Functional Maturation of Sensory Neurons in the Developing Nervous System
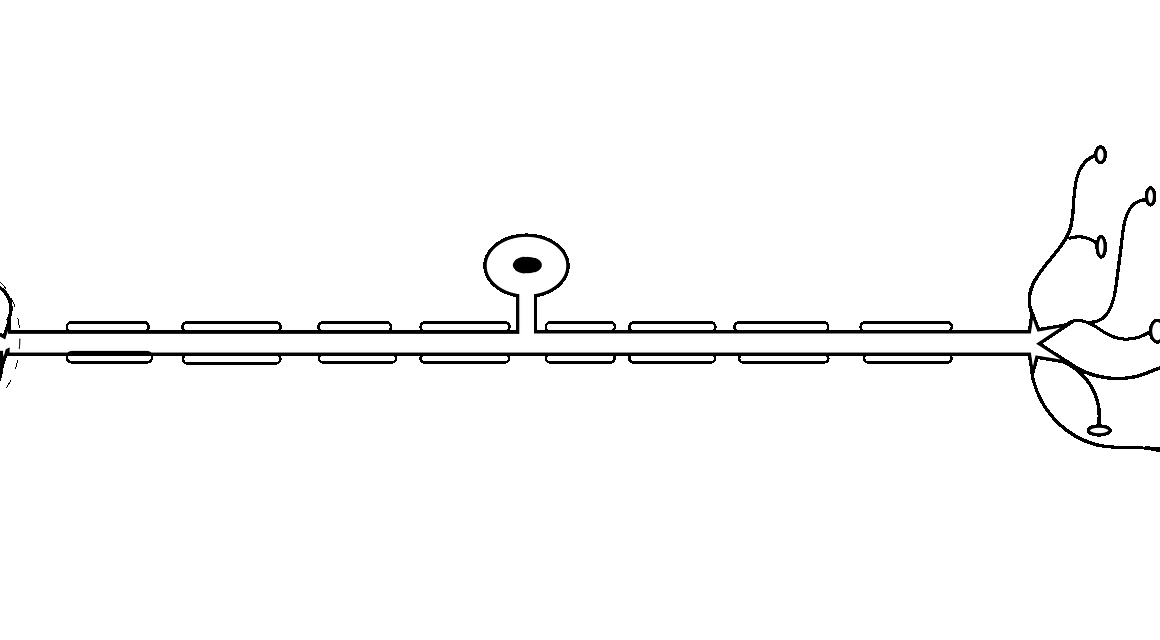
The development of sensory neurons is a complex process crucial to the functionality of the nervous system. Early in the embryonic stage, sensory neurons arise from neural progenitor cells, undergoing differentiation. The functional maturation involves a series of sequential events including proliferation, migration, and maturation. Sensory neurons play an essential role in detecting environmental stimuli, translating them into electrical signals that travel through the nervous system to the brain. Research indicates that sensory neurons must develop various properties like excitability and synaptic connections for effective communication with other neurons, leading to the integration of sensory information. Proper functioning of sensory neurons is critical for behaviors dependent on sensory input. Disruptions in the process can result in sensory deficits, emphasizing the importance of understanding sensory neuron maturation. According to studies, both intrinsic genetic factors and extrinsic signals influence this maturation process. Factors such as neurotrophic growth factors contribute significantly to the survival and development of these neurons. Further exploration into these processes will provide insights into potential therapeutic approaches for sensory processing disorders in humans.
The Role of Growth Factors
Growth factors are proteins that significantly influence the development of sensory neurons during their maturation process. The neurotrophic factors, such as Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF), play pivotal roles in guiding the developmental pathways of these neurons. NGF is critical for the survival and differentiation of sensory neurons, particularly those associated with pain and temperature sensation. BDNF, on the other hand, is essential for the differentiation and maintenance of various sensory neurons. These growth factors bind to specific receptors on neurons, activating intracellular signaling pathways that promote growth, survival, and synaptogenesis. In vitro studies have demonstrated that neurons exposed to these factors exhibit enhanced growth and improved neuron survival rates compared to controls lacking growth factor treatment. This dependence on growth factors underscores their essential contribution to establishing a robust and functional sensory system. Disruption in the signaling pathways of these growth factors can lead to inadequate neuron maturation and deficiencies in sensory processing. Understanding the precise mechanisms by which growth factors influence sensory neuron maturation is crucial for developing treatments addressing sensory dysfunction.
Another critical aspect of sensory neuron development is the establishment of functional synaptic connections. The process of synaptogenesis involves the formation of synapses between sensory neurons and their target cells, including other neurons and muscle fibers. This intricate process relies on both pre-synaptic and post-synaptic mechanisms, ensuring effective communication and integration of sensory signals. Vice versa, sensory neurons must choose their appropriate targets to establish correct connectivity, ensuring they function properly within neural circuits. Many studies have focused on the role of cellular adhesion molecules in recognizing and binding to target cells during synapse formation. These molecules facilitate the clustering of neurotransmitter receptors, providing direction for synaptic development. Furthermore, activity-dependent mechanisms contribute to refining synaptic connections, underscoring the need for sensory activity during development. Proper sensory experiences during critical periods enhance the capacity of sensory neurons to form and strengthen synapses. Consequently, the establishment of precise synaptic connections is essential for effective sensory processing. Ongoing research continues to elucidate the factors influencing synaptogenesis, emphasizing the complexity of developing functional sensory systems.
