Exploring the Tyrannosaurus Rex: King of the Dinosaurs
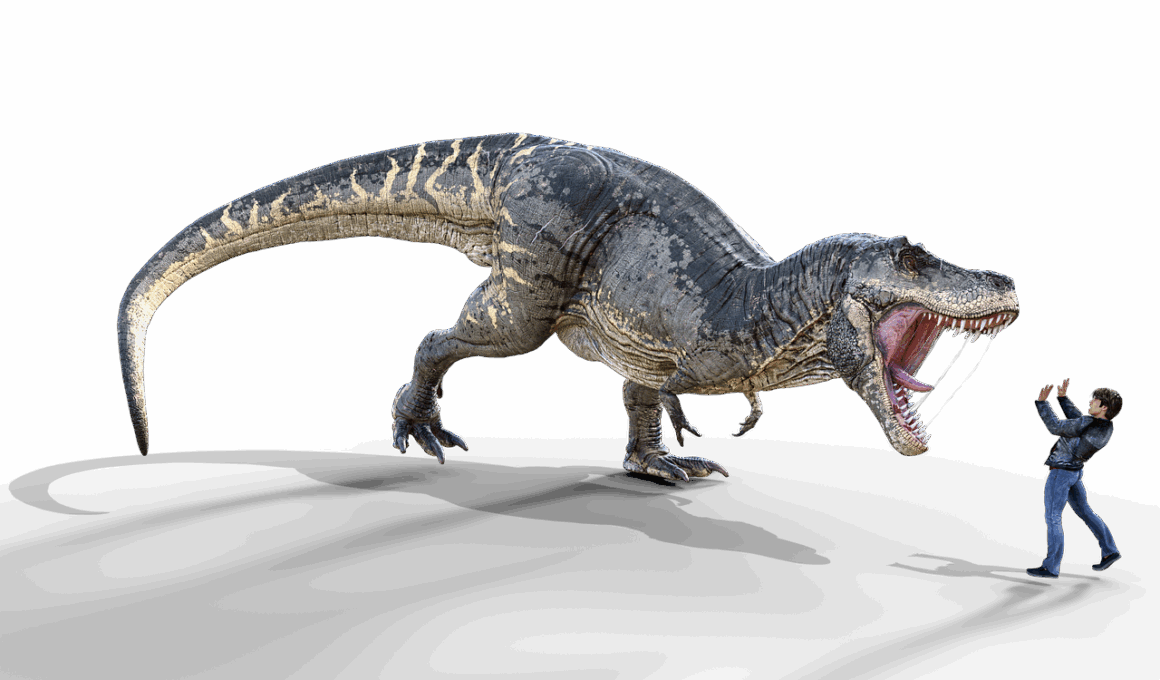
The Tyrannosaurus Rex, commonly known as T. rex, stands as one of the most iconic dinosaurs in history. This massive carnivore roamed the Earth during the late Cretaceous period, roughly 68 to 66 million years ago. Fossils of T. rex have been discovered predominantly in North America, providing significant insights into its life and environment. With an enormous skull measuring up to 5 feet long, it had powerful jaws that could crush bone with ease. The three-fingered forelimbs might seem small compared to its massive body, but they likely played vital roles. Many scientists speculate that the T. rex was a top predator, feasting on herbivorous dinosaurs of its time. To explore its hunting strategies, paleontologists study the structure of its bones and teeth. Through various findings, we know that T. rex had a keen sense of smell. These adaptations backed its predatory prowess, allowing it to thrive. Furthermore, the contemporary popular culture often features T. rex in films, literature, and art, solidifying its status as the quintessential dinosaur in the minds of both scientists and enthusiasts.
Physical Characteristics and Adaptations
The Tyrannosaurus Rex was a formidable creature, reaching lengths of up to 40 feet. Its body was not only long but also heavy, weighing around 9 tons on average. The large skull featured sharp teeth that could grow over 12 inches long, designed perfectly for tearing through flesh. This dinosaur possessed powerful hind limbs which allowed it to run swiftly, although estimates suggest it was not as fast as once believed. The long tail provided balance and stability while it maneuvered its massive body. Its keen eyesight allowed for effective hunting during the day, while the advanced olfactory senses could detect prey from miles away. The T. rex possessed a binocular vision, offering depth perception crucial for hunting. Furthermore, studies indicate that the skin of the T. rex was likely textured and covered in scales, similar to modern reptiles. This physical complexity showcases its adaptations to survive in a varied environment. Additionally, scientists believe that these adaptations evolved over millions of years, a testament to the incredible journey of evolution that gave rise to such an extraordinary predator.
The diet of the Tyrannosaurus Rex primarily consisted of herbivorous dinosaurs, making it a renowned carnivore. Evidence from fossilized remains suggests that T. rex was an opportunistic feeder, often scavenging when hunting proved challenging. With its powerful bite, it could consume virtually any prey it encountered, including smaller predators. The sheer size of its jaws allowed T. rex to exert tremendous pressure, enabling it to crunch through bones and access nutritious marrow. Research has also shown that T. rex engaged in cannibalistic behavior under conditions of scarcity. This adaptability underscores the dinosaur’s resilience in varying habitats. Moreover, tooth wear patterns provide essential clues about its feeding habits and diet efficiency. While some believe T. rex was mainly a predator, others argue it might have also functioned as a scavenger. This ongoing debate highlights the complexity of its ecological role. Additionally, its hunting tactics suggest a degree of intelligence that raises questions about its behavior. Through meticulous studies, paleontologists aim to unlock the mysterious lifestyle of the T. rex, further illustrating the intricate web of life during the Cretaceous period.
