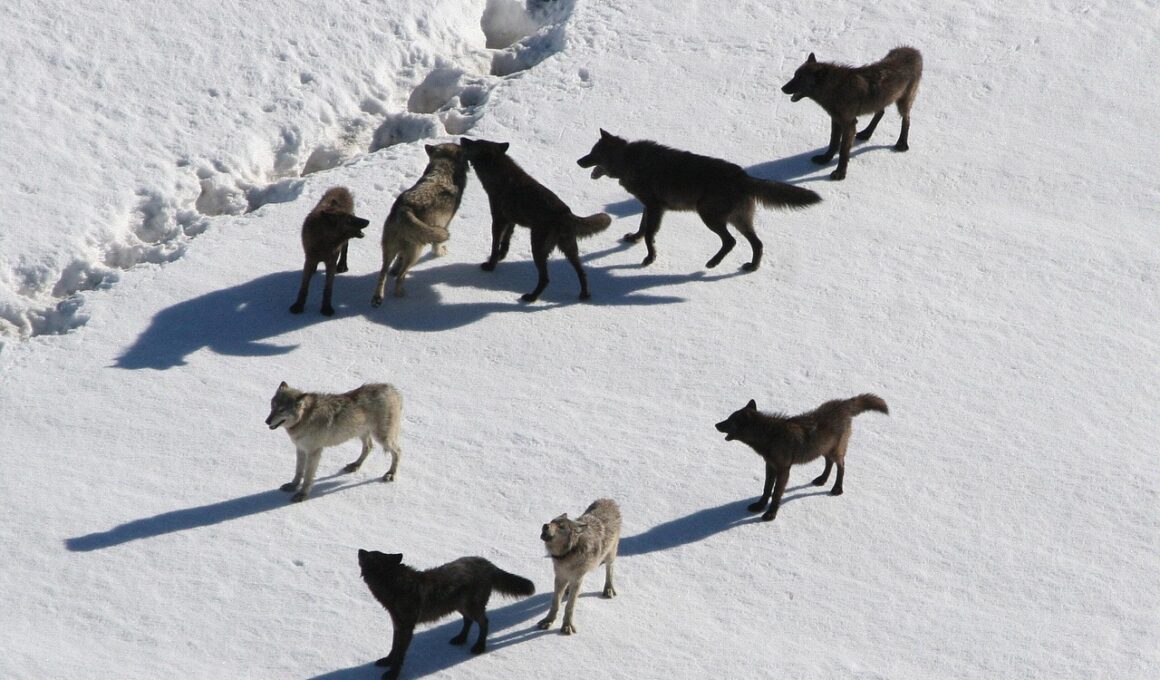
The Role of Carnivora in Controlling Prey Populations
Carnivora, representing a significant class within Mammalia, plays a critical role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. Members of Carnivora, including species like lions, wolves, and bears, serve as apex predators, which means they are at the top of the food chain. By preying on herbivores, these carnivores regulate prey populations, preventing overgrazing and depletion of vegetation. Overpopulation of prey species can lead to severe consequences, such as habitat destruction and loss of biodiversity. Additionally, the presence of Carnivora often influences prey behavior, leading to greater movement and foraging strategies that promote healthier landscapes. This natural selection process fosters the survival of the fittest among herbivores, enhancing genetic diversity. The ecological balance facilitated by Carnivora ensures the stability of various ecological niches. Understanding the consequences of removing these predators can highlight the intricate relationships within ecosystems. Protecting these species is essential for the future of wildlife conservation. Preserving their habitats and controlling hunting practices can ensure that they continue to thrive and fulfill their role in ecosystem management.
Impact of Carnivores on Biodiversity
Carnivores not only manage prey populations but also promote greater biodiversity within ecosystems. Predation pressure has a cascading effect on species distribution and dynamics, as it creates environments where multiple species can coexist. For example, if a specific predator, like the gray wolf, is removed from its habitat, it can lead to an explosion in elk populations. This overpopulation can subsequently result in overgrazing in selected areas, significantly reducing plant diversity. In turn, decreased plant diversity affects other herbivores and insects that rely on those plants for food and habitat. Consequently, the absence of Carnivora can disrupt the food web, leading to fewer available resources for various species, which harms overall biodiversity. In contrast, introducing or preserving carnivores can maintain healthy ecosystems. By regulating the populations of herbivores, these carnivores also protect plant species and prevent monocultures in forests and grasslands. Hence, the presence of Carnivora enhances resilience to environmental changes and disturbances, therefore preserving ecosystem functions and promoting adaptability in wildlife populations.
Carnivores possess complex ecological behaviors that impact prey species in unique ways. For instance, apex predators often target specific age classes or the sick and weak, thereby enhancing the health of prey populations. This selective predation aids in the natural selection process, allowing only the most robust individuals to breed and thrive. Furthermore, the fear of predators influences herbivore foraging behaviors. Prey animals often adjust their grazing patterns and habitat use to evade their hunters, leading to varied grazing pressure across landscapes. This phenomenon known as the ‘landscape of fear’ can promote vegetation recovery in overgrazed areas, as animals avoid high-risk zones. Interestingly, this behavioral adaptation also contributes to the overall health of ecosystems, as it allows for the regeneration of plants and maintaining biodiversity. The intricate relationships between Carnivora and their prey establish a dynamic equilibrium essential for ecological balance. Conservation efforts often focus on preserving these complex interactions, emphasizing the need to understand predator-prey relationships further. Recognizing the importance of carnivores will direct rehabilitation and management strategies in wildlife conservation initiatives.
