Dinosaur Footwear as a Factor in Ecosystem Dynamics
Dinosaur footwear, while seemingly an odd topic, significantly influenced the dynamics of their ecosystems. Dinosaurs evolved diverse foot structures, adapting perfectly to their habitats. For instance, different species had variations like broad or narrow feet, which affected how they moved through various terrains. These adaptations ensured the survival of species and shaped the land they roamed. The unique footprints left by dinosaurs provided insights into their behavioral patterns, migration routes, and social structures. Paleontologists study these prints to understand interactions within ecosystems, such as predator-prey dynamics and competition for resources. This evolutionary trait led to specific interactions with flora and fauna, influencing plant growth patterns through trampling and feeding behaviors. Various dinosaur species also contributed to soil aeration and seed dispersal via their movements. As they migrated, they likely affected the distribution of plants and animal species across their ranges. Consequently, dinosaur footwear played a significant role in biodiversity and the overall structure of ancient ecosystems. Therefore, the study of these fascinating features gives us valuable insights into how interconnected life forms adapt and thrive in an ecosystem, contributing to the rich history of Earth’s biological diversity.
The morphology of dinosaur feet varied greatly among species, showcasing evolutionary ingenuity. For instance, theropods had three-toed feet adapted for predation and speed, while sauropods developed massive, column-like legs for weight support. This anatomical diversity can be traced back to how each species adapted its feet to its ecological niche. Foot structure affected not only movement but also how dinosaurs exploited their environments. In forested areas, broader feet facilitated balanced locomotion on uneven ground, while in open plains, agility became key for hunting and escaping predators. Additionally, studies propose that the interaction between their feet and the ground affected soil composition. Dinosaurs’ walking patterns contributed to marking pathways through dense vegetation. These paths, often overlaid by subsequent plant life, revealed the influence of dinosaur movement on habitat structure. The delicate balance of ecosystem dynamics often hinged on the evolutionary pressures affecting foot morphology. Adaptations to foot structure were crucial components of survival in a world filled with competition for resources. Importantly, the implications of these evolutionary steps resonate within the ecological frameworks that formed over millions of years, providing context to the understanding of historical biodiversity.
Impact on Flora and Fauna
Dinosaur footwear significantly affected plant life and contributed to shaping ancient ecosystems, marking their interactions with flora. Dinosaurs acted as both herbivores and carnivores, each leaving distinct traces through their feeding and movement patterns. Some giant herbivorous dinosaurs, like the Apatosaurus, would have trampled expansive areas, affecting the growth of various plant species. Their massive weight compressed the earth, leading to more nutrient-rich soil, which fostered diverse plant ecosystems. Meanwhile, carnivorous dinosaurs, such as the Tyrannosaurus rex, would have influenced prey species’ behaviors, forcing them to adapt to avoid predation. This dynamic created a reciprocal relationship between dinosaurs and existing flora and fauna. Furthermore, the footprints of dinosaurs provided a pathway for smaller species, which utilized them for movement and protection. Interactions between dinosaurs and their environments resulted in diverse plant communities adapted to these pressures. Many plants evolved defensive traits, deterring herbivory through thorns, spines, and toxins. Furthermore, the mobility of dinosaurs allowed for widespread seed dispersal, enhancing biodiversity. Hence, the impact of dinosaur footwear extended far beyond mere locomotion, embedding them deeply into the evolutionary narratives of the plants and animals of their time.
The concept of ecological niches emphasizes the role of dinosaurs in shaping their environments, particularly through their foot dynamics. Footprints tell stories of interactions and cultivate an understanding of habitat preferences. Large dinosaurs required specific habitats based on their foot structure and behavior, leading to variations in vegetation types and availability. Herbivore footprints may have altered the density and distribution of plant life. Behavioral adaptations among dinosaurs orchestrated the maintenance of ecosystem health. Grazing behaviors would have influenced the evolutionary trajectory of plants coexisting with these massive creatures. The mobility of dinosaurs facilitated their access to various ecosystems, ensuring captive resource availability. Carnivores, on the other hand, dictated prey movements, indirectly affecting the evolutionary outcomes of both predator and prey species. Understanding these dynamics illuminates how the extinction of dinosaurs potentially led to significant shifts in flora and fauna, resulting in the rise of mammals and other life forms. The patterns of dinosaur footprints reflect behavioral ecology’s significance, intertwining the survival of different organisms with their interconnectedness within the ecosystem. This emphasizes the crucial role dinosaurs played, not merely as individual species but as architects shaping the landscapes of their time.
