How Predator Conservation Benefits Biodiversity
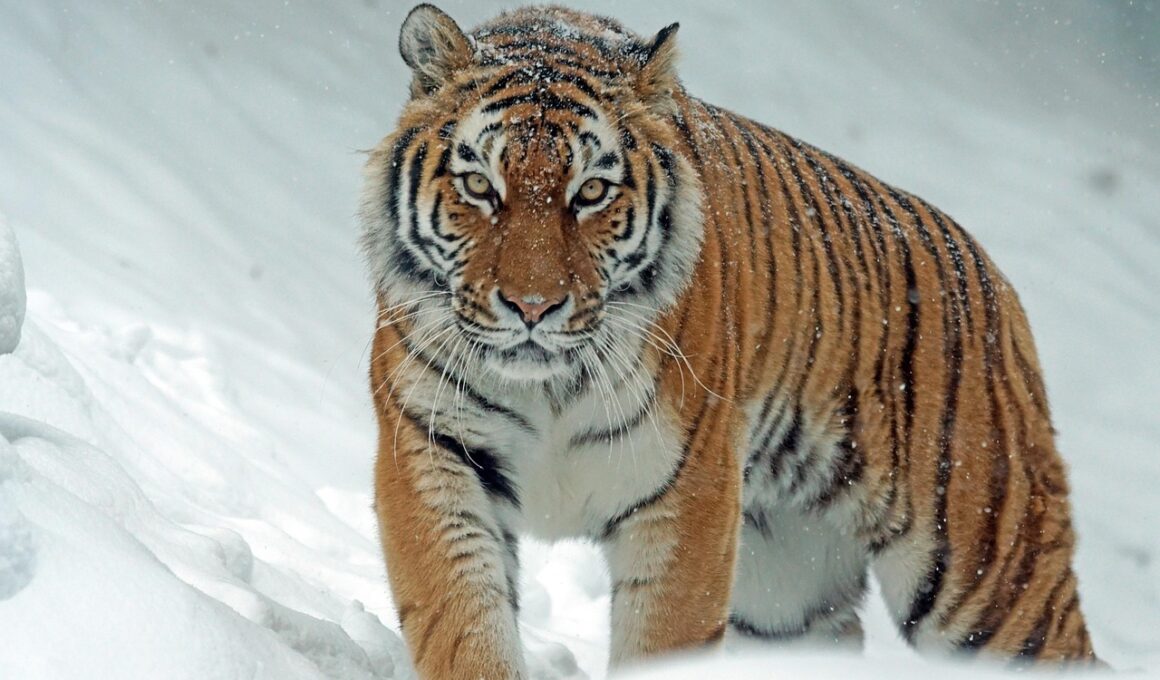
Predator conservation is a critical effort that is essential for maintaining the balance of ecosystems. These apex predators play a vital role in food webs, controlling prey populations and promoting healthy habitats. By keeping herbivore populations in check, predators prevent overgrazing, which could lead to habitat degradation. The loss of predators can trigger a cascade effect, disrupting entire ecosystems and leading to decreased biodiversity. Conservation initiatives aim to protect and sustain these valuable species, allowing them to fulfill their ecological roles. Engaging local communities, raising awareness about the importance of predators, and resisting poaching are key components of successful conservation strategies. International collaborations can also facilitate information sharing and resource pooling. By emphasizing the interconnectedness of nature, these efforts can lead to more robust and resilient ecosystems. The protection of predators simultaneously encourages a variety of other wildlife, fostering an environment where biodiversity can thrive. Thus, protecting predators is not merely about ensuring species survival but is fundamentally about preserving the intricate web of life that sustains our planet. Effective predator conservation can therefore yield dividends that benefit not just the predators themselves, but also countless other species in their habitats.
The Role of Apex Predators in Ecosystems
Apex predators, such as wolves, tigers, and eagles, occupy the top of the food chain and are crucial for ecological health. They regulate prey populations, ensuring that they do not exceed the carrying capacity of their environment. This predation helps maintain a balanced ecosystem, allowing for diverse plant and animal species to flourish. Without these predators, prey populations can boom, leading to overgrazing and habitat destruction. Additionally, apex predators can influence the behavior of other species, creating a ripple effect known as a trophic cascade. For instance, the reintroduction of wolves in Yellowstone National Park has demonstrated remarkable ecological improvements, including increased biodiversity and healthier rivers. This case exemplifies how predator conservation can result in more vibrant ecosystems. It’s essential to acknowledge the interconnectedness of life and recognize that the health of predator populations directly impacts the overall quality of the environment. Conservation strategies aimed at protecting these species inevitably bolster biodiversity and ecosystem resilience. By prioritizing apex predator conservation, we foster a healthy balance within ecosystems, which in turn supports agriculture, tourism, and overall environmental sustainability, benefiting both nature and human communities.
Habitat preservation is equally vital for the conservation of predators and the ecosystems they support. Many predators rely on large territories for hunting and breeding; therefore, the destruction of their habitats due to urbanization, agriculture, and climate change can severely impact their populations. Protected areas, wildlife corridors, and sustainable land-use practices are crucial measures employed to safeguard these habitats. Effective habitat conservation not only helps to sustain predator populations but also protects diverse plant and animal species coexisting within these environments. Furthermore, community involvement in conservation efforts fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility towards biodiversity. Education programs raising awareness about local wildlife issues are essential for garnering public support for habitat preservation. Engaging the next generation in conservation initiatives also cultivates a deeper respect for wildlife and their habitats. Successful predator conservation relies on collaboration between government agencies, NGOs, and local communities. These partnerships can mobilize resources and expertise effectively to tackle challenges. By preserving natural habitats, we create healthier ecosystems capable of supporting a wide array of species. This leads to improved biodiversity within communities, all of which ultimately benefits both wildlife and human endeavors.
