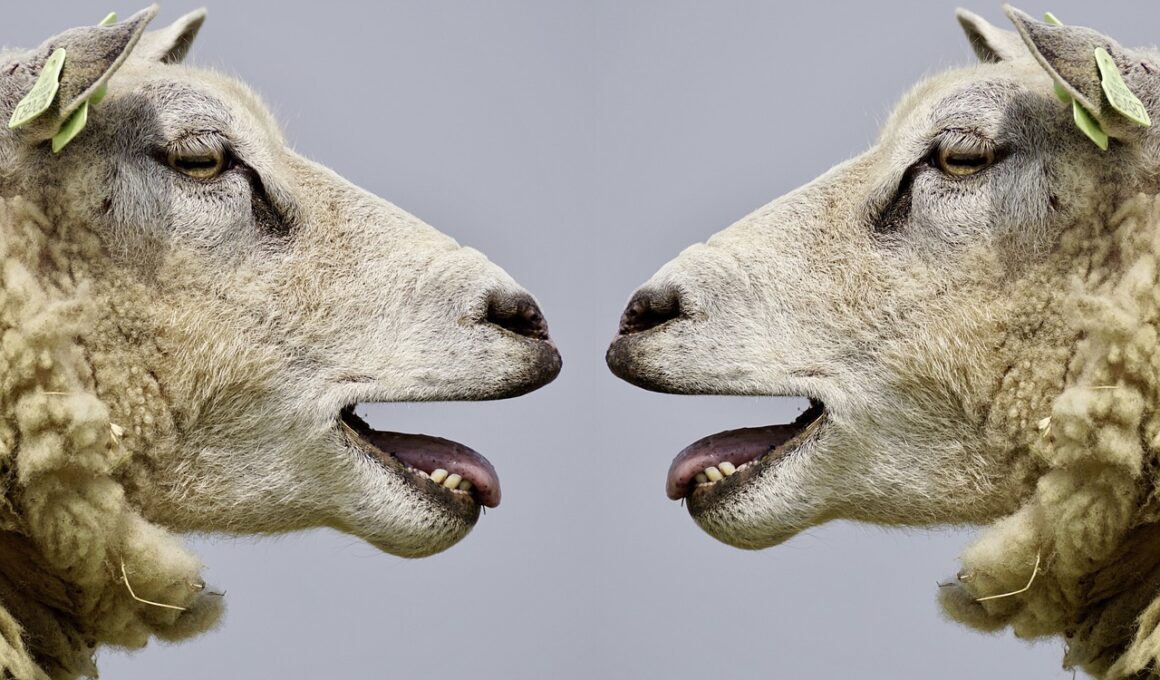
How Mammals Recognize Each Other Through Communication
Mammal communication is an intricate process that plays a vital role in their social structure. Various species utilize diverse methods to recognize each other, fostering relationships and ensuring survival within their environments. These communication strategies are essential, especially in densely populated habitats where individual identification is crucial. Vocalizations, body language, scent marking, and tactile communication are among the prominent methods mammals employ. Each species has tailored its communication techniques for effective interaction. For example, wolves utilize a combination of howls, growls, and body postures to signal their identity or status within the pack. Elephants produce infrasound, low-frequency sounds imperceptible to humans, to communicate over long distances, sharing important information about their location and societal dynamics. Moreover, marine mammals such as dolphins use clicks and whistles to establish social bonds and navigate their underwater environments. Understanding these unique communication methods provides insight into mammal behavior, social structures, and ecological adaptations. Each type of communication not only helps in recognizing individuals but also facilitates group cohesion that is essential for their survival.
Mammals employ vocalizations extensively to convey information among themselves. These sounds vary greatly, providing different meanings based on context. For instance, a dog’s bark may indicate excitement, warning, or playfulness, with variations in pitch and duration enhancing clarity. Similarly, the vocalizations of primates, like howler monkeys, serve to establish territory and communicate with group members. Research has shown that many mammals can interpret these complex sound patterns to discern the emotional state or intentions of others. In social mammals, such as elephants, vocal communication is critical for maintaining bonds within family units. Additionally, mammals often incorporate body language alongside vocalizations to convey messages further. Tail movements, ear positions, and facial expressions provide nuanced communication that helps clarify intentions. The combination of visual and auditory signals strengthens social dynamics, enabling mammals to interact more effectively. Furthermore, research into these communication methods has practical applications in fields like animal behavior and conservation efforts. Understanding how mammals communicate can inform strategies to protect endangered species and ensure their survival in rapidly changing environments. This knowledge is invaluable for creating supportive habitats that accommodate natural behaviors.
The Role of Scent in Mammal Communication
Scent marking constitutes another crucial aspect of mammal communication. Various species use olfactory signals to identify individuals, establish territories, and convey reproductive status. Mammals like foxes and coyotes leave scent marks from glands on their bodies or urine to communicate presence and reproductive readiness. This form of communication allows them to communicate over distances and for extended periods, effectively informing others of their identity and status. In social species, such as wolves, scent plays a role in maintaining pack cohesion, helping members recognize each other strengthens social bonds. In addition to territory marking, scent also plays a part in mating rituals. Female mammals, like many ungulates, release pheromones to signal readiness for mating, attracting males from considerable distances. The interplay between olfactory signals and vocalizations creates a multifaceted communication strategy that enhances social interaction among mammals. Understanding how scent marking and olfactory communication work provides insight into the complexities of mammal behavior and can help researchers better comprehend the dynamics of their social structures. Scent communication also highlights the importance of preserving habitats that allow these essential interactions among mammals.