Social Behavior and Ecology
Paleontologists have debated the social behavior of the Tyrannosaurus Rex for years. Some suggest that T. rex may have exhibited solitary behavior, primarily living and hunting alone. Alternatively, recent discoveries propose a possible social structure among T. rex, indicating the potential for pack gatherings during breeding or juvenile rearing. Evidence from fossilized trackways suggests that multiple individuals traveled together at times. The environmental context of the late Cretaceous period plays a crucial role in understanding T. rex’s social interactions. In certain ecological niches, competition for food could necessitate closer familial ties. Additionally, their territorial instincts might have shaped their interactions with others. Understanding social dynamics among such large predators requires multidisciplinary approaches. Relationships with other species, such as prey and competitors, would influence hunting and reproductive strategies. Therefore, the T. rex’s ecological role isn’t just as a solitary monster; it’s part of a larger, interconnected ecosystem. Future studies and fossil discoveries continue to inform our ever-evolving understanding of the T. rex, helping to clarify its behavioral patterns and interactions with contemporary fauna.
Recent advancements in technology have dramatically influenced our perception of the Tyrannosaurus Rex. Modern imaging techniques, like high-resolution CT scanning, enable researchers to visualize internal structures of fossils without destructive methods. These innovations have opened avenues for new research on T. rex physiology and biomechanics. For instance, by examining the bone density and overall structure, scientists can gain insights into its growth patterns and possible metabolic rates. Genetic studies, albeit challenging, are also underway to understand the evolutionary ties between modern birds and their dinosaur ancestors. This tech-driven research spotlight reveals not only the physical aspects of T. rex but also potential behavioral traits. As a result, paleontology is entering a new era where ancient life can be analyzed with unprecedented detail. Moreover, public interest in dinosaurs continues to surge, leading to collaborative efforts between scientists and educational institutions to promote awareness. This interplay aims to inspire the next generation of paleontologists through exciting discoveries. As we delve deeper into the life of the T. rex, we recognize our growing fascination with dinosaurs, bridging science and popular culture in fascinating ways.
The Tyrannosaurus Rex in Popular Culture
The Tyrannosaurus Rex has transcended scientific inquiry to become a cultural icon. Its appearances in films, books, and educational materials have ignited public imagination for decades. The blockbuster film “Jurassic Park” played a pivotal role in cementing T. rex’s status as a symbol of raw power and ferocity. This portrayal, coupled with stunning visual effects, brought the dinosaur to life, captivating audiences worldwide. Furthermore, the depiction of T. rex in various media often stimulates interest in paleontology. Children and adults alike are inspired to learn more about dinosaurs, leading to increased enrollment in science programs. Museums often showcase T. rex fossils to attract visitors, creating an engaging experience for dinosaur enthusiasts. Additionally, the character’s representation varies, from terrifying predator to misunderstood creature, reflecting societal perceptions about nature. In literature, authors explore the complex relationship between humans and dinosaurs, raising ethical questions about extinction and conservation. Consequently, T. rex embodies both the awe of prehistoric life and prompts discussions around biodiversity. Its lasting impact on culture demonstrates how science and storytelling can intertwine, shaping our understanding and appreciation of ancient history.
Conservation of wildlife today echoes the lessons learned from the extinction of dinosaurs like the T. rex. The phenomenon of mass extinction serves as a cautionary tale about the fragility of ecosystems. As T. rex disappeared from Earth approximately 66 million years ago, various factors contributed, including climate change, volcanic activity, and asteroid impacts. Understanding these events is critical in today’s context, as biodiversity continues to dwindle due to human activities. The need for conservation efforts has never been more urgent, paralleling ancient events with modern-day challenges. By studying the T. rex and its environment, we can better appreciate the interdependencies of life forms. This newfound knowledge equips us with tools to promote sustainability and ecological responsibility. Scientific endeavors in paleontology inspire conservationists to engage communities actively. People are encouraged to appreciate our planet’s diverse species, ensuring their survival. Thus, the history of the T. rex holds valuable lessons for contemporary society. By reflecting on the past, we can forge a path toward a healthier planet. Exploring T. rex’s legacy, we reinforce the importance of preserving life for future generations, making it a crucial endeavor.
Conclusion: The Legacy of Tyrannosaurus Rex
The legacy of the Tyrannosaurus Rex is profound, influencing both science and popular culture. As a fascinating subject of research, it offers glimpses into the Earth’s distant past, highlighting evolutionary processes. The continuous exploration of T. rex reveals valuable lessons about adaptation and survival. Ongoing scientific discoveries from fossil finds integrate advanced technologies with traditional paleontological practices. This amalgamation of methods enhances our understanding of T. rex and the dynamics of prehistoric ecosystems. Additionally, the cultural resonance of T. rex showcases its enduring appeal. It highlights our fascination with ancient giants and serves as a bridge connecting us to our evolutionary origins. Through the arts and media, T. rex has become a metaphor for strength, power, and the unknown. This portrayal encourages conversations around extinction, preservation, and coexistence with nature. The intersection of science and culture surrounding T. rex invites individuals to explore broader themes of life and its myriad forms. The story of Tyrannosaurus Rex is not merely a recounting of past events but an ongoing dialogue about life on Earth. Its enthralling history will inspire generations of scientists and enthusiasts alike.