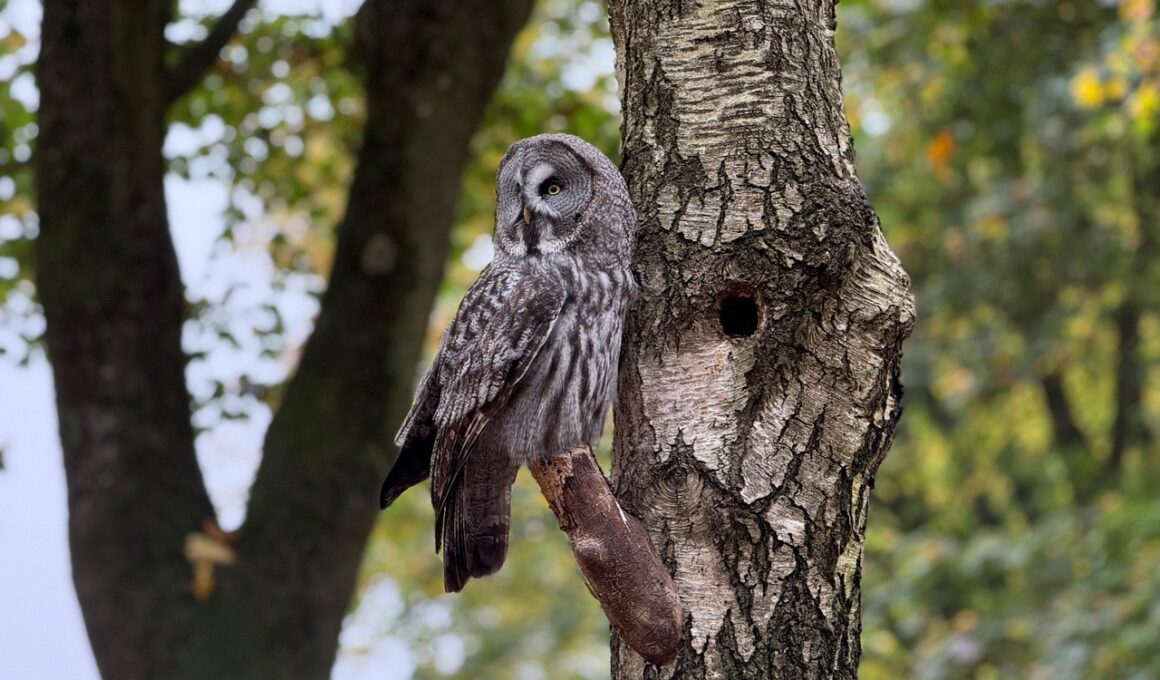
Understanding the Vocalizations of Owls
Owls are fascinating creatures known for their distinctive vocalizations. Their sounds play a crucial role in communication, helping them navigate their environment and interact with other owls. Each species of owl has unique calls, which can range from hoots and whistles to screeches and barks. These vocalizations are often used to establish territory, attract mates, and signal distress. For birdwatchers and wildlife enthusiasts, understanding these calls can greatly enhance the experience of observing these nocturnal birds. In this exploration, we will delve into the different types of owl calls and their purposes. Owl vocalizations can be categorized into several types, including hoots, barks, whistles, and screeches. Hoots are commonly associated with great horned owls, while barred owls are famed for their distinctive “who cooks for you” call. By studying these sounds, researchers can gain insights into the behaviors and interactions of owls within their habitats. Furthermore, environmental factors can influence these vocalizations, affecting how far and effectively the calls travel through the night. Let’s uncover the mysteries behind these nocturnal sounds.
Types of Owl Calls
When examining the vocalizations of owls, it is essential to recognize the various types of calls they produce. Each type serves a specific purpose within the social structure of owls. Primary calls include hoots, which function primarily in territorial claims, and these sounds can resonate over long distances. Other calls, like barks or screeches, are often associated with alarm or warning signals. The characteristic call of the barred owl serves as a prime example, showcasing a unique cadence that is easily identifiable. Additionally, some owls employ softer whistles during courtship rituals, aiding in mate attraction. In terms of social communication, fledglings often produce begging calls, which help parents locate and feed them. Each call’s pitch and tone can indicate the bird’s emotional state, such as aggression or fear. Genetic, geographical, and ecological factors can influence the variation in vocalizations across different owl species. This variation is important for proper identification and understanding the relationship between various species across their habitats. Thus, recognizing these sounds can deepen our appreciation for these remarkable nocturnal animals.
