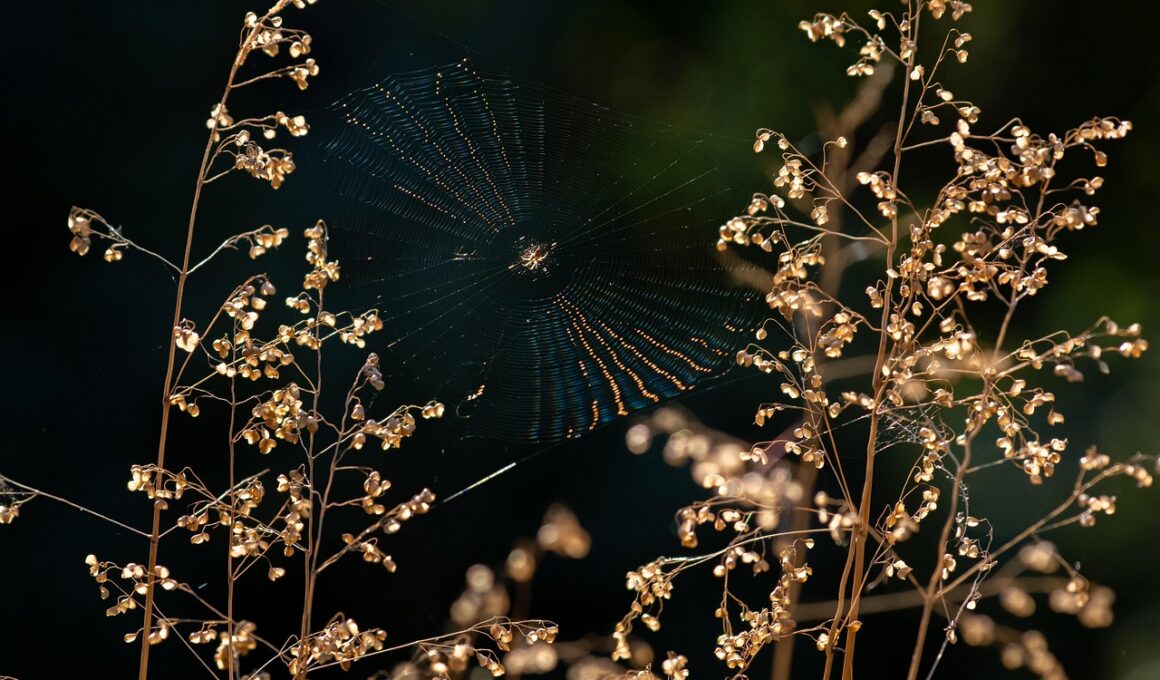
Conservation Status of Diverse Arachnid Taxa
The conservation status of arachnid taxa varies significantly, reflecting their ecological roles and habitat requirements. Many arachnids, such as spiders and scorpions, play crucial roles in regulating insect populations and maintaining ecosystem balance. However, habitat destruction, climate change, and pollution threaten many species, leading to declines in their populations. Conservation efforts are vital to preserve these creatures and ensure their contributions to ecosystems continue. Recent assessments show that various arachnid species are becoming endangered or are already facing extinction due to habitat fragmentation and overcollection. Conservationists emphasize the need to raise awareness and promote protective measures. Initiatives may include establishing protected areas and habitat restoration projects. Education about the importance of arachnids to biodiversity can inspire conservation actions. Furthermore, studying arachnid behavior and ecology helps identify which species are more vulnerable. This understanding can inform conservation priorities, guiding funding and resources towards the most at-risk taxa. Collaborations among researchers, policymakers, and communities are crucial in these efforts, focusing on developing comprehensive strategies to mitigate threats to arachnids. Sustaining arachnids will also benefit agriculture and human health by controlling harmful pest populations.
In addition to habitat preservation, research into the life cycles and population dynamics of arachnids is essential. Such studies reveal patterns that can inform conservation strategies and highlight interactions within ecosystems. For instance, understanding predator-prey relationships can illuminate how arachnids contribute to pest control. Many arachnids have specialized adaptations that enable them to thrive in specific environments, making them especially vulnerable to changes. Recognizing these adaptations helps identify which species may struggle to survive in shifting climates. Moreover, international collaboration is necessary to protect migratory arachnids, such as certain spider species. Migration patterns often cross multiple regions, leading to challenges in jurisdiction and conservation efforts. Creating guidelines for cross-border management can facilitate collaborative conservation strategies that safeguard these species. In this context, the Convention on Biological Diversity plays a pivotal role in providing a framework for international cooperation. Governments and NGOs can develop actionable plans that prioritize arachnid conservation while also addressing broader ecological concerns. Ultimately, enhancing conservation efforts for diverse arachnid taxa ensures the preservation of biodiversity and ecosystem services that benefit all forms of life, including humans.
The classification of arachnids involves numerous taxa, including spiders, scorpions, ticks, and mites. Various families within these groups exhibit different ecological adaptations and lifeways, contributing to the vast diversity among arachnids. The accurate classification of these taxa is crucial for identifying conservation priorities. By understanding the phylogenetic relationships among arachnid groups, researchers can better determine which taxa are at risk and require immediate conservation efforts. For instance, members of the order Araneae exhibit incredible diversity with varying life histories and habitat preferences. Notably, some spider species are already classified as vulnerable or endangered, highlighting the urgent need for targeted conservation actions. Furthermore, cryptic species – those that look similar yet are genetically distinct – complicate classifications and, subsequently, conservation strategies. This lack of understanding can lead to inadequate protection measures if policies are based on misconceptions. Researchers advocate for detailed surveys and genetic studies to accurately assess the status of these groups. Such efforts can reveal hidden diversity among arachnids, emphasizing the necessity of comprehensive conservation planning. In summary, improving taxonomic knowledge lays the groundwork for effective arachnid conservation.
