Behavioral Patterns of Medically Important Arachnids Affecting Human Exposure
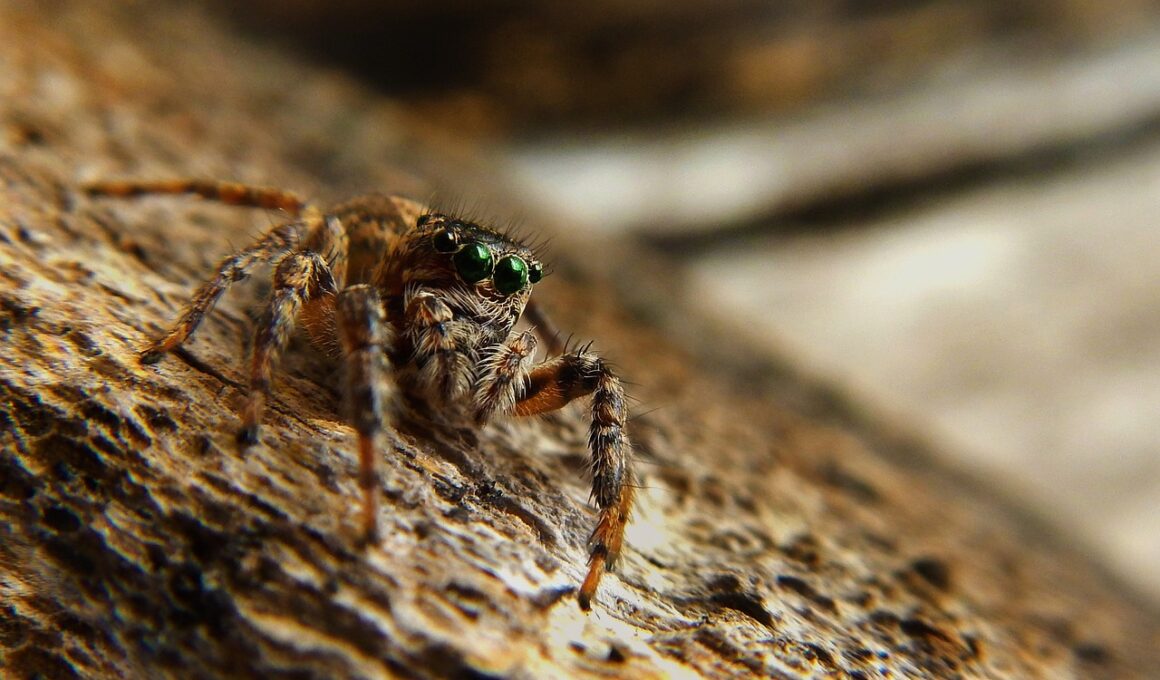
The study of arachnids, including spiders, ticks, and scorpions, reveals profound behaviors that significantly impact human health. Arachnids are remarkable for their diverse adaptations, which often dictate their interactions with humans. For instance, the behaviors of ticks during their quest for a host display various hunting strategies. These can include questing behavior, where ticks climb vegetation to wait for potential hosts. Additionally, some tick species can detect body heat and carbon dioxide, honing their ability to find humans and animals. This sensitivity is crucial in transmitting diseases like Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Furthermore, certain spiders exhibit aggressive behaviors when feeling threatened, potentially leading to bites that can cause systemic reactions in humans. Scorpions, too, possess venom with varying degrees of potency, and their nocturnal activity pattern increases the risk of human encounters. Understanding these behavioral patterns is essential for devising strategies for minimizing risks and mitigating exposure to potentially harmful arachnids. Risk assessments and public education about these behaviors can enhance human safety, contributing to greater public health initiatives aimed at managing the dangers posed by medically important arachnids.
In addition to their foraging and defensive behaviors, mating rituals among arachnids play a critical role in their life cycles that can indirectly influence human exposure to them. Some arachnids, such as the black widow spider, exhibit unique courtship behaviors that can determine the survival of potential mates. This complex mating ritual often involves intricate movements and vibrations that may attract potential predators, including humans. The aggressive nature displayed during courtship can lead to harmful encounters when humans inadvertently disturb these rituals. Similarly, scorpions engage in a courtship dance, which may increase their vulnerability to human encounters. Understanding these mating practices helps in predicting the seasonal patterns of arachnids, as such events often lead to increased arachnid activity. Public awareness campaigns aimed at educating people about these behaviors could reduce accidental bites and stings. Moreover, enhancing community understanding of arachnid behavior, including mating habits, is vital for developing effective preventive measures. Programs that inform people about identifying and safely managing areas with high arachnid activity could lead to improved safety and reduced encounters with these medically significant creatures.
Habitat Preferences and Human Interaction
The habitat preferences of medically important arachnids also contribute to human exposure. Many arachnids favor environments that overlap with human spaces, increasing the likelihood of encounters. For instance, ticks thrive in tall grasses and wooded areas, which are common in suburban and rural landscapes. This proximity enables them to hitch rides on unsuspecting humans and pets, allowing for disease transmission without mutual awareness. Similarly, certain spider species are attracted to human habitations, seeking shelter in cracks, crevices, and even basements. This leads to opportunities for bites when people inadvertently provoke these spiders. Scorpions are known to inhabit desert areas but can also wander into homes, particularly during warmer months seeking cooler indoor climates. Therefore, understanding these habitat preferences is integral to preventing exposure to arachnids. Implementing measures such as maintaining clean yards, reducing clutter, and ensuring proper sealing of homes can significantly mitigate the risk of unwanted encounters. Furthermore, public education about the local arachnid species and their habitats fosters proactive approaches to reducing human exposure and promotes safety in areas where these species are common.