Community Involvement in Predator Conservation
Community involvement is a vital aspect of effective predator conservation efforts. Local communities often have a profound understanding of their environment and the species that inhabit it. By engaging communities in conservation projects, we not only benefit from their knowledge but also foster stewardship attitudes towards wildlife. Programs that encourage residents to participate in monitoring wildlife, habitat restoration, or anti-poaching efforts can be extremely effective. Training workshops and educational outreach can empower communities to take an active role in conservation, promoting coexistence between humans and wildlife. Such initiatives can reduce human-wildlife conflict, ensuring that local people can thrive alongside apex predators. Collaboratively addressing issues like livestock loss or crop damage through sustainable practices is essential. Community-led conservation has proven successful in various regions worldwide, with models emphasizing respect for the traditions and needs of local populations. By intertwining cultural values with conservation goals, we can create sustainable strategies that work in harmony with local societies. This fosters a sense of pride while achieving biodiversity goals. Ultimately, when communities believe they have a stake in preserving biodiversity, it leads to more robust and long-lasting conservation outcomes that benefit both wildlife and people.
Promoting awareness about the importance of predators is crucial for garnering public support for conservation efforts. Educational campaigns can highlight the ecological roles of these species while dispelling myths and misconceptions that often surround them. Social media platforms and community workshops provide essential venues for disseminating information and inspiring action. Collaborating with local schools, NGOs, and wildlife organizations can broaden the impact of these programs while enriching community engagement. Creative approaches such as storytelling, art projects, and citizen science initiatives can be effective methods to capture public interest. Highlighting successful predator conservation stories and their positive impacts on ecosystems can inspire collective action. Media and conservation organizations should spotlight the contributions of predators to economic activities, such as tourism, which rely on healthy ecosystems. Engaging the public through citizen science allows individuals to contribute meaningfully to wildlife monitoring and data collection efforts. This not only increases awareness but fosters a sense of agency and empowerment. When people understand the direct benefits of predator conservation to their wellbeing and environment, support for these initiatives is likely to increase. This creates a positive feedback loop, where proactive communities work towards sustaining both wildlife and their shared habitats.
Conservation Technologies and Their Impact
Modern conservation techniques play a significant role in promoting predator conservation and biodiversity. Technological advances, such as camera traps and GPS tracking, provide critical data on predator behavior, populations, and movements. This information aids conservationists in developing targeted management strategies to protect vulnerable species. By analyzing movement patterns and habitat preferences, conservationists can create more effective protected areas that meet the needs of both predatory and prey species. Additionally, engaging in field surveys and remote sensing equips researchers with valuable insights into habitat changes due to human activities. These technologies not only enhance ongoing conservation efforts but also foster innovative approaches to educating communities about wildlife. Technology can assist in implementing anti-poaching measures by using drones for surveillance and monitoring critical habitats. Engaging communities in technology-driven initiatives creates opportunities for knowledge sharing and promotes an appreciation for wildlife conservation. Moreover, social media serves as a platform for fundraising and awareness-building campaigns that increase the resources available for conservation. By marrying technology with traditional conservation methods, we pave the way for smarter, more effective approaches. These advancements ultimately contribute to the long-term sustainability of predator populations and the ecosystems they inhabit.
Addressing climate change is also paramount for the success of predator conservation efforts. As climate shifts alter habitats, many predators face challenges in finding food and suitable breeding grounds. Conservation strategies must adapt to these changes while promoting ecosystem resilience. By improving land management practices, such as restoring habitats and enhancing connectivity, we can help mitigate the impacts of climate change on predator populations. Researching and implementing adaptive strategies is essential to ensure the survival of both predators, and their habitats. Collaboration between scientists, policymakers, and communities is crucial to formulate effective adaptive strategies that consider future climate scenarios. Fostering climate resilience within ecosystems enhances the overall health of environments and broadens biodiversity. Protecting and connecting habitats serve as crucial lifelines for predatory species facing climate-induced challenges. Furthermore, promoting sustainable practices within local communities can yield benefits that extend beyond conservation. By emphasizing the importance of original ecosystems, we can lead communities toward sustainable livelihoods that align with conservation goals. Ultimately, addressing climate change as part of predator conservation frameworks contributes to securing the health of biodiversity for generations to come. This in turn benefits not just wildlife, but also human populations reliant on healthy ecosystems.
Conclusion: The Interconnectedness of Conservation
In summary, predator conservation is a cornerstone of biodiversity preservation. The critical roles apex predators play in ecosystems elevate their significance, making their conservation essential for maintaining ecological balance. As we recognize the importance of protecting these species, we also uncover the interconnectedness of life on Earth. Conservation efforts need to account for various strategies, including community involvement, habitat preservation, technology, and addressing climate change. Each component works synergistically to bolster biodiversity and sustain the ecosystems we rely on. The successful implementation of predator conservation has far-reaching benefits, enhancing both ecological and human well-being. By acknowledging the intrinsic value of wildlife and their roles within ecosystems, we can create a sustainable future. It is our collective responsibility to champion the cause of apex predators, fostering environments where biodiversity thrives. For lasting change, we must work collaboratively, unifying efforts toward a common goal of preserving wildlife and habitats. Only then can we ensure the continuity of rich ecosystems, the intricate networks of species, and the biological heritage we share with all forms of life on our planet. The conservation of apex predators stands as a testament to our commitment to safeguarding Earth’s biodiversity.