Another fascinating aspect of mammal communication is the use of tactile signals. Physical touch can convey affection, aggression, or simply functionality in social interactions. For instance, grooming behaviors observed among primates like chimpanzees promote bonding within groups, revealing societal hierarchies and reinforcing relationships. Similarly, elephants display tactile communication through trunk touches and hugs, displaying their understanding of each other’s emotional states. Such touch-based interactions play a critical role in establishing and maintaining strong social bonds. Tactile communication is not just limited to social relations but can also signal the need for immediate attention or response in urgent situations. In various species, tactile communication can initiate mating behaviors or provide reassurance during stressful moments. Understanding these interactions sheds light on the emotional intelligence of mammals and the significance of non-verbal cues in their relationships. The nuanced communication styles among mammal species inspire considerable research and exploration within behavioral ecology, highlighting the connections formed through physical interactions. Investigating these methods reveals a wealth of information about how mammals navigate their social environments, utilizing a blend of sensory inputs for effective communication.
The Impact of Environment on Mammal Communication
The environment has a profound impact on mammal communication styles and methods. Factors such as habitat type, population density, and predation pressure shape how species communicate. For instance, mammals living in dense forests may rely more on vocal sounds, while those in open fields may communicate using visual signals or scents. Additionally, acoustic properties of various environments dictate vocalization. In forested areas, low-frequency sounds may travel further than higher frequencies. Consequently, species like howler monkeys have adapted their vocalizations to suit their habitats for effective communication. Urbanization also influences how mammals interact. Animals in metropolitan areas may adjust their vocalizations in response to city noise, developing new patterns to ensure their messages are conveyed. Understanding these adaptations is essential in conservation efforts, particularly as habitats continue to change due to human activity. Furthermore, this knowledge can aid in predicting how mammals may adapt to future environmental changes, allowing for proactive conservation strategies. It’s vital to preserve diverse habitats that support natural communication methods. This insight aids researchers in crafting effective management practices for sustaining mammal populations and their ecological interactions.
Social learning and cultural transmission are significant aspects of mammal communication that demonstrate how behaviors are passed between individuals. Species like dolphins and elephants showcase intricate social structures, where younger members learn communication methods from older, more experienced individuals. This learning process goes beyond mere imitation; it involves complex interactions where social bonds deepen through shared experiences. Cultural transmission has powerful implications as it fosters group identity and cohesion, ensuring that knowledge relevant to survival, such as foraging techniques or danger recognition, is maintained across generations. Additionally, studies have shown that cultural learning influences vocalizations among cetaceans, with distinctive dialects developed within pods. Understanding these communication nuances highlights the role of intelligence in mammals and the social contexts of their interactions. It emphasizes how contextual understanding shapes behavior, revealing a more profound societal complexity than previously assumed. Conservation initiatives can benefit from incorporating knowledge about cultural transmission, focusing on maintaining social structures that facilitate effective learning. Protecting habitats that allow these complex social interactions ensures the resilience and longevity of mammal populations that rely on communication for survival in varied environments. This perspective broadens the scope of research in animal behavior.
Conclusion on Mammal Communication
Mammals exhibit a rich tapestry of communication methods that play vital roles in their social dynamics and survival. Through diverse means such as vocalizations, scents, tactile signals, and social learning, mammals can recognize each other, forge bonds, and adapt to their environments. The complexity of communication among mammals highlights their cognitive abilities and emotional intelligence, underscoring the importance of understanding these behaviors in the context of conservation efforts. As their habitats face ongoing challenges from human intervention and environmental changes, insights into how mammals communicate can guide effective management strategies to preserve these species. Encouraging and supporting natural communication processes must be a priority in conservation initiatives, ensuring that social structures and behaviors are maintained. Further study into mammal communication can reveal even more intricate dynamics, opening avenues for further understanding of animal behavior. As researchers continue to explore these fascinating interactions, their findings can contribute significantly to the broader field of behavioral ecology. In conclusion, recognizing and appreciating the depth of communication among mammals not only broadens our knowledge but also strengthens our commitment to protecting their diverse habitats.
This closing note emphasizes the need to protect and preserve mammal communication capabilities through habitat conservation and responsible ecological practices. Understanding the nuances of mammal communication offers profound implications for species preservation. The studies aimed at recognizing patterns and methods can aid in developing conservation strategies that focus on maintaining ecosystems where these species thrive. By learning and respecting mammal communication dynamics, we contribute to a balanced and harmonious coexistence with the animal kingdom. Ultimately, the intricate web of connections forged through communication among mammals underscores the importance of biodiversity for the ecosystem. Engaging in dialogue about these phenomena encourages public interest and support for initiatives to protect wildlife. As ecologists delve deeper into the complexities of these interactions, they foster a greater appreciation for the role mammals play within their environments. Encouraging collaboration among researchers, conservationists, and local communities can lead to practical solutions for addressing the challenges faced by mammals worldwide. The path forward necessitates a comprehensive understanding of mammal communication, ultimately aiming for a sustainable future where diverse species can coexist, thrive, and communicate freely.