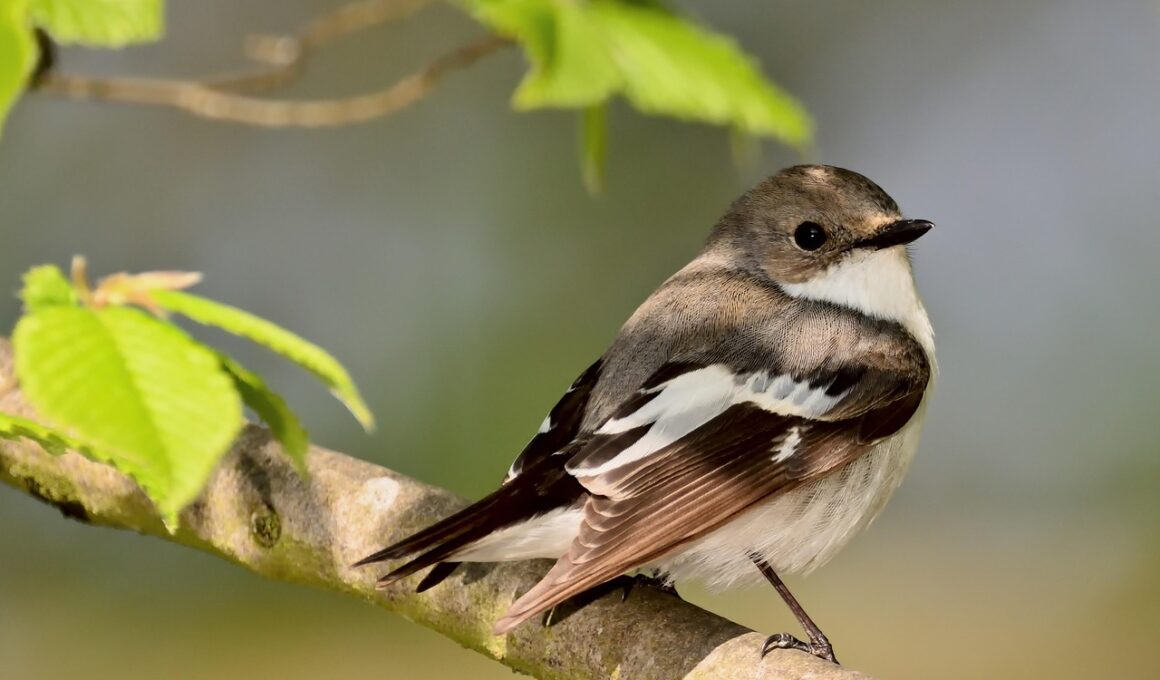
Impact of Climate Change on Songbird Species
Climate change significantly affects songbird species, altering their habitats and migration patterns. As global temperatures rise, many songbirds face challenges in finding suitable breeding grounds. The changing climate influences food availability, impacting the survival of hatchlings. Furthermore, shifting weather patterns can result in unexpected storms that disrupt nesting sites. Songbirds are also affected by habitat loss due to urban development and deforestation, which exacerbate climate impacts. Rising temperatures can force songbirds to migrate earlier or later than usual, causing mismatches in their food supply. For instance, insects, crucial for feeding young, may emerge at different times, leading to food shortages. Studies show a decline in populations of specific songbird species attributed to these changing dynamics. Conservation efforts must address these issues to ensure songbird survival. Protecting land and implementing sustainable practices are crucial. Moreover, public awareness is vital in supporting conservation initiatives. By understanding the threats posed by climate change, we can foster more resilient ecosystems. Promoting climate-friendly policies at local and national levels will be beneficial. The future of songbirds hinges on the actions taken today to mitigate climate disturbances.
An increasing concern in the avian world is how climate change affects songbird behavior and reproduction. Songbirds rely on precise environmental cues for breeding. With climate change altering the timing of seasonal changes, these cues may not align with the necessary resources. For instance, studies indicate that temperature fluctuations can lead to mismatched breeding times, resulting in reduced reproductive success. Some species may find themselves breeding at suboptimal times with insufficient food supply. Moreover, songbirds may alter their migratory patterns, leading to territory disputes and increased competition for food and nesting sites. As habitats shift, new competitors may emerge, exacerbating tensions between species. Consequently, songbirds’ adaptability is tested under these changing conditions. It is crucial for ornithologists and ecologists to monitor these shifts and develop strategies to protect vulnerable songbird populations. Programs aimed at habitat restoration play an essential role in these efforts. Encouraging biodiversity can help buffer against climate impacts. Educating communities about the importance of songbirds in ecosystems fosters a connection that inspires conservation action. Policies promoting sustainable land use and climate resilience will enhance habitat quality for future generations of songbirds.
Effects on Migration Patterns
One of the most evident impacts of climate change on songbirds is the alteration of migration patterns. Many songbird species depend on seasonal changes for migration cues, such as temperature and daylight duration. With climate change, these cues become unreliable, leading to premature or delayed migrations. Early arrivals at breeding grounds can result in a lack of food; thus, hatchlings may not survive. Similarly, if songbirds migrate too late, they may miss optimal breeding opportunities. In some regions, songbird migration routes are shifting northward as habitats become inhospitable due to rising temperatures. This phenomenon places additional stress on species that are not adaptable to rapid changes. Moreover, songbird populations that rely on specific routes face heightened risks associated with climate change. Habitat fragmentation and loss along migratory paths magnify the challenges. Consequently, conservation groups have begun mapping critical migration corridors to secure safe passages for songbirds. Protecting these corridors from development and maintaining resilient habitats are key steps in combating climate challenges. Governments can implement policies that provide avenues for wildlife conservation, ensuring songbirds continue to thrive in a warming world.
