Parasites in Animals: Prevention and Treatment Strategies
Parasites are organisms that live on or in an animal host, drawing nutrition at the host’s expense. They can wreak havoc on the health of domestic and wild animals. Prevention is key to keeping animals healthy and parasite-free. Owners should regularly check for signs of parasitic infections such as weight loss, lethargy, or unusual behaviors. Environmental management is equally important in parasite control. Keeping living areas clean and minimizing exposure to fecal matter helps break the lifecycle of various parasites. Additionally, certain preventive medications should be administered regularly as per veterinary recommendations. These often include deworming protocols and external parasite controls like flea and tick preventatives. Awareness plays a crucial role in practicing parasite prevention effectively. Reading veterinary guidelines can provide critical insights into specific parasites affecting different animal species. It is essential to stay informed about seasonal outbreaks or regional parasite trends, as these can inform treatment decisions. Research shows that educating pet owners about the importance of regular veterinary check-ups significantly reduces parasite-related health issues in pets. Knowledge empowerment creates a proactive community, benefiting overall animal health, making parasite prevention a priority for responsible pet ownership.
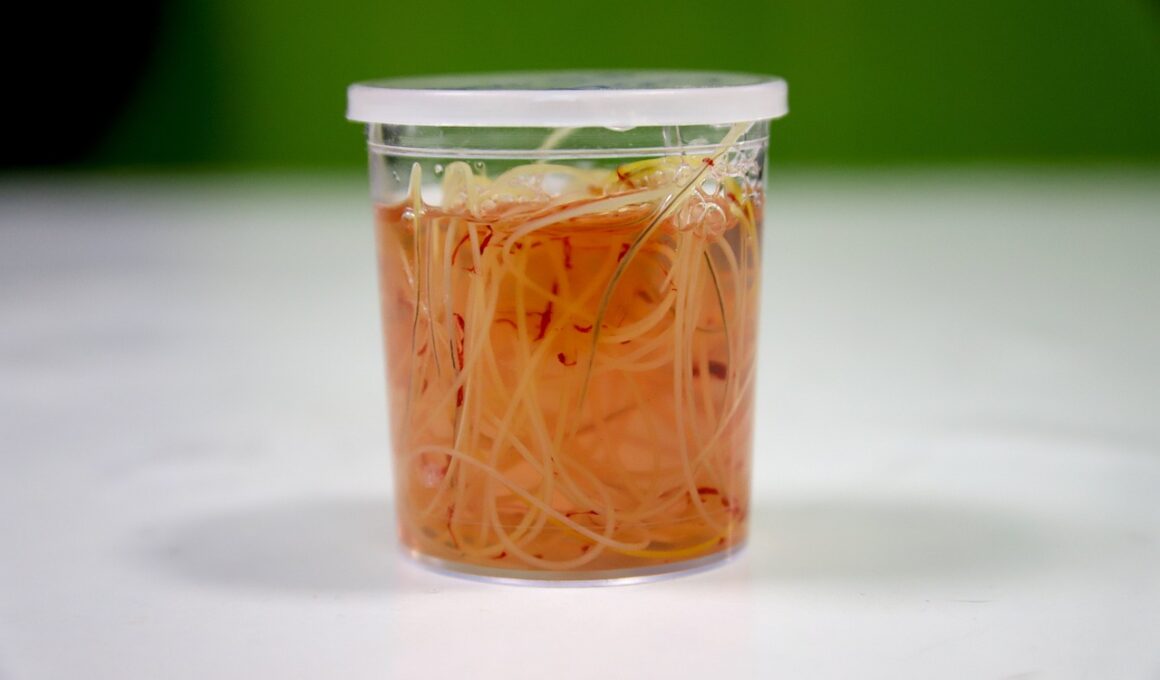
Parasites can cause numerous diseases in animals, affecting both their physical health and overall well-being. Common parasites include fleas, ticks, worms, and protozoa, each presenting unique challenges to animal health. Fleas, for example, can lead to skin irritations and anemia, while ticks can transmit serious diseases like Lyme disease or ehrlichiosis. Internal parasites, such as roundworms and tapeworms, reside within the gastrointestinal tract and can cause malnutrition and discomfort. Owners must be vigilant and recognize the symptoms associated with parasitic infections. This may include changes in appetite, unusual shedding, or gastrointestinal disturbances. Routine fecal examinations are crucial, allowing for early detection of internal parasites. Treatment often involves targeted deworming medications, which are usually effective when administered as per veterinary advice. It’s important to adhere to the prescribed dosages to ensure complete elimination of the parasites. Furthermore, animals recovering from parasitic infections may require supportive care, such as improved nutrition or hydration. Preventative measures should not end with treatment; ongoing monitoring and maintenance of a clean living environment are vital. Keeping animals safe from parasites requires continuous effort and a proactive approach in educating oneself about emerging risks.
