Sea Turtles and Climate Change: Adaptation and Survival
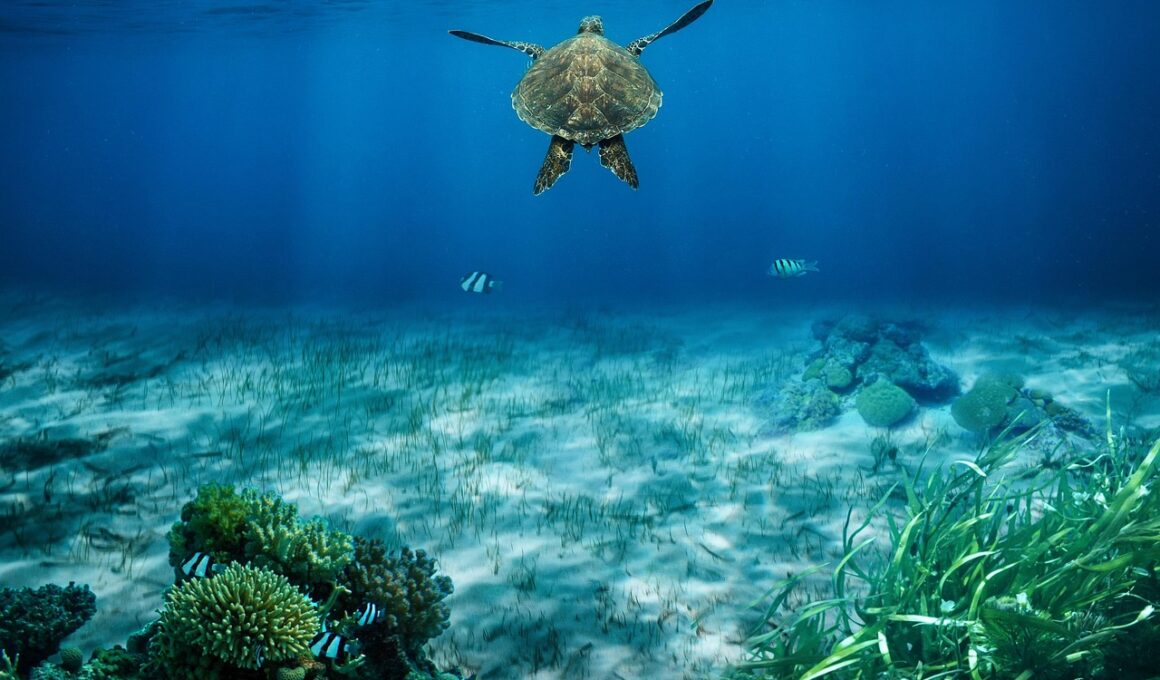
Sea turtles are remarkable creatures, not only for their beauty but also for their vital role in marine ecosystems. These ancient reptiles have been on Earth for millions of years, but climate change poses significant threats to their survival. Rising ocean temperatures impact the availability of food sources and nesting sites. Moreover, increased ocean acidity affects their primary food sources, such as seagrasses and jellyfish. Sea turtles are dependent on stable marine environments, and disruptions to these can lead to population declines. The increase in extreme weather events can also lead to flooding of nesting beaches, further compromising their ability to reproduce. Turtles are already facing multiple threats, including habitat loss and pollution, making adaptation to climate change crucial. Conservation efforts focusing on protecting nesting beaches and reducing pollution are vital for their survival. By understanding how climate change impacts sea turtles, we can better formulate strategies to protect them. Efforts to combat climate change, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions, also play a significant role in helping these majestic creatures thrive. They are key indicators of ocean health and should be protected for future generations.
Sea turtles exhibit unique adaptations that help them survive in diverse marine environments. Their streamlined bodies and powerful flippers allow them to cover vast distances. Some species can migrate over thousands of miles in search of food or nesting sites. However, adaptation also means adjusting to gradual environmental changes. For instance, rising temperatures play a crucial role in determining the sex of hatchlings. Temperature-dependent sex determination means that warmer sands produce more females. This shift in sex ratios raises concerns about future breeding and population viability. Furthermore, sea turtles must contend with changing ocean currents and nutrient distributions due to climate change. Their innate navigation skills are essential for finding food, but altered currents could jeopardize their feeding strategies. Additionally, turtles have developed some resilience to environmental changes through their dietary flexibility. They consume a variety of marine organisms, which allows them to exploit different feeding opportunities. However, the availability of these food sources is diminishing due to climate change. Protecting critical habitats and ensuring food supply continuity are vital for the future of these extraordinary reptiles as they navigate a changing world.
Impact of Climate Change on Sea Turtles
The repercussions of climate change extend beyond immediate environmental stressors impacting sea turtles. Global warming, primarily driven by human activity, leads to rising sea levels that threaten nesting beaches along coastlines worldwide. Many shorelines are eroding, which compromises the areas where female turtles lay their eggs. In addition, flooding events increase in frequency and can wash away nests, leading to decreased hatching success. Conservationists face the challenge of protecting these vital habitats from losing ground to climatic changes. Strategies such as relocating nests to safer environments have been implemented. However, these interventions require significant resources and strategic foresight. Furthermore, pollution exacerbates the impacts of climate change. For example, marine debris can entangle sea turtles or cause them to ingest plastic, leading to severe health issues. Oil spills and chemical runoff further compromise their habitats, diminishing their chances of survival. As the oceans change, so too must our strategies for protecting sea turtles. Increased collaboration among governments, non-profits, and local communities is essential. By addressing both climate change and pollution, we can bolster protections for sea turtles in their natural habitats.