Another critical factor influencing human exposure to arachnids is their activity patterns. Many medically relevant arachnids display nocturnal behaviors which can lead to increased encounters with humans during the night. Scorpions are primarily nocturnal hunters, using specialized adaptations to navigate and hunt in darkness, which can result in humans inadvertently stepping on them or disturbing them in their habitats. Similarly, many spiders are also more active during dusk or nighttime, which can increase the risk of bites when people are outdoors during these times. Desensitization toward arachnids often leads to human complacency about their presence during nighttime activities. Awareness of these activity patterns can guide behavior modification strategies, enhancing individual safety. For instance, wearing appropriate footwear in known scorpion habitats during evening hours can reduce the likelihood of painful stings. Furthermore, encouraging individuals to perform routine checks for lethal arachnids in their surroundings can promote a safer living environment. Public campaigns aimed at educating people about safe practices, especially regarding nocturnal activities, will help mitigate risks linked to medically important arachnids.
Climate Change and Arachnid Behavior
Climate change is expected to have significant effects on the distribution and behavior of arachnids, potentially increasing human exposure. As temperatures rise, many arachnid species are expanding their ranges into new areas, including urban environments. For instance, warmer climates can allow certain ticks to thrive outside their native ranges, increasing their availability in previously unaffected regions. This shift poses new challenges for public health as these ticks may come with unfamiliar pathogens. Additionally, changes in precipitation patterns can influence arachnid habitats, impacting their behavior and nesting patterns. Arachnids may adjust their activity levels in response to these new environmental conditions, potentially increasing encounters with humans. Increased awareness regarding how climate change impacts arachnid behaviors is necessary for public safety. By educating communities on these concerns and teaching preventive measures, we can adapt our interactions with arachnids accordingly. For instance, adapting land-use policies to consider arachnid behaviors and climate implications can help foster environments that minimize contact. Understanding these connections will be pivotal as they relate to human health and the management of medically important arachnids.
The influence of urbanization on arachnid behavior and human interactions cannot be overlooked. Rapid urban development creates new habitats that may attract various arachnid species. Urban environments often provide numerous hiding places and food resources for spiders and other arachnids. With increased human populations in cities, the likelihood of encountering these creatures also rises. Additionally, construction sites often disturb the natural habitats of arachnids, forcing them to migrate into populated areas seeking refuge. Moreover, human activities, such as gardening and landscaping, can inadvertently encourage arachnid presence by providing conducive environments. To combat these challenges, it is essential to implement management strategies that focus on coexistence with arachnids in urban settings. Strategies may include community awareness programs educating residents on minimizing risks while living in proximity to arachnids. Creating arachnid-friendly zones in urban spaces can also enhance biodiversity while decreasing the chances of dangerous encounters. Ultimately, fostering an understanding of arachnids’ roles within urban ecosystems will contribute to safer interactions as urban areas continue to expand and intersect with arachnid habitats.
Conclusion: Promoting Awareness and Safety
The complex interplay of behavioral patterns among medically important arachnids necessitates a comprehensive approach to public health and safety. With their ability to thrive in both natural and human-altered environments, arachnids present unique challenges for mitigating human exposure. Effective management strategies should take into account the distinct behaviors, habitat preferences, and activity patterns of these creatures. By maximizing awareness and understanding of how arachnids operate within our ecosystems, we can better anticipate and prevent potentially dangerous encounters. Public education campaigns that inform citizens about arachnid risks and promote safety measures, such as wearing protective clothing and conducting periodic checks, will significantly enhance community safety. Furthermore, collaborations between public health officials and arachnid researchers could develop evidence-based guidelines to minimize risks associated with arachnid exposure. As urbanization and climate change continue to reshape environments, this knowledge will become increasingly essential. Ultimately, fostering a wider awareness of arachnids and their behaviors will empower individuals and communities to coexist safely with these fascinating and, at times, dangerous creatures.
Awareness and understanding of the risks associated with medically important arachnids are crucial for the safety of the public. By providing clear information and practical prevention strategies, communities can significantly reduce harmful encounters with these creatures. Streamlining educational outreach in schools, community centers, and through online platforms ensures that people are informed about the behaviors and habitats of arachnids. Encouraging personal responsibility and proactive measures fosters a culture of safety regarding arachnid interactions. Collaborative efforts between health departments, educators, and researchers can lead to the development of informative resources, including brochures and online articles, dedicated to educating the public. Such initiatives may encompass interactive workshops to share knowledge about identification, safe handling, and preventive practices for arachnid encounters. Additionally, training healthcare providers to recognize symptoms linked to arachnid bites will enhance treatment and management on an individual level. Implementing these educational frameworks can cultivate a safer environment, especially in areas where medically important arachnids are prevalent. Ultimately, raising public awareness about behaviors, risks, and preventive strategies serves as the best defense against the health threats posed by medically significant arachnids.