Owls not only use vocalizations for communication but also to enhance their hunting capabilities. The sounds they make can help create a sense of presence in the woodland habitat and may even attract smaller prey. For instance, a great horned owl’s deep hoots can resonate through the trees, guiding its next meal closer by startling unsuspecting rodents. Additionally, the strategic use of calls allows owls to survey their territory during the night effectively. Through vocalizations, they can gauge the responses of other local wildlife, including competing predators. This auditory awareness complements their extraordinary eyesight, making them highly effective nocturnal hunters. Additionally, some owl species, such as the burrowing owl, utilize vocalizations in combination with physical displays to deter predators and protect their nesting sites. The interplay between sound and behavior enhances their survival strategies in the wild. To truly understand owls, one must consider the multifaceted role of their vocalizations—not merely as sounds but as tools for successful navigation, hunting, and social interaction. Such insights contribute greatly to wildlife conservation efforts and our understanding of biodiversity.
Observing owls in their natural habitat offers a unique opportunity to experience their vocalizations firsthand. To enhance this experience, enthusiasts can engage in night walks equipped with audio recording devices, enabling them to document these fascinating sounds. Additionally, participating in local owl monitoring programs can provide a deeper insight into the behavior and ecology of these nocturnal predators. Many organizations conduct nightly surveys in which volunteers are trained to identify vocalizations and assist in data collection. This citizen science approach enriches community engagement while contributing valuable knowledge to wildlife conservation. Moreover, dedicated owl watching events attract bird lovers from diverse backgrounds, creating a platform for education and awareness. Workshops are often held that focus on owl ecology, vocalizations, and conservation efforts. Such initiatives not only foster a greater understanding of owls but also help raise awareness about the importance of their habitats. By participating in these activities, individuals can become advocates for owl conservation and the protection of their ecosystems. Understanding the intricate lives of owls through their sounds can be a rewarding endeavor, bridging a connection between humans and wildlife.
The Role of Environmental Factors
The environment plays a significant role in the auditory communication of owls. Factors such as habitat type, weather conditions, and even urban noise can influence how well owl calls travel and their effectiveness. For example, dense forests can muffle sound, making it more challenging for owls to communicate over long distances. Conversely, open areas allow their calls to resonate more freely. Additionally, during rainy or windy conditions, owls may alter their vocalizations, using softer tones or reducing calling frequency. Urban environments present a unique challenge, as increased background noise can interfere with their natural calls. Consequently, researchers have noted changes in owl behavior in cities, where they are forced to adapt their communication methods. Some species have been observed using higher frequency calls to cut through urban sound clutter. Meanwhile, habitat loss and fragmentation continue to threaten these magnificent birds, necessitating further research to evaluate their responses to environmental changes. By understanding how these factors affect owl vocalizations, conservationists can implement strategies to protect both the birds and their habitats. Such knowledge is crucial for maintaining biodiversity and balancing ecosystem dynamics.
It is paramount to raise awareness about the significance of vocalizations in the study and conservation of owl species. As one of nature’s most enigmatic predators, owls have become symbols of wisdom and mystery throughout cultures. However, their survival is increasingly threatened by habitat destruction and climate change. Educating the public about owl vocalizations can foster greater appreciation for these birds and emphasize the importance of conservation efforts. Community outreach programs aimed at schools and local organizations can effectively promote awareness about owl sounds and their ecological roles. By incorporating interactive demonstrations and workshops, individuals are encouraged to engage with their natural surroundings actively. Moreover, online platforms can serve as valuable resources for sharing information on owl calls, enabling enthusiasts to learn and contribute to ongoing conversation efforts. Encouraging people to report sightings or sounds can further enhance research efforts, establishing a citizen science approach to owl conservation. Through education, society can inspire action to protect these remarkable aerial hunters. Recognizing that every owl call carries a story can deepen our understanding of their ecological significance and the need for collective protective measures.
In conclusion, the vocalizations of owls represent a vital aspect of their behavior, ecology, and conservation. By understanding the various calls and their functions, we can appreciate the complex social interactions of these majestic birds. Each species contributes uniquely to the ecosystem, and their calls serve as a window into their lives. Moreover, environmental factors significantly influence how these sounds are produced and perceived, affecting owl communication strategies. Awareness and education are essential components in promoting owl conservation, as understanding fosters empathy. By embracing citizen science initiatives and participating in local wildlife activities, individuals can contribute to the protection of owls and their natural habitats. Furthermore, as we continue to advance our knowledge of owl vocalizations, we empower ourselves to become advocates for wildlife. This journey highlights the interconnectedness of all living creatures, emphasizing the importance of preserving our natural world. Ultimately, the enchanting sounds of owls remind us of the beauty of nature and the necessity of safeguarding it for future generations. Let us commit to protecting the vocal guardians of the night and ensure that their calls resonate throughout the world.