Reptile Behavior Patterns and Social Structures
Reptiles are fascinating creatures that demonstrate an array of intricate behavior patterns and social structures. Many species exhibit unique adaptations that enable survival in varying environments. Notably, reptiles engage in complex patterns of communication and social interaction. These behaviors are often characterized by territorial aggression, courtship displays, and kin recognition. A crucial aspect of their social structures is the establishment of dominance hierarchies, critical for mating rights and access to resources. For example, in some lizard species, males establish territories that they vigorously defend against rivals. The maintenance of these territories requires not only physical prowess but also insightful behavioral strategies. Social structures may differ significantly between species and even within populations based on ecological conditions. Understanding these diverse behavioral patterns can provide insight into the evolutionary adaptations that reptiles have developed over millions of years. Moreover, observing these traits in a natural habitat sheds light on the ecological roles they play within their ecosystems. This knowledge is vital, especially as habitat destruction poses significant threats to reptilian populations worldwide, making it essential to protect their natural environments.
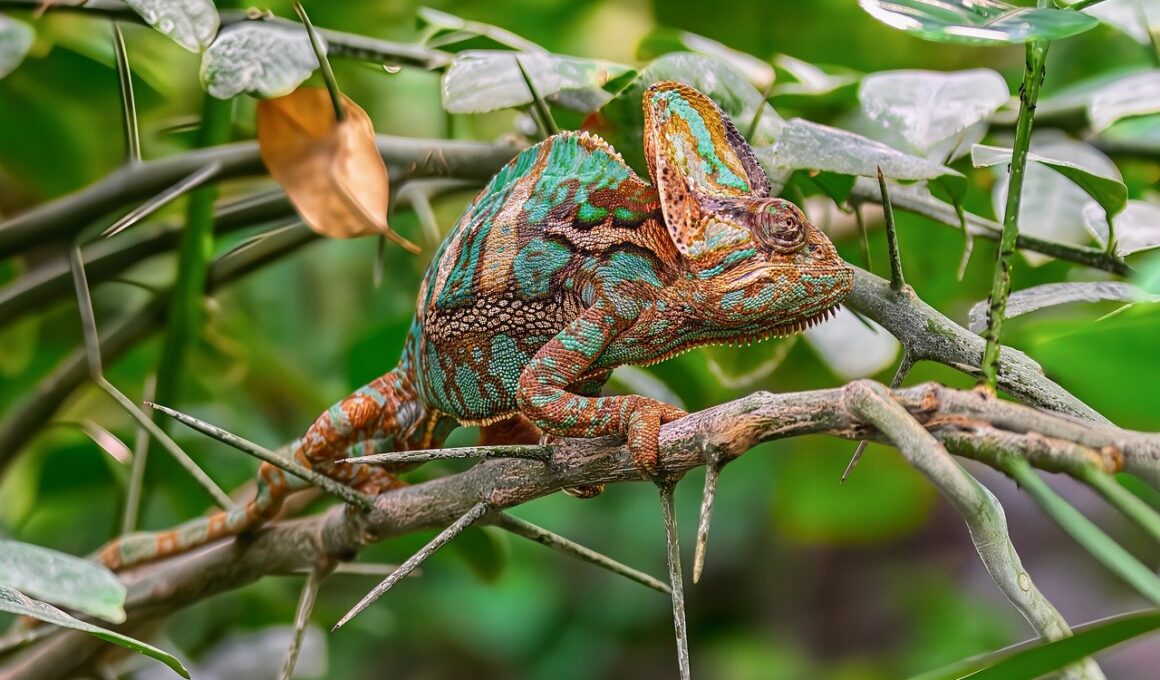
Among reptiles, communication is vital for facilitating interactions, especially during mating. Many species utilize visual signals, such as displays of vibrant colors or unique postures. For instance, chameleons change color to communicate moods, intentions, and attract mates. Furthermore, some snakes utilize pheromones to convey reproductive status, signaling their readiness to mate. This chemical communication method is not only efficient but also discreet, as it allows them to interact without overwhelming exposure. Additionally, some reptiles employ vocalizations to maintain social bonds and establish territory. However, their sound repertoire is often limited compared to mammals. Interestingly, these vocalizations vary widely among species, with distinct calls intended for communication across various distances. Additionally, social interactions often revolve around establishing dominance hierarchies, particularly in species that exhibit social living. Female reptiles also play an essential role in fostering social structures, as their choice of mate is crucial for genetic diversity. As a result, male reptiles frequently engage in competitive displays aimed at winning female approval. Understanding these communication methods helps researchers appreciate the complexity of reptile interactions within their respective habitats and communities.
Social Structures in Reptile Communities
Reptile communities exhibit remarkable diversity in social structures, influenced by their specific environments. For example, some species, like certain turtles, exhibit solitary behaviors while others, such as some lizards, are more social. In communal living, reptiles often form groups to take advantage of benefits like protection against predators and improved thermoregulation. Solitary species, on the other hand, rely on camouflage for survival, making them harder to detect. These differences result in variations in behavior patterns, ranging from solitary foraging to social basking behaviors. Furthermore, group dynamics can often shift in response to environmental pressures. For instance, during the breeding season, social interactions become more pronounced as individuals compete for mates. Cooperative breeding behaviors have also been observed, particularly in species like monitor lizards. In these scenarios, individuals aid each other in nesting and caring for young, exemplifying complex social dynamics. Conversely, competition for habitats often results in conflict, leading to the establishment of dominance hierarchies. Through these hierarchies, resources are distributed, ensuring survival and reproductive success among individuals in reptilian populations.
