Conservation Strategies for Endangered Freshwater Species
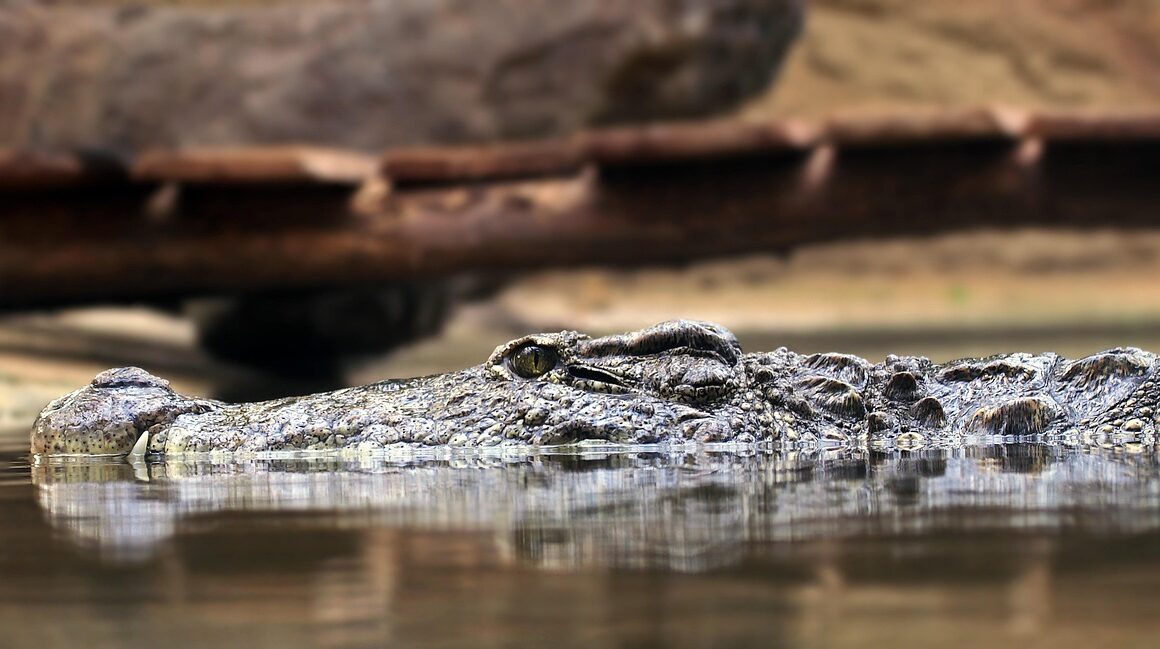
Freshwater ecosystems are vital for biodiversity and essential for numerous environmental processes. Unfortunately, many freshwater species face alarming threats, including habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change. Conservation strategies are imperative to safeguard these vulnerable species and their habitats. Effective strategies include habitat restoration, pollution prevention, and sustainable water management. One key approach is identifying critical habitats for endangered species and prioritizing their protection. Conserving wetlands, rivers, and lakes helps maintain ecosystems that provide food and breeding grounds for various aquatic species. Furthermore, community engagement is crucial for conservation initiatives, as local stakeholders often have valuable knowledge and vested interests. By involving local communities, conservationists can promote sustainable practices that help maintain these important habitats while fostering economic development. Additionally, educational programs can increase public awareness about the significance of freshwater species and the pressing threats they encounter. Collaborative efforts between government agencies, non-profit organizations, and local communities can make a substantial impact on conservation efforts. Developing policies that promote sustainable practices and protect freshwater habitats is essential for the long-term persistence of endangered freshwater species.
One of the most effective methods to conserve freshwater species is through protected areas. These regions serve as safe havens for endangered species, allowing them to thrive without human interference. Implementing protected areas often includes creating reserves or parks where vulnerabilities can be mitigated. Furthermore, these zones play an essential role in maintaining ecological integrity in freshwater habitats. Monitoring these areas helps evaluate the effectiveness of conservation efforts and allows for adaptive management practices. Restoration projects in degraded areas are another crucial element of freshwater conservation. These projects involve rehabilitating ecosystems by replanting native vegetation and removing invasive species. Restoring riverbanks and wetlands enhances habitat quality, enabling the resurgence of native species populations. In many cases, habitat restoration can involve a combination of techniques tailored to specific ecosystem requirements. Collaboration among researchers, government agencies, and conservation organizations is vital while conducting these projects. Such partnerships enable knowledge sharing and resource pooling for greater impact. Innovative approaches, including the introduction of captive-bred individuals into wild populations, can strengthen genetically isolated groups. By ensuring genetic diversity, we enhance the overall resilience of endangered freshwater species.
Community Involvement in Conservation
Promoting community involvement in freshwater conservation is crucial for sustainable biodiversity management. Engaging local communities empowers them to protect their natural resources and fosters a sense of stewardship. Initiatives that involve education, fundraising, and training can greatly influence local attitudes towards conservation efforts. By establishing monitoring programs, communities can contribute valuable data about local freshwater species to inform conservation strategies. Workshops and informational campaigns raise awareness about species at risk and ways to mitigate threats. Community-based conservation projects allow for direct participation, enhancing the effectiveness of measures taken to protect freshwater habitats. Additionally, recognizing traditional ecological knowledge can improve project outcomes by integrating indigenous practices and cultural insights. Furthermore, employing local individuals for habitat monitoring and management can incentivize conservation behavior while providing employment opportunities. Building partnerships between conservation organizations and local groups fosters a collaborative approach to preserving freshwater ecosystems. Involving local leaders and influencers is essential for garnering support for initiatives. Success in community engagement has the potential to strengthen the bonds among individuals, nature, and each other, ultimately benefiting entire ecosystems and enhancing the resilience of freshwater species.
