The Role of Algal Blooms in Fish Toxicity Events
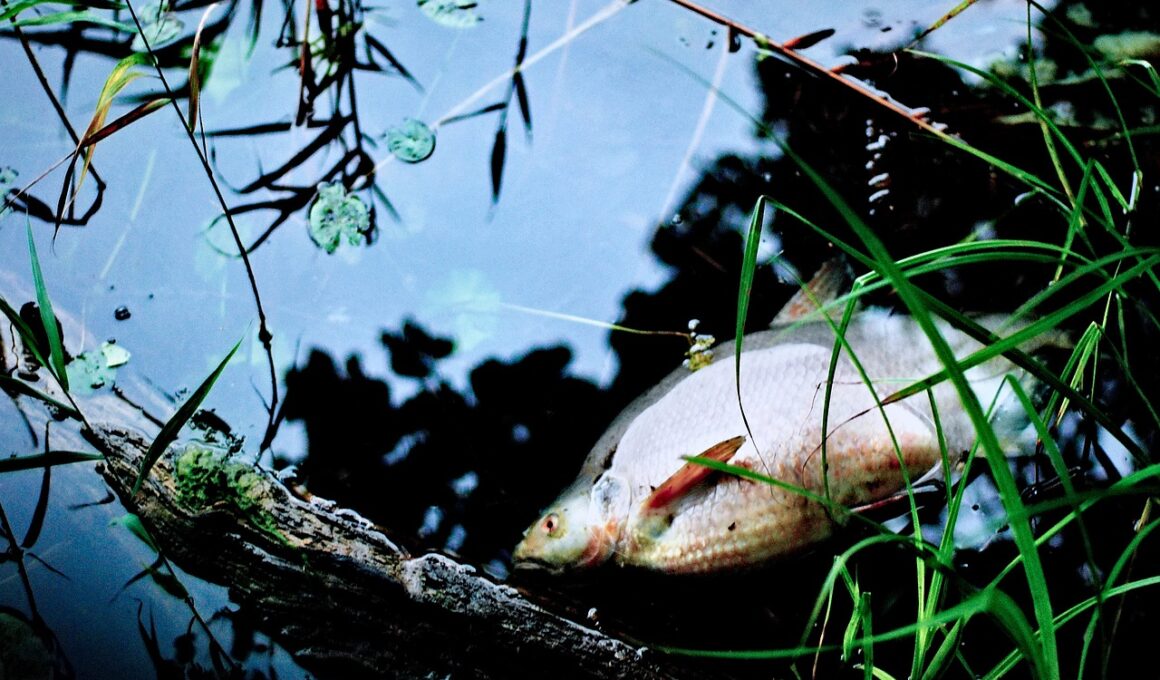
Algal blooms are significant ecological events characterized by excessive growth of algae in aquatic systems. These blooms can lead to detrimental water quality, particularly harmful algal blooms (HABs) that produce toxins. Fish populations can suffer from several impacts due to these toxic substances. Research suggests that toxins may disrupt fish physiology by impeding respiratory functions, leading to hypoxia. Additionally, the presence of such toxins can effectively alter the food web and disrupt ecological balance. Environmental factors like nutrient pollution from agricultural runoff often contribute to the proliferation of algal blooms. This creates an urgent need for monitoring water quality and implementing practices to limit nutrient input. Key strategies include the adoption of sustainable agricultural practices and creating riparian buffers. Furthermore, public awareness initiatives can engage communities in protecting water resources. The implications of algal blooms also extend to human health, as toxins may enter the food chain. Protecting aquatic environments requires cross-sector collaboration between government agencies, researchers, and communities. Continued research into the complex interactions between algal blooms and fish species remains crucial for mitigating these events.
Fish are critical indicators of water quality, and algal blooms have far-reaching consequences for their health and viability. Physiological stress in fish, due to exposure to toxic algal species, is evidenced by altered behavior and impaired reproduction. Observations indicate that fish can exhibit erratic swimming motions or reduced feeding, suggesting neurological impacts from toxins. These phenomena can have cascading effects throughout aquatic ecosystems, impacting predator-prey relationships. Moreover, HABs are linked to declining fish populations, and this becomes a significant concern for fisheries and local economies. Investigating the specific pathways through which toxins affect fish organs, such as gills and liver, is vital to understanding the full scope of toxicity. As researchers delve into these mechanisms, they are discovering the importance of genetic variations in fish and their responses to algal toxins. For instance, certain species may possess built-in defenses that allow them to resist or tolerate harmful substances better. Fisheries management must adapt to these insights, ensuring that strategies prioritize ecosystem resilience. Additionally, collaboration between scientists, policymakers, and stakeholders can facilitate more effective management of water quality and prevention of toxic blooms.