The Role of Human Activity
Human activities significantly impact Carnivora populations and, consequently, their role within the ecosystem. Habitat destruction due to urbanization, agriculture, and deforestation poses a severe threat to these carnivores. Fragmented habitats may isolate populations, limiting their ability to hunt and interact, ultimately leading to declines in local biodiversity. Furthermore, hunting practices, whether legal or illegal, have drastically reduced carnivore numbers worldwide. The loss of apex predators due to human exploitation disrupts the balance of ecosystems that depend on their predatory roles. Management policies that center on habitat conservation are crucial for maintaining healthy populations of Carnivora. Measures such as establishing protected areas, wildlife corridors, and sustainable land-use practices can enhance the survival of these vital species amid human encroachment. Community engagement in conservation efforts is essential to promote coexistence with Carnivora. Education and awareness programs can help cultivate an understanding of the ecological importance of these predators, garnering support for wildlife protection. By balancing human development with ecological preservation, we can ensure the survival of both communities and their natural environments.
Carnivora adaptations exhibit fascinating traits that enhance their predatory success in the wild. These adaptations include physical characteristics such as sharp claws, keen senses, and powerful muscles, allowing them to pursue and capture prey efficiently. For instance, felines possess retractable claws that enable stealthy approaches while hunting, increasing their chances of success. Additionally, adaptations in teeth, such as carnassials, allow them to shear flesh effectively. Behavioral adaptations also significantly enhance their survival. Social species like wolves hunt cooperatively, leveraging group dynamics to take down larger prey. Such collaborative behaviors are vital in maintaining prey population control. Furthermore, social structures influence breeding, ensuring species continuity even amid environmental pressures. The adaptability of Carnivora to changing ecological circumstances ensures their ongoing role as predator regulators. As they evolve, these species continue to find innovative methods of hunting and social cooperation. Understanding the evolution of these adaptations provides valuable insights into the resilience of Carnivora populations worldwide. Conserving these predators is paramount as they navigate challenges posed by climate change and human interference, ensuring that they can maintain their essential roles.
Conservation Efforts for Carnivora
Conservation efforts focused on Carnivora have gained traction in recent years, acknowledging their significance in ecosystem health. International treaties aim to protect endangered species through habitat conservation and restoration initiatives. Notable examples include the establishment of protected areas, wildlife corridors, and breeding programs designed to bolster declining populations. Awareness campaigns educate the public about the ecological roles of Carnivora, increasing support for wildlife conservation initiatives. Collaboration among various stakeholders, including governments, NGOs, and local communities, is vital for effective management practices. Furthermore, leveraging technology, such as GPS tracking and camera traps, assists in monitoring populations, behavior, and habitat use, providing valuable data for conservation strategies. Sustainable hunting practices and ecotourism also present alternative livelihoods for local communities while generating funds for conservation projects. Engaging local populations in conservation efforts fosters a sense of responsibility towards preserving their natural heritage. As societal and environmental changes occur, adaptive management plans are essential for ensuring the long-term conservation of Carnivora. Advocating for these apex predators strengthens ecological balance, solidifying the importance of their roles within the greater ecosystem.
Ultimately, understanding the role of Carnivora in controlling prey populations highlights their importance in maintaining ecological integrity. They regulate herbivore populations, influence the health of landscapes, and contribute to biodiversity. The removal of these predators can lead to cascading effects throughout ecosystems, emphasizing the need for effective wildlife conservation measures. Strategies must integrate habitat protection, community involvement, and adaptive management practices to ensure the survival of both Carnivora and their ecosystems. As apex predators, Carnivora play a crucial role in shaping the dynamics of the environments in which they reside. Continued research into their behavior, ecological roles, and interactions with prey species will provide further insights into the complexities of these relationships. Supporting conservation efforts will aid in securing the future of these essential predators. Ultimately, as we work to protect Carnivora, we safeguard the intricate web of life that sustains our planet. The fate of these magnificent creatures lies in our hands, and it is our responsibility to ensure they can continue to fulfill their vital roles for generations to come.
In the context of ecosystem management, the presence of Carnivora is invaluable. Their roles as top predators enable ecological balance, influencing not only prey populations but also the overall health of their habitats. Through a balance of predation and habitat, Carnivora contribute to the natural processes that regulate numerous species within their ecosystems. In managing conservation programs, it is essential to recognize that these species are frequently a reflection of their environments. By protecting Carnivora, we also maintain the habitats that other species rely upon for survival, creating a more robust and diverse ecological community. Each species within the Carnivora order possesses unique attributes that are critical to their predation and survival. By conserving these animals, we are investing in biodiversity and ecology while also protecting our heritage. This complex web of relationships plays a significant role in sustaining natural balances. Understanding these dynamics promotes a broader vision of environmental stewardship required for the future of our planet. Collaborating with diverse stakeholders in conservation efforts can bridge gaps between human activities and the landscapes we share. Empowering communities to be stewards of their environment can foster positive change and conservation partnerships.