Regulation of Neuronal Activity
The regulation of neuronal activity is vital for the maturation of sensory neurons in the developing nervous system. Neural activity influences gene expression, ultimately leading to the development of key features necessary for functional sensory processing. Activity plays a role in several aspects, including dendritic growth and branching, synapse formation, and neuronal survival. Emerging evidence suggests that sensory experiences during critical developmental windows shape the functionality of sensory neurons. For instance, tactile and auditory stimuli can significantly influence the structural and functional properties of sensory neurons. These experiences can reinforce synaptic connections and promote adaptive changes in neuronal circuits. Additionally, disuse of sensory pathways may lead to impairments in neuronal growth and synaptic structure, highlighting the importance of sensory input during maturation. Research has demonstrated that altering patterns of sensory activity during development can lead to alterations in the excitability of sensory neurons and their responsiveness to stimuli. Understanding how neuronal activity regulates maturation could provide insights into potential intervention strategies for sensory processing disorders arising from atypical development during early life stages. Investigating these regulations is critical for fulfilling gaps in neurodevelopment research.
The maturation of sensory neurons involves not only intrinsic neural mechanisms but also various extrinsic environmental factors. These factors greatly influence the trajectory of sensory neuron development and functional maturation. The surrounding glial cells, signaling molecules, and the extracellular matrix all provide essential support to developing sensory neurons. Glial cells, such as Schwann cells and astrocytes, play supportive roles, assisting with myelination and promoting neuronal survival. The extracellular matrix provides structural support and also harbors signaling molecules that affect neuron behavior. Furthermore, environmental cues, including nutrient availability and physical activity, contribute to sensory neuron health. Studies have indicated that enriched environments positively impact the maturation process of sensory neurons, leading to enhanced cognitive functions. Conversely, sensory deprivation environments can negatively affect the growth and synaptic connectivity of sensory neurons. Research emphasizes how these environmental interactions underscore the dynamic relationship between sensory neurons and their surroundings. This understanding can guide therapeutic approaches designed to enhance sensory processing by leveraging environmental manipulations. Overall, it remains evident that sensory neuron maturation is intricately linked to a myriad of factors encompassing both neural and non-neural components of the nervous system.
Clinical Implications of Sensory Neuron Maturation
The maturation of sensory neurons has profound clinical implications, especially in understanding sensory processing disorders. Various conditions, such as autism spectrum disorder, sensory processing disorder, and neuropathies, underscore the significance of proper sensory neuron development. Early identification of atypical sensory maturation can inform intervention strategies. The timing and nature of sensory input during critical development periods can significantly influence functionality. Interventions aimed at enhancing sensory experiences can potentially improve outcomes for individuals with sensory processing difficulties. Therapeutic strategies may include sensory integration therapies and tailored activities designed to enrich the sensory environment. Additionally, understanding the mechanisms underlying sensory neuron maturation guides the development of pharmacological treatments targeting specific growth factors and signaling pathways. Research has also explored gene therapy approaches to address deficits in neuronal connectivity related to sensory processing disorders. Enhancing the maturation process through these innovative avenues presents exciting opportunities for advancing clinical practices. As researchers continue to unravel the complexities of sensory neuron maturation, translating this knowledge into clinical applications will be crucial to working towards effective therapies for challenging conditions that affect sensory processing.
The ongoing investigation into the maturation of sensory neurons offers hope for novel therapeutic interventions that enhance sensory processing capabilities. As brain plasticity remains a central theme in understanding neurodevelopment, the adaptability of the nervous system provides potential for rehabilitation strategies. The insights into the mechanisms governing sensory neuron maturation will enrich existing knowledge of synaptic plasticity and neurodevelopmental pathways. Adaptation to sensory input underscores the foundational role of environmental factors and neural circuitry in shaping sensory experiences. Moreover, the timeline of sensory neuronal maturation offers critical targets for intervention. Identifying and modifying parameters that influence early developmental stages may enable clinicians to optimize procedural outcomes. Educational and therapeutic practices could be tailored to stimulate appropriate sensory experiences during sensitive periods. Emphasizing early detection and intervention can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals facing sensory processing challenges. Investigating various methodologies to facilitate sensory neuron maturation is essential for future research endeavors. Overall, the ongoing research highlights the dynamic interplay of genetic, activity-dependent, and environmental influences in shaping the functioning and health of sensory neuron systems.
The understanding of sensory neuron maturation lays a foundation for comprehending the broader aspects of neural development and its implications for health. This foundational knowledge provides a framework for exploring the interconnectedness between sensory systems and cognitive functions. Recent advancements in neurobiology have underscored the intricate relationships that exist between sensory neuron development, synaptic plasticity, and overall brain maturation. These relationships affirm the importance of a holistic approach in studying nervous system development and function. Insights gleaned from sensory neuron maturation research can be translated into educational frameworks, therapeutic practices, and targeted interventions. Furthermore, the interplay between sensory processing and cognitive abilities aligns with ongoing discussions about neurodevelopmental disorders. Understanding how sensory processing influences cognitive development can enrich approaches used in supporting individuals with developmental delays. As scientific inquiry continues to prioritize innovative methodologies in studying neuron maturation, researchers are paving the way towards establishing improved standards for educational and therapeutic practices. Accepting the complexity of sensory neurons within the broader spectrum of neural development enables a more comprehensive perspective on growth, adaptation, and health across the lifespan. Promoting further investigation into neuron maturation is essential for fostering advancements in both basic research and clinical applications.