Impacts of Toxic Algal Blooms on Aquatic Life
Toxic algal blooms pose a significant risk to surface water ecosystems, profoundly affecting fish and other aquatic organisms. Research increasingly highlights the interconnectedness of various species and their sensitivity to toxins produced during blooms. Fish experience various health complications due to the bioaccumulation of these toxins in their systems. This bioaccumulation can lead to decreased reproductive success and increased mortality rates. Furthermore, it has been shown that toxin exposure can weaken fish immune systems, rendering them more susceptible to various diseases. This aspect is essential not only for maintaining fish populations but also for preserving overall aquatic biodiversity. Algal toxins can cause direct kills as well, which can devastate entire local fish populations in affected regions. Management efforts to address algal blooms must consider the health of all aquatic life, including invertebrates and microorganisms, which play crucial roles in nutrient cycling. Monitoring programs that assess water quality and the composition of algal communities are vital. Communities should also be educated about the significance of preventing nutrient runoff. Efforts to restore balance in these ecosystems require a multidisciplinary approach and proactive governance.
The intersection of toxicology and fish health extends beyond immediate impacts, encompassing long-term ecological shifts in aquatic ecosystems. Algal blooms can lead to anoxic conditions, dramatically reducing available oxygen and creating uninhabitable environments for fish. This species displacement forces fish to migrate, resulting in issues such as overpopulation of particular areas or increased competition. As a result, the resilience of fish populations diminishes. Well-established fish species may struggle to adapt to changing conditions caused by blooms, each with its specific ecological niche. The resulting biodiversity loss can have detrimental effects on food webs, significantly impacting predatory fish species. Additionally, research into the mechanisms by which algal toxins induce stress is crucial. Investigating physiological changes and expressing biomarkers in fish can enhance understanding, providing vital insights into the health of aquatic ecosystems. Moreover, recreational fishing and commercial markets suffer when fish populations decline due to toxicity effects. Awareness campaigns promoting sustainable practices can engage the public. By understanding the importance of healthy aquatic ecosystems, proactive measures can help preserve fish populations and maintain biodiversity, benefiting both the environment and human health.
Preventing Algal Bloom Occurrences
Preventing harmful algal blooms is essential for the sustainability of aquatic ecosystems and fish populations. Addressing nutrient pollution, particularly from agriculture and urban development, is critical. Strategies such as implementing best management practices on farms and promoting responsible land use can significantly reduce nutrient runoff into water bodies. In urban areas, enhancing stormwater management systems can mitigate nutrient loadings during rainfall events. Additionally, restoring wetlands plays a crucial role in filtering pollutants and improving water clarity. Public outreach campaigns can educate citizens on the importance of protecting local waterways. Engaging local businesses and communities in stewardship projects can foster a shared commitment to reducing pollution. Integrating scientific research into policy decisions can also guide efforts to limit the occurrence of blooms. Moreover, establishing monitoring systems to track water quality allows for timely interventions when algal blooms are detected. This proactive approach not only safeguards aquatic life but also ensures that recreational areas remain safe for human use. Fisheries often rely on clean water resources; thus, protecting these ecosystems is vital for the economy. Collaborative efforts involving various stakeholders can pave the way for more resilient aquatic environments.
Research scientists work tirelessly to comprehend the complex interactions between algal blooms and the resulting effects on fish. Understanding the nuances of toxicity can provide valuable insights into managing aquatic health. For instance, studies have demonstrated that not all algal blooms create toxins, emphasizing the need for targeted research. Early detection of harmful blooms can prevent widespread impacts on aquatic organisms and ecosystems. Advanced techniques, such as spectrometry, are increasingly utilized for studying algal species, making identification of toxic strains more efficient. Moreover, fostering partnerships between academic institutions, government agencies, and non-profit organizations can enhance knowledge-sharing and data collection. Knowledge generated from these partnerships can lead to the creation of more effective environmental policies. Promoting best practices is essential for combating nutrient pollution and maintaining water quality. Conducting regular assessments of the ecosystem’s health can provide progress indicators, allowing adaptive management strategies to be refined. Integration of new technologies, like remote sensing, offers innovative methods to track changes in algal populations. As research continues, it is crucial to raise public awareness and encourage individual actions that contribute to the protection of aquatic ecosystems.
Conclusion on Algal Blooms and Fish Toxicity
In conclusion, algal blooms significantly impact fish health and overall aquatic ecosystems. The interactions between toxins and fish populations delineate a complex web of ecological consequences. While progress has been made in understanding the dynamics of these events, there is still much to learn about their long-term effects. Mitigating the factors contributing to blooms, such as nutrient pollution, requires comprehensive efforts on multiple fronts. Public education and innovative legislative acts can promote sustainable practices that maintain water quality. By ensuring healthy fish populations, the balance of aquatic ecosystems can be preserved. Studies focusing on the genetic diversity of fish species in response to toxins represent a promising avenue for future research. As we strive to enhance the health of our waterways, there should also be a focus on the socio-economic implications of fish toxicity, particularly in communities dependent on local fisheries. Collaborative approaches that leverage community participation, research, and government policies are essential. The health of fish and aquatic ecosystems is a collective responsibility that requires concerted efforts across various sectors.