Recognizing Parasitic Infections in Animals
Recognizing parasitic infections in animals is crucial for prompt treatment. Pets may display symptoms like persistent scratching, biting at the skin, or noticeable weight loss. Increased thirst or lethargy can also be indicative of a parasitic burden. In some cases, parasites may not produce visible signs until the infestation is significant, which is why regular checkups are important. Different animals manifest the effects of parasites in unique ways, depending on their species and overall health. Fleas and mites may cause severe itching, leading to secondary skin infections. Meanwhile, gastrointestinal parasites can cause diarrhea, vomiting, or even abdominal pain. Early intervention can make a considerable difference and avoid severe health issues. If parasites are suspected, veterinary consultation is paramount to confirm diagnosis and initiate appropriate treatments. Diagnostic tests, including blood work or fecal examinations, help identify the specific parasites present. Immediate treatment improves animal comfort, health, and quality of life. Pets that have had previous parasite infestations should be monitored closely due to the possible recurrence. Owners must remain proactive, utilizing all available resources to manage animal health effectively and reduce the risk of parasitic infections.
Prevention remains the best strategy against parasites in animals, as treatment alone may not suffice. Ensuring that proper hygiene practices are observed in pet living areas can significantly decrease the likelihood of infestations. Regular cleaning of bedding, toys, and surrounding areas minimizes the chances of parasites residing in the environment. Additionally, maintaining a controlled outdoor environment can limit an animal’s exposure to wild hosts, which may carry parasites, including rodents and other wildlife. Pet owners should prioritize routine deworming and preventive medications based on their veterinarian’s recommendations. Some areas may experience seasonal parasite outbreaks, underscoring the necessity to adapt health plans accordingly. Regular vaccinations may also play a role in maintaining overall animal resilience to certain diseases associated with parasitic infections. Nutritional support cannot be overlooked, as a well-fed and healthy animal is less susceptible to infection. Ensuring balanced diets rich in essential nutrients strengthens the immune systems of animals, allowing them to fend off parasites better. Co-management with veterinary professionals helps develop an individualized healthcare plan tailored to each pet’s specific needs. Empowered with knowledge, pet owners can cultivate sustained parasite prevention in their animal companions.
Common Treatments for Parasite Infestations
Treatment for parasite infestations varies depending on the type of parasite involved, with several effective options available. Anthelmintics are commonly used to eliminate internal parasites, such as roundworms or hookworms, in dogs and cats. These medications target the lifecycle of the parasites, ensuring they are expelled from the host’s system effectively. Fleas and ticks can be addressed with topical treatments, oral medications, or environmental sprays, all designed to disrupt their lifecycle and prevent reinfestation. It’s essential to follow veterinary guidance closely while selecting treatments, as some products may not be safe for all animal species, including young or sensitive pets. Additionally, even when pests appear eliminated, follow-up treatments are often recommended to ensure all life stages have been addressed. Regular monitoring of affected animals is vital after treatment, as side effects can occur, and some parasites may regain a foothold if left unmonitored. Always report any unusual symptoms or reactions to your veterinarian promptly. Successful management of parasitic infestations ultimately involves a combination of effective treatments, education, and preventive measures working together to maintain animal health.
There is a significant need for increased awareness and education regarding parasites in animals among pet owners. Many parasites can lead to severe consequences if left untreated, yet knowledge about their prevention and treatment remains inadequate. Community outreach programs can help bridge this gap. These initiatives can educate pet owners on parasite risks, symptoms, and effective prevention measures. Topics like environmental management strategies, grooming practices, and routine veterinary care should be emphasized in outreach efforts. The importance of educating new pet owners, in particular, cannot be overstated, as they may not be aware of the potential health risks. Workshops and seminars can also empower communities by providing essential resources and supportive environments for pet owners. Furthermore, veterinarian-led campaigns can raise awareness about lesser-known parasites that may affect the animals in the region. The impact of awareness outreach is significant; informed pet owners are less likely to encounter severe parasitic issues. This proactive approach uplifts community standards of animal health. Ultimately, fostering a culture of knowledge around parasite prevention contributes to enhancing the well-being of pets in society.
Conclusion: The Importance of Vigilance
In conclusion, the prevalence of parasites in animals underscores the importance of vigilance for pet owners. Understanding the cycle of parasites, recognizing symptoms, and employing preventive measures is critical for safeguarding animal health. Regular veterinary visits establish a foundation for ongoing health checks, while knowledge of seasonal trends aids in preparedness against outbreaks. Surveillance and proper hygiene in environments where animals reside greatly reduce parasite exposure risks. Thorough monitoring of pets following treatments ensures their complete recovery and protects them from future infestations. Continuous education among pet owners contributes to lasting health benefits not only for pets but also for the community at large. Healthier pets equate to less strain on veterinary resources and contribute to overall public health. Community initiatives sharing information about parasites and proper practices can further bolster awareness and encourage cohesive approaches against common infections. As diligent caretakers, owners must commit to making informed choices, carrying out effective preventive measures, and supporting veterinary recommendations. Through shared knowledge and responsible practices, a remarkable decrease in parasite-related issues can be achieved, promoting healthier, happier pets and stable communities.