Scientific research plays a vital role in the conservation of endangered freshwater species. Research helps identify key threats, monitor population dynamics, and assess habitat quality. Conducting comprehensive studies allows conservationists to develop targeted strategies tailored to specific concerns. Population assessments provide crucial insights into the status and trend of different species, helping establish priorities for conservation actions. Furthermore, research informs adaptive management strategies, allowing for dynamic interventions based on emerging findings. Collaborative research initiatives, involving universities and conservation organizations, can enhance knowledge transfer and resource sharing. Advanced techniques, such as genetic testing, can assess population health and understand genetic diversity. Moreover, utilizing citizen science programs invites community members to contribute to data collection efforts, fostering greater involvement in conservation. Access to relevant information can further equip stakeholders to make informed decisions regarding freshwater resource management. Additionally, documenting traditional ecological knowledge brings cultural perspectives into scientific considerations. It is essential to balance scientific inquiries with local practices and perspectives to ensure conservation efforts are inclusive and effective. By integrating research and cultural knowledge, we can develop holistic conservation strategies for endangered freshwater species.
Policy and Legislative Frameworks
A strong policy and legislative framework is essential for the effective conservation of freshwater habitats and species. Governments and international organizations must establish regulations that protect freshwater ecosystems from exploitative activities. Environmental protection laws and guidelines should focus on sustainable development while considering the ecological balance of freshwater systems. Policies governing water management, fishing, agriculture, and urban development greatly influence the state of freshwater habitats. Implementing strict regulations on pollution and resource extraction helps ensure ecosystems remain intact and resilient. Furthermore, recognizing and enforcing protected areas for threatened species is critical. Advocacy for responsible policies requires collaboration across all levels, including government, industry, and civil society stakeholders. Engaging the public in the decision-making process can promote accountability and encourage informed choices. Awareness campaigns can stimulate public support for policy initiatives aimed at freshwater conservation. Additionally, international cooperation is vital to address transboundary resource issues and promote sustainable practices globally. There is a necessity for international treaties that govern critical freshwater bodies. By fostering solidarity among countries, we can collectively propel these initiatives forward and contribute to the preservation of global freshwater biodiversity.
Climate change poses significant challenges for freshwater species, necessitating adaptive management strategies. Changing temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events impact aquatic habitats and their inhabitants. Developing strategies that incorporate climate resilience is essential for sustaining freshwater ecosystems. Conservationists must assess climate vulnerabilities and adapt their approaches accordingly. For example, establishing climate refugia, areas that remain suitable for certain species amidst changing conditions, can facilitate species survival. Furthermore, incorporating climate adaptation techniques into habitat restoration projects bolsters resilience. By prioritizing and implementing practices that mitigate climate-related threats, we can ensure viable habitats for endangered species. Integrating climate considerations into freshwater management plans is essential for success. Engaging with scientists and policymakers helps align conservation strategies with wider climate adaptation goals. Community involvement is equally important in developing localized solutions to climate threats. Enhancing the resilience of freshwater ecosystems will require cross-disciplinary efforts, blending ecology with climate science. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable land and water management practices, we can additionally bolster conservation efforts. Protecting freshwater species must reflect an understanding of dynamic environmental conditions while striving to safeguard future generations.
Emerging Technologies in Conservation
Emerging technologies present innovative solutions to enhance freshwater conservation strategies. Advancements in remote sensing, data analytics, and artificial intelligence open new avenues for monitoring freshwater habitats and species effectively. Remote sensing tools allow conservationists to gather large-scale data on water quality, habitat changes, and species distribution. Such information can lead to informed decision-making and prompt action on emerging challenges. Moreover, deploying drones and automated monitoring systems greatly improves data collection efficiency. Artificial intelligence can analyze complex datasets to highlight patterns, predict future trends, and suggest strategic interventions. Citizen science applications enable community members to report sightings and changes in local ecosystems, empowering public participation. Innovations in genetic monitoring enable precise assessments of biodiversity and population dynamics, offering valuable insights for conservation planning. Furthermore, technology can facilitate habitat restoration efforts through precision agriculture and mapping applications, allowing for more effective and targeted interventions. Collaboration among technology developers, scientists, and conservation organizations is crucial for harnessing the potential of these emerging tools. As technology continues to evolve, it is essential to integrate new solutions into existing conservation frameworks, ensuring long-term success for endangered freshwater species.
In conclusion, effective conservation strategies for endangered freshwater species require a multifaceted approach. Combining community involvement, scientific research, policy frameworks, climate adaptation, and emerging technologies will optimize efforts to protect these vital ecosystems. Each strategy contributes uniquely to the overall conservation landscape, addressing specific threats facing freshwater species. Stakeholder collaboration strengthens the impact of conservation initiatives on local and global scales. By fostering partnerships between governments, scientists, communities, and conservation organizations, we can enhance ecosystem resilience. It is essential to recognize the importance of the interconnectedness of species and habitats when planning conservation efforts. Community-driven solutions provide valuable insights into local ecosystems, while scientific research grounds strategies in ecological realities. Additionally, effectively implemented policies and legislation lay the foundation for sustainable freshwater management. Addressing climate change impacts ensures long-term viability for many freshwater species. By embracing innovative technologies and encouraging adaptive management practices, we can continuously improve conservation outcomes. Each step taken will advance towards a more sustainable future for freshwater ecosystems and their inhabitants, ultimately ensuring a legacy for future generations.