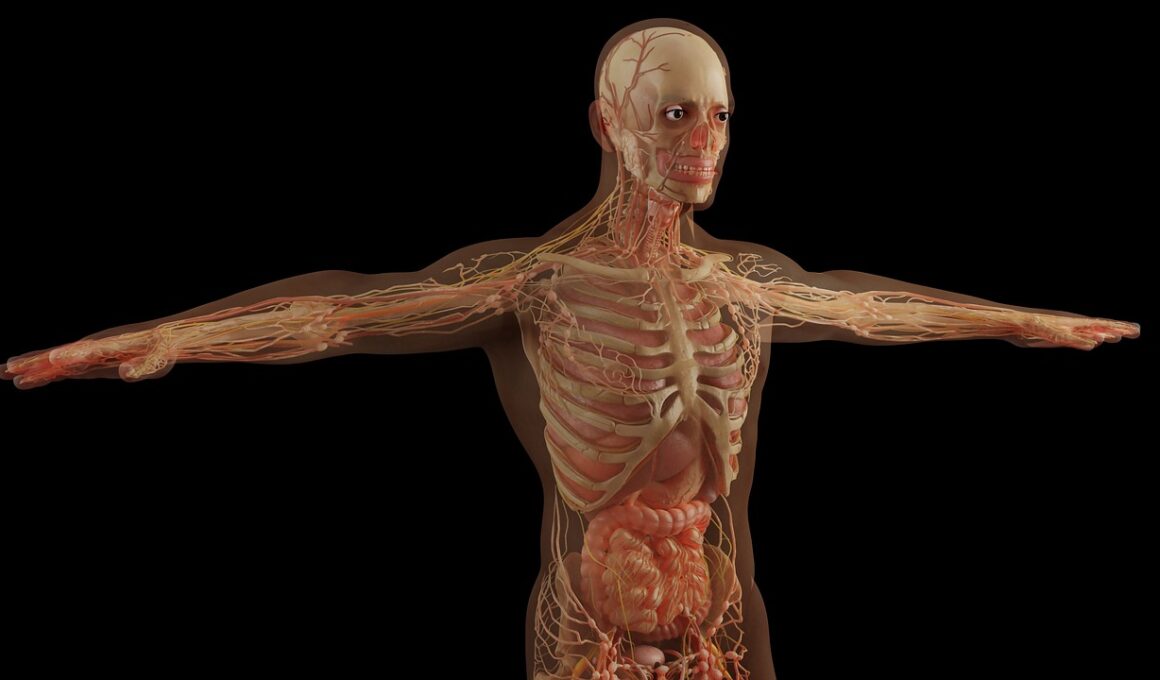
Animal anatomy reveals fascinating structures called body cavities. These cavities play critical roles in the organization and protection of internal organs. Different species manifest various body cavity configurations, reflecting their evolutionary adaptations. The primary body cavities include the thoracic cavity, the abdominal cavity, and pelvic cavities. Each serves unique purposes, housing organs vital for survival. For example, the thoracic cavity contains the heart and lungs, which are essential for circulation and respiration respectively. Likewise, the abdominal cavity houses organs involved in digestion and metabolism. These cavities are lined with protective membranes, such as the peritoneum, ensuring minimal friction and safeguarding organs against trauma. Furthermore, body cavities allow for the expansion and contraction of organs like the lungs, which is fundamental for breathing. The organization within cavities also aids in compartmentalization, reducing the risk of inter-organ interference. Understanding body cavities is crucial for veterinary medicine and biology, inspiring researchers and educators to emphasize their importance in animal anatomy studies. Knowledge of these structures is integral to improving diagnostic methods and treatment strategies in veterinary practice. Thus, further exploration of body anatomy remains essential for effective education.
Structural Significance of Body Cavities
From a structural standpoint, body cavities provide significant advantages for organ function and protection. These cavities form compartments that help to stabilize organs, preventing excessive movement during locomotion or physical activity. For example, the rib cage provides a rigid barrier that protects the heart and lungs from external forces. Additionally, animal body cavities help maintain organ position through connective tissues and ligaments that anchor them in place. This support is particularly essential in the abdominal cavity, where various organs are suspended and arranged for optimal functioning. The segmentation of body cavities also contributes to physiological efficiency; every cavity contains organs that specialize in specific tasks, such as digestion in the abdominal cavity or gas exchange in the thoracic cavity. Research continues to show that proper organization within these cavities also contributes to disease prevention. Conditions leading to organ displacement can lead to complications, emphasizing the necessity of a stable arrangement. Moreover, the evolutionary significance of body cavities highlights how life forms have adapted over millennia, with each species developing unique cavity structures suited to their ecological niches and lifestyle requirements.
Body cavities are crucial in facilitating various biological processes, including circulation and digestion. The separation of cavities allows for compartmentalized organ systems, which function independently yet cohesively. For instance, the heart, housed in the thoracic cavity, circulates oxygenated blood through the body. In contrast, the digestive organs within the abdominal cavity break down food into metabolites for energy. This separation is advantageous, as it prevents the mixing of systems that require distinct environments. Protective membranes that line each cavity also contribute to the overall efficiency of internal processes. They reduce friction between organs, enhancing the smooth operation required for functions like heartbeats or intestinal movements. Furthermore, disturbances in one organ system can have significant repercussions on others, thus maintaining distinct environments is vital for homeostasis. Academic institutions emphasizing animal anatomy must recognize the significance of these internal structures in nurturing a comprehensive understanding of physiology. By addressing the distinct roles modifiers of cavities contribute to the interplay between organs, more informed and effective educational programs can emerge. Therefore, continued research on body cavities is essential for advancing both anatomical knowledge and practical applications in medicine.