Habitat loss represents another severe consequence of climate change on songbird species. Deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural expansion consistently degrade habitats vital for songbirds. These activities also deplete resources essential for nesting and brooding functions. Additionally, human-induced climate changes have caused forests to shift, creating unfavorable conditions for some songbird species. Altered ecosystems result in fewer food sources, compelling songbirds to adapt by migrating longer distances or occupying new territories. Some species struggle to compete against invasive species that thrive in these altered environments. Conservation strategies aimed at habitat restoration and protection are essential to mitigating these effects. Initiatives can include maintaining natural landscapes and implementing sustainable land use practices. Furthermore, urban areas can integrate green spaces that support songbird populations, creating buffer zones. Community engagement in conservation efforts enhances the impact of these strategies. With education and awareness, local populations can contribute to creating songbird-friendly environments. Promoting reforestation and protecting existing habitats is vital for maintaining biodiversity. Ultimately, safeguarding the natural habitats of songbirds directly relates to their ability to survive and thrive amidst climate challenges.
Impact on Food Supply
Another critical aspect of climate change affecting songbird species is the availability of food sources. As climate shifts, the life cycles of insects and plants that songbirds depend on can become misaligned. This misalignment leads to food scarcity during crucial breeding seasons, directly impacting songbird fitness and reproductive success. For example, many songbirds feed their young insects, which may emerge earlier due to warmer temperatures. If songbirds do not adjust their breeding times, hatchlings may starve due to a lack of available food. Additionally, climate change can influence the distribution of plants and insects, forcing songbirds to exploit new areas for nourishment. This added stress can lead to increased competition among songbird populations. Habitat loss exacerbates the problem, as fewer resources are available to support the remaining populations. These dynamic changes necessitate research into the feeding ecology of songbirds under changing climatic conditions. Conservation efforts must consider the effects of climate change on food supply to implement effective measures. Educating the public on the importance of preserving local biodiversity can bolster these initiatives. Addressing these issues early will help mitigate the long-term impacts on songbird species worldwide.
Finally, understanding the effects of climate change on songbird species requires monitoring and long-term research. Conservationists must gather data on population dynamics, migration patterns, and reproductive success to develop effective strategies. Utilizing citizen science can enhance data collection efforts, engaging the public in tracking songbird populations. Additionally, researchers can employ technology such as GPS tracking devices to study migration behaviors effectively. This information helps identify critical habitats and migratory routes essential for songbird survival. Climate change will continue to challenge songbird populations; thus, proactive measures need implementation. Engaging policymakers in conservation discussions ensures that songbird preservation remains a priority, leading to the development of robust strategies. Encouraging collaboration between scientists, governments, and communities can yield significant benefits. Implementing adaptive management practices that respond to environmental changes will be essential for protecting songbirds. Furthermore, public outreach can foster community involvement in conservation actions. Together, these combined efforts can mitigate the impacts of climate change on songbird species. Ultimately, the future of songbirds relies on local actions supported by broad environmental policies that prioritize climate resilience.
Future Conservation Strategies
To safeguard songbird species from the impacts of climate change, innovative conservation strategies must be embraced. Restoration of critical habitats should be prioritized, which involves planting native vegetation and combating invasive species that threaten songbird populations. Preserving connectivity between habitats will also ensure that songbirds can move freely in search of resources. Engaging in conservation agriculture can help maintain existing natural habitats while allowing agricultural productivity. Moreover, promoting sustainable forestry practices will foster healthy forest ecosystems for songbirds. Education and outreach programs aimed at communities can increase awareness about the importance of protecting songbirds and their environments. By enabling consumers to make informed choices, these programs can influence policy decisions supporting songbird conservation. Additionally, involving local communities in conservation initiatives empowers them to take ownership of preserving songbird habitats. Collaborative efforts between researchers, policymakers, and local communities will lead to innovative solutions addressing the complexities of climate impacts. On a broader scale, international cooperation is essential for addressing migratory songbird conservation needs across borders. Together, concerted efforts can create a greater impact, enhancing the resilience of songbird populations facing climate changes.
In conclusion, climate change poses significant challenges for songbird species, impacting migration patterns, food availability, and overall habitat. Understanding these effects is critical for developing comprehensive conservation strategies. Engaging scientists, policymakers, and communities in collaborative efforts will bolster research on vulnerabilities faced by songbirds in a changing climate. By implementing adaptive management approaches, conservationists can respond effectively to these challenges. Public education will enhance awareness of the importance of songbirds in ecosystems and the need for their preservation. Through dedicated action, we can mitigate adverse climate impacts, safeguarding future generations of songbirds. Prioritizing habitat protection and restoration will create resilient ecosystems capable of supporting diverse bird populations. Ultimately, safeguarding songbirds requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses habitat conservation, community involvement, and research. The fight against climate change is ongoing, but with concerted efforts, we can ensure the survival of these beautiful songbird species. Together, we have the power to create a more sustainable future for songbirds and support biodiversity. Through collaboration and commitment to environmental stewardship, we will help songbirds thrive as integral members of our ecosystem.