The impact of human activities on arachnid populations cannot be understated. Urban development, agriculture, and climate change all exacerbate habitat loss, directly threatening arachnid diversity. For example, the intensification of agriculture often leads to the use of pesticides, drastically reducing arachnid populations that serve as natural pest controllers. When arachnids are removed from the ecosystem, it may lead to an overabundance of pests, ultimately affecting agricultural outcomes. Similarly, urban sprawl replaces natural habitats with impermeable surfaces, disrupting the life cycles of arachnid species unable to adapt to these changes. Conservationists emphasize the importance of urban planning that incorporates green spaces to support arachnid populations. Special attention to the construction of wildlife corridors can facilitate the movement of arachnids between habitats, allowing for genetic exchange and population stability. Additionally, raising public awareness about the value of arachnids can promote community-led conservation initiatives. Community engagement in monitoring arachnid populations yields valuable data that can inform conservation policies. To minimize detrimental impacts on arachnids, adopting sustainable practices and integrating biodiversity preservation into everyday activities is essential.
Case Studies in Arachnid Conservation
Several successful case studies underline effective conservation strategies for arachnids. One notable example is the conservation efforts surrounding the endangered Hawaiian happy-face spider. In response to declining populations, habitat restoration initiatives have been implemented in Hawaii’s rainforest ecosystems. Collaborative efforts involving local communities, researchers, and government agencies have focused on controlling invasive species that threaten the spider’s habitat. Continued ecological monitoring tracks population recovery, demonstrating the effectiveness of well-coordinated conservation approaches. Other examples include the reintroduction of specific arachnid species into habitats where they have become extinct. Such initiatives often require meticulous planning to ensure that ecological conditions are suitable for reintroduction. For these programs to succeed, they must consider interspecies relationships and environmental conditions. Furthermore, the impact of climate change requires adaptive management to maintain resilient arachnid populations. The unpredictability of climate effects necessitates ongoing research to inform conservation strategies. As we learn more about the complexities of arachnid ecosystems, targeted interventions become increasingly vital. These initiatives highlight how successful conservation hinges on collaboration, community involvement, and ongoing scientific research.
In conclusion, preserving the conservation status of diverse arachnid taxa is imperative for global biodiversity. Recognizing the ecological significance of arachnids leads to actionable conservation strategies and public engagement. Research into arachnid classification and population dynamics provides essential insights for prioritizing conservation efforts. Despite the challenges presented by human activities and climate change, innovative solutions continue to emerge. Collaboration among various stakeholders—including researchers, policymakers, and local communities—can forge effective conservation pathways. Case studies illustrating successful conservation efforts demonstrate that when communities unite for a common cause, positive results can be achieved. Furthermore, education and advocacy play important roles in rallying support for arachnids, elevating their status within the conservation dialogue. As our understanding of arachnid diversity deepens, it becomes increasingly apparent that their survival is intertwined with the health of ecosystems globally. In this light, investing in arachnid conservation safeguards both these remarkable creatures and the invaluable ecosystem services they provide. By cultivating an appreciation for arachnids, we create a future where diverse arachnid taxa can not only survive but thrive in their natural environments.
The collective effort to conserve arachnids must involve integrating knowledge from various fields, including ecology, genetics, and social sciences. Collecting long-term data on arachnid populations and their habitats is crucial for monitoring changes and informing policy decisions. Moreover, fostering partnerships between conservation organizations and academic institutions enhances research capacity. Collaborative programs that engage underrepresented communities can create more inclusive conservation dialogues, addressing the need for equitable environmental stewardship. In addition, public outreach campaigns raise awareness and promote engagement in arachnid conservation activities. Initiatives that involve citizen science can mobilize individuals to participate actively in monitoring and protecting arachnid populations. By harnessing community resources and knowledge, localized conservation efforts can ensure that diverse arachnid taxa receive the attention they deserve. Ultimately, holistic approaches that embrace scientific insight while engaging communities provide the foundation for effective arachnid conservation. The dynamic interplay between environmental conservation and outreach efforts strengthens our commitment to preserving biodiversity. By addressing the various factors influencing arachnids’ survival, we can pave the way for a sustainable future where ecological stability remains intact.
Implementing long-term conservation plans for arachnids requires adequate funding and political support. Advocacy efforts aimed at influencing policy can initiate conversations regarding arachnid protection at various governance levels. Researchers can provide vital data to support proposals that frame the conservation of arachnids as essential for ecological resilience. Supporting local economies by promoting responsible eco-tourism centered around arachnids can also generate revenue to fund conservation initiatives. By highlighting the intrinsic value of arachnids within ecosystems, we can drive investment towards their protection. Moreover, collaborations between governments and non-profit organizations facilitate resource sharing and expertise exchange, maximizing the efficiency of conservation efforts. Engaging youth through education campaigns empowers the next generation to advocate for environmental issues. As we face global biodiversity crises, the role of arachnids in maintaining ecological harmony must be elevated. Addressing threats to their populations through a multi-faceted approach not only preserves these species but also ensures their continued contributions to ecosystems worldwide. By embracing a comprehensive strategy that includes education, policy advocacy, and community involvement, we can foster a sustainable future for diverse arachnid taxa.