Implications for Veterinary Medicine
A solid understanding of animal body cavities significantly impacts veterinary medicine, enhancing diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. For instance, knowing the locations and protective roles of these cavities allows veterinary professionals to perform thorough examinations and swift interventions when necessary. Moreover, when animals suffer from internal injuries or diseases affecting their organs, veterinarians can correlate symptoms with relevant cavities. Learning to recognize signs related to organ dysfunction, such as those linked to abdominal pain, assists in timely treatment. The knowledge of body cavities also informs surgical practices, as veterinarians rely on precise anatomical maps during procedures. Understanding the spatial relationships between organs minimizes the risk of damage during surgical interventions. Additionally, advancements in imaging technologies, such as ultrasound and MRI, allow for a non-invasive examination of organs within these cavities. These innovations permit veterinarians to monitor the health of animals accurately. Moreover, veterinarians can track the progression of diseases that affect these body areas, enhancing patient outcomes. Furthermore, educational resources focusing on body cavity anatomy serve to cultivate knowledgeable professionals prepared to address emerging challenges in animal health effectively.
Moreover, animal body cavities play a significant role in the overall health and functional capabilities of an organism. The structural compartmentalization allows for the effective functioning of systems without interference; for instance, the respiratory and digestive systems operate independently within their respective cavities. This independence is crucial because it helps maintain specialized conditions that promote optimal biochemical processes. In mammals, variations in body cavities can indicate adaptations to specific lifestyles; mammals like dolphins exhibit unique thoracic cavity adaptations that facilitate life in aquatic environments. Different functions inherent in body cavities reflect the evolutionary responses to environmental pressures, mystifying researchers and educators alike. This information emphasizes the importance of understanding form, function, and evolutionary significance in anatomy education. Furthermore, enriching educational materials by incorporating real-world examples of how body cavities influence daily animal life enhances student engagement. Such resourceful insights inspire students to consider careers in veterinary sciences or related fields by demonstrating the dynamic interplay between structure and function in anatomy. This connection motivates aspiring veterinarians to explore the intricacies of animal physiology actively, fostering a future generation of knowledgeable practitioners dedicated to animal care.
Conclusions on Body Cavities and Protection
In conclusion, the role of animal body cavities is pivotal safeguarding internal organs from external injury while enabling physical autonomy in biological functions. The thoracic and abdominal cavities serve as protective shields, ensuring that vital organs remain secure and operational. The effective compartmentalization within these cavities also boosts the efficiency of various physiological processes, showcasing the integration of form and function in anatomy. Moreover, educators emphasize the relevance of body cavities in veterinary studies, highlighting their importance in diagnosing conditions and devising appropriate treatments. Continual research is necessary to unravel complexities associated with these structures, including adaptations in various species. Strong resources centered on the anatomy of body cavities are indispensable in fostering a more robust understanding among students and aspiring veterinary professionals. Furthermore, insights gained through ongoing studies motivate the development of cutting-edge veterinary practices, ultimately benefitting animal welfare. Overall, recognizing the significance of body cavities and their protective roles not only enriches educational pursuits but also enhances practical applications in the field of veterinary medicine. This dual impact showcases the necessity for continued sustainability in anatomy education and research.
As our understanding of animal anatomy continues to deepen, the study of body cavities will undeniably remain a focal point for students, educators, and practitioners. Exploring these structures offers profound insights into health, disease, and the complexities of life itself. Preferences in research, coupled with advancements in educational methodologies, promise innovative ways for future veterinary professionals. Ultimately, the exploration of animal body cavities serves to highlight the intricate balance between protective structure and essential functionality in all living organisms. The implications of this knowledge extend beyond the classroom, shaping an understanding that translates into better health outcomes across animal species. This importance will only increase as the veterinary field faces new challenges and opportunities for growth. Embracing the intricacies of body cavities fosters nurturing care for animals that are marginalized or struggling with health issues. With a passion for promoting understanding in the anatomy of life, educators and practitioners can inspire the next generation of veterinary professionals. Thus, as we advance in this vital area of study, collaborative efforts in research, education, and practice will lead us toward improved animal welfare and healthcare.
The Future of Anatomy Education
The future of anatomy education lies in an integrative approach that encompasses the significance of animal body cavities. Innovative pedagogies leveraging technology, such as virtual dissection and interactive software, promise to enhance student engagement and understanding. Integrating traditional learning with digital resources provides rich educational experiences that cater to diverse learning styles. Emphasizing critical thinking along with anatomical knowledge prepares students for the evolving challenges in veterinary medicine. Developing interdisciplinary curriculums that connect anatomy with physiology, pathology, and surgical practices can lead to a more comprehensive education. These collaborative efforts can inspire students to appreciate the interconnectedness of various systems within living organisms. Continued research into animal body cavities’ role will also ensure that educational content stays current and relevant to modern veterinary practice. Ongoing input from practitioners into academic programs guarantees that students learn from experienced professionals facing real-world challenges. Therefore, bridging gaps between academic institutions and the veterinary field is essential for effective training. Building a future where the importance of body cavities is thoroughly understood will empower veterinary professionals and enrich animal health outcomes for generations to come.