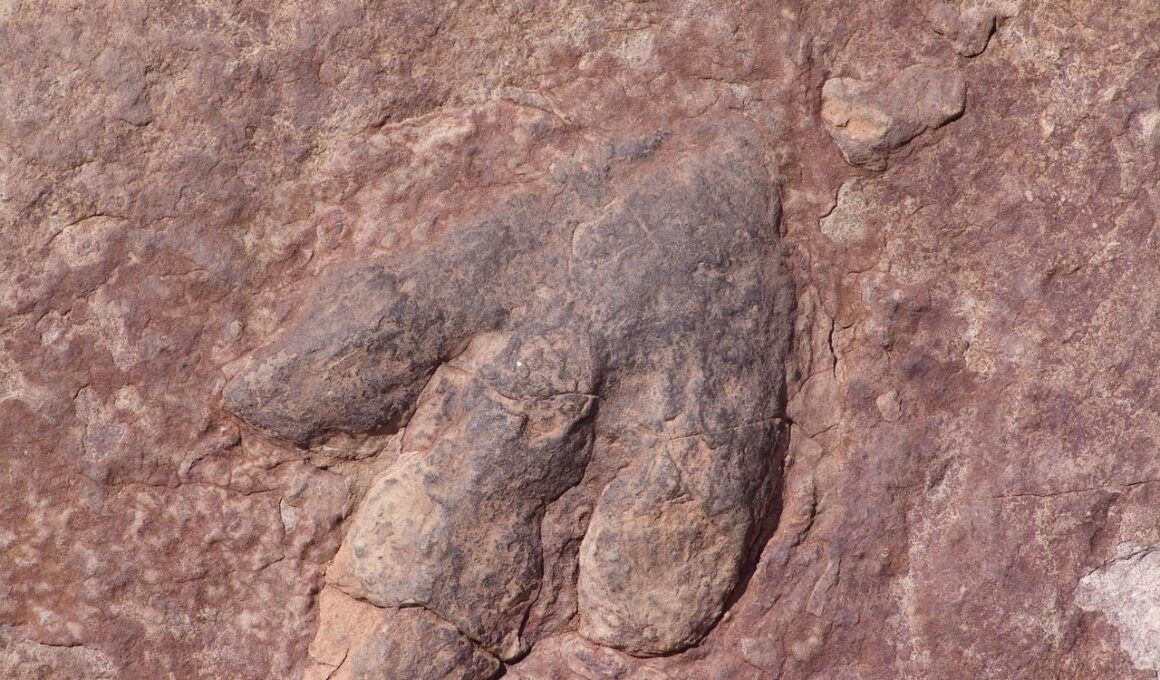
Fossil Records and Footprints
Fossil records provide tremendous insights into the relationships between dinosaurs and the ecosystems they inhabited. Dinosaur footprints, often preserved in rock layers, serve as vital indicators of past environmental conditions. By analyzing these tracks, scientists gather data on dinosaur behavior, interaction, and habitat preferences. The size, depth, and spacing of footprints reveal critical information about locomotion patterns, group behavior, and migration. Different types of trails indicate whether dinosaurs traveled alone or in herds, offering clues about social structures. Analyzing fossil footprints contributes to our understanding of ancient biodiversity, as they demonstrate the coexistence of diverse species in specific regions. Pattern analysis of footprints allows scientists to reconstruct ancient environments, suggesting predominant flora and responding animal species in various ecosystems. Additionally, identifying the foot structure helps scientists infer functional morphology and biomechanics linking physical traits to ecological roles. The combination of fossil footprints provides a deeper understanding of the dynamics at play in ancient ecosystems. This data ultimately leads to a more comprehensive understanding of the evolution of life on Earth, showcasing how integral these footprints are to piecing together the stories of the past.
Dinosaur footwear offers fascinating insights into the evolutionary relationships between species. The unique adaptations in foot structures led to varying levels of agility and strength, which dictated their respective ecological roles. Species with robust feet could access a broader range of habitats due to their ability to navigate harsh terrains effectively. Conversely, more agile foot structures gave certain theropods competitive advantages for hunting fast prey. Such adaptations illustrate the complexities of predator-prey dynamics where evolutionary adaptations are deeply intertwined. The evidence gleaned from studying dinosaur footprints reveals that these adaptations were crucial for survival amidst fierce interspecies competition. Furthermore, the evolution of dinosaur feet represents broader evolutionary trends seen throughout Earth’s history. Each unique structural adaptation allowed species to exploit different niches, further diversifying ecosystems. Additionally, the changes in foot morphology over time reflect the environmental shifts experienced by these ancient creatures. Considering the impact that climate and geographical changes had on their distribution illustrates how critical adaptability was for survival. Thus, the exploration of dinosaur footwear enhances our appreciation for the interconnectedness of life in ancient ecosystems, showing the delicate balance that sustained diverse forms of life.
Conclusion: The Legacy of Dinosaur Footwear
The legacy of dinosaur footwear continues to fascinate scientists and enthusiasts alike, opening discussions about how ancient life shapes current ecosystems. Understanding these adaptations enhances comprehension of evolutionary biology and ecology. These evolutionary traits directly impacted the development and sustainability of ecosystems. Potential parallels can be drawn between how present-day species adapt and how those adaptations arose during the age of dinosaurs. The study of dinosaur feet provides critical abilities to understand how organisms interact with their environments and each other. Present-day biodiversity owes much to the evolutionary legacies of these charismatic giants. Species do not exist in isolation, and the dynamics of ancient ecosystems highlight the importance of interdependent relationships. The adaptations expressed in dinosaur footwear resonate profoundly in understanding the history of life on Earth. As modern science progresses, the insights gained from these ancient tracks can inspire future conservation efforts. Recognizing the importance of preserving both our natural environments and the stories behind them is vital. Dinosaur footwear underscores the interconnectedness of all life, serving as a reminder of the significant impact that one group of organisms had on shaping the planet as we know it today.
Future research on dinosaur feet may lead to new discoveries about their roles in ancient environments. Innovative technologies like 3D modeling and simulation have opened new avenues for studying fossilized tracks. By using advanced imaging techniques, researchers are able to recreate the ecosystems in which these creatures lived. This scientific endeavor can lead to improved insights about their interactions with flora and fauna. Improved visualizations may even allow paleontologists to reconstruct behavioral patterns more accurately than ever before. The ongoing dialogue among scientists aims to uncover the subtle nuances of dinosaur interactions with their environments. The exploration of dinosaur footwear expands our knowledge of evolutionary processes, ecological relationships, and environmental responses. Ultimately, as we delve deeper into this area of research, more information could arise about the complex dynamics that defined ancient ecosystems. The rich tapestry woven by the threads of evolutionary history can inform modern ecological principles. Preservation, conservation, and education about these findings stand as crucial steps in connecting the past with the present. Understanding dinosaur footwear underscores the importance of acknowledging our planet’s evolutionary heritage as we strive to protect the natural world around us.