In addition to habitat threats, sea turtles face dangers from fishing activities exacerbated by climate change. As fish populations shift in response to warmer waters, industrial fishing practices can disrupt turtles’ access to food. Bycatch, the unintended capture of non-target species, threatens turtles’ survival rates significantly. Many populations are already struggling, and further complications can diminish their chances of recovery. Conservation initiatives must prioritize minimizing bycatch, implementing better fishing practices, and utilizing turtle-excluder devices in trawl fisheries. Educating fishers about sustainable practices that reduce bycatch is crucial. Moreover, promoting community engagement around responsible fishing helps foster a culture of care for marine ecosystems. Beyond fishing practices, addressing threats from marine tourism is equally important. Increased tourist activity can lead to disturbances in nesting areas, impacting reproductive success. Responsible tourism practices, such as regulated access to nesting sites, are being developed to mitigate these impacts. Local communities can play an active role in advocating for practices that protect sea turtles, balancing conservation with economic benefit. By merging conservation with sustainable tourism practices, we can provide safer environments for turtles while enriching human experiences with wildlife.
Conservation Efforts for Sea Turtles
To combat the numerous threats posed by climate change, a multifaceted approach toward conservation is essential. Organizations worldwide focus on protecting sea turtles through various initiatives. These include habitat restoration projects, legal protections, and public education campaigns. Partnerships between various stakeholders such as governments, NGOs, and local communities significantly enhance the effectiveness of these initiatives. Raising awareness about turtles and their precarious situation can foster a more profound collective responsibility towards preserving them. Community-based conservation has shown substantial positive outcomes in certain regions. Engaging local populations in turtle monitoring programs ensures that the needs of turtles and people are aligned. Schools can incorporate marine education to instill respect for the environment among younger generations, emphasizing sea turtles’ ecological importance. Active campaigns that protect nesting sites from development and pollution are also crucial. Additionally, leveraging technology, such as GPS tracking, helps researchers gather invaluable data about sea turtle migration patterns. This information is vital for developing further protection measures. Innovative solutions, such as nesting network collaborations, allow resources and knowledge to be shared among various communities, enhancing conservation efforts. Balancing human activity and wildlife needs remains a critical challenge.
As sea turtles navigate through a transformative environment, their survival will depend heavily on international collaboration. Climate change knows no borders, and collective action is fundamental to effective conservation. Global partnerships should focus on sharing data, strategy, and resources to build more resilient marine ecosystems. Policymakers around the globe must prioritize environmental issues that directly impact vulnerable species like sea turtles. International treaties must reinforce commitments to address climate action by reducing emissions and protecting essential habitats. The ocean is a shared resource, and its health significantly impacts global biodiversity. Local, national, and international governance structures need to integrate biodiversity and ecosystems’ sustainability into their frameworks. Funding for conservation projects, especially in at-risk regions, is also vital. Research organizations can pursue innovative financing options, including social impact bonds and eco-tourism funding initiatives, that benefit local communities while promoting turtle conservation. Moreover, educating and involving communities fosters collaboration that leads to better ecosystem management practices. As stewards of the seas, we must unite our efforts to ensure that sea turtles continue to thrive in a rapidly changing world. Their survival is critical not only to marine ecosystems but also to our shared heritage.
In summary, the challenges presented by climate change are significant, but so too are the opportunities for innovation and collaboration. Sea turtles have survived for millennia; with the right conservation efforts, they can continue to thrive despite changing conditions. Their ecological role is crucial, as they help maintain the balance of marine ecosystems. By actively participating in conservation initiatives, we can ensure future generations inherit a healthy ocean. Educating the public about the importance of turtles can inspire action, prompting individuals to make better choices regarding marine conservation. Innovations in technology and science can aid in addressing the many threats faced by these animals. Research continues to reveal crucial information concerning their behaviors and needs. The goal must always be to create environments where these magnificent creatures can adapt and survive, maintaining their populations and genetic diversity over time. Each one of us can play a part in this journey, whether through personal choices, supporting conservation initiatives, or advocating for policy changes. The plight of sea turtles calls us to unite for collective action, ensuring our oceans are vibrant and healthy for turtle populations and all marine life. Together, we can foster a more sustainable future.
Future Research Directions
The role of research in shaping the future of sea turtle conservation cannot be overstated. Continued studies focusing on the impacts of climate change will illuminate exactly how our configurations of the environment affect turtle species. Researching the adaptability of sea turtles can lead to new insights on their resilience or vulnerabilities. Furthermore, ongoing monitoring programs can provide valuable data on population health and dynamics. Technologies such as satellite tracking enhance our understanding of their extensive migrations, revealing breeding patterns and habitat use. Additionally, researching food supply and reproductive success links the influence of climate change on sea turtle survival in tangible ways. Collaborations among research institutions can multiply the resources available for studying these phenomena. Importantly, integrating indigenous and local knowledge systems enhances the research narrative surrounding sea turtles. This cooperation can reveal cultural connections and traditional wisdom that informs current conservation practices. Participatory research frameworks can empower communities, encouraging them to take ownership of local conservation efforts. Ultimately, the nexus of human responsibility and scientific inquiry will play a pivotal role in ensuring the enduring legacy of sea turtles. Together, we can transform knowledge into tangible actions that positively impact these magnificent creatures and their oceans.