Sexual selection is often a driving force behind the development of social structures in reptiles. Males frequently engage in dramatic displays of strength and coloration to attract females. In various snake and lizard species, mating rituals can involve elaborate courtship behaviors. These rituals can sometimes include behaviors such as head bobbing, tail waving, and even physical combat. Female selection is critical, as they assess male qualities based on display behaviors. The success of these interactions can dictate the genetic profile of future generations. Additionally, the ability to secure territories plays a fundamental role in these display strategies. Reptiles that can defend their territories are more likely to find mates and reproduce. However, the dynamics of these selections can shift dramatically based on environmental changes or human intervention. Habitat loss and climate variation can place additional challenges on mating strategies and behavioral patterns. Research indicates that understanding these impacts can inform conservation efforts aimed at preserving endangered reptile species. By studying their unique mating systems, biologists can develop effective management practices that allow for successful coexistence between reptile populations and human activities.
Impact of Environment on Behavior
The environment in which reptiles live significantly influences their behavior and social structures. From temperature fluctuations to geographical limitations, environmental factors shape how reptiles adapt to survive. For example, iguanas bask in the sun to regulate their body temperature. These thermoregulatory behaviors drive their social interactions as they gather in communal basking sites during specific hours. Additionally, habitat-specific resources dictate the formation of feeding patterns. As a result, species that thrive in arid environments may develop different foraging strategies compared to their counterparts in lush habitats. Furthermore, the availability of resources such as water and food significantly dictates reproductive strategies. In harsh desert environments, reptiles may exhibit slower reproductive rates, resulting in fewer offspring. Conversely, healthy ecosystems may foster larger populations and more complex social networks. Negative impacts from climate change, habitat destruction, and urbanization pose grave threats to reptiles, necessitating an urgent global response. Understanding the relationship between each species and its environment is critical for ensuring their survival and conserving biodiversity. Through research and conservation initiatives, measures can be taken to support these ancient creatures as they face modern challenges.
Moreover, group dynamics are also conditionally dictated by the presence of predators in an environment. In habitats where predation risk is high, reptiles tend to exhibit more social behavior compared to solitary ones. This adaptation allows for increased vigilance and reduces the risk of predation through collective awareness. Communal living can act as an effective defense mechanism, improving survival rates among individuals. Species such as some social lizards exhibit these dynamics, often forming groups close to secure basking sites or fruitful foraging areas. Similarly, nesting behaviors can evolve based on environmental pressures influencing group sizes. In species that provide parental care, group nesting becomes advantageous, allowing shared responsibilities among adults. Coordination among group members can further enhance the survival of their young. Nonetheless, competition among individuals for limited resources often leads to conflict within groups. These conflicts can manifest as aggressive territorial displays among males, determining access to prime resources. Studying these influences can improve our understanding of how reptiles respond to their surroundings. This knowledge can inform conservation efforts and ultimately lead to more effective actions aimed at preserving reptile populations and their habitats.
The Importance of Social Behavior in Conservation
Reptile social behavior plays a crucial role in the conservation of diverse species across the globe. Understanding their interaction patterns can help conservationists develop more effective strategies to protect their habitats. By recognizing the social structures that define reptile groups, it becomes possible to anticipate responses to environmental changes. Education campaigns aimed at informing the public about the social dynamics of reptiles can foster a deeper appreciation for their ecological roles. Moreover, policymakers must consider the implications of disruptive human activities, such as urbanization or deforestation. Supporting research initiatives focused on reproductive behavior and social interactions can lead to significant conservation advancements by ensuring the genetic health of populations. Practical management programs should prioritize preserving critical habitats that support complex social structures, allowing reptiles to thrive. Moreover, it is vital to engage communities that coexist with these reptiles, providing them with the necessary tools to balance human needs while protecting crucial habitats. By emphasizing the importance of conserving reptile behavior and the structures within their ecosystems, we can create a sustainable future for many reptilian species.
In conclusion, understanding reptile behavior patterns and social structures is essential for their conservation. The diverse interactions, from territorial displays to group dynamics, reflect highly adaptive strategies developed over time. These patterns not only enhance survival but also play a role in maintaining ecosystem balance. Additionally, comprehensive studies focused on these behaviors contribute valuable insights into evolutionary biology. As environmental pressures continue to mount, the significance of these behaviors becomes even more pronounced. Scientists, conservationists, and the general public must work together to protect these vital ecosystems and their inhabitants. Continuous observation and research on reptile behavior can inform best practices and encourage sustainable coexistence. Specialized programs tailored towards educational outreach can help dispel myths surrounding reptiles, fostering a more positive image of these often-misunderstood animals. Ultimately, a collective effort is necessary to ensure the survival of these ancient species. By prioritizing their needs, emphasizing habitat preservation, and enriching public awareness, we pave the way for a better future for reptiles and the ecosystems they inhabit. This ongoing commitment is critical for maintaining biodiversity and ecological health for generations to come.