The Lifecycle of Arachnid Pests and Effective Control Methods
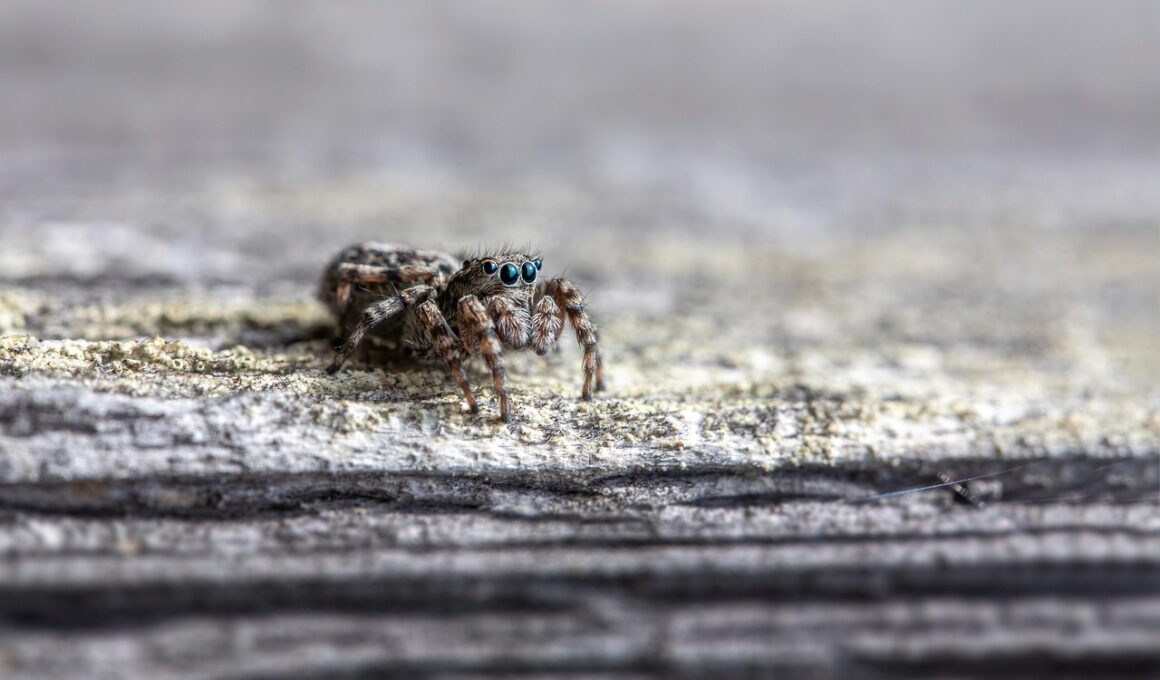
Arachnids are a diverse group of arthropods that include spiders, scorpions, ticks, and mites. Understanding their lifecycle is crucial for effective pest control. Arachnids generally undergo several stages: egg, immature, and adult. They initiate their lifecycle by laying eggs in protected areas, ensuring the survival of the next generation. The eggs hatch into larvae, where they may not resemble adults. These immatures will molt multiple times before reaching adulthood, gaining size and features characteristic of their species. Each stage is vulnerable to specific environmental threats. Consequently, identifying these stages aids in implementing targeted control measures. Approaches can vary depending on whether you deal with spiders, scorpions, or ticks. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) incorporates monitoring and environmentally sensitive solutions, promoting the least hazardous methods first. Natural predators can also provide a measure of control. Chemical controls, when necessary, should be selected carefully to minimize collateral damage to beneficial organisms. In conclusion, understanding the lifecycle of arachnids allows for more informed pest management decisions, leading to effective control while balancing ecological concerns.
Effective pest control begins with an understanding of the population dynamics of arachnids. Arachnids are often found in diverse habitats, including gardens, forests, and human dwellings. Identifying their specific habitats can help in predicting their activity and potential invasions. For example, certain spider species thrive in moist environments, while scorpions prefer arid conditions. When managing arachnid populations, it’s essential to regularly inspect these environments for signs of infestation. Regular monitoring allows you to spot increases in their numbers early on, leading to more effective responses. Non-chemical methods such as sealing cracks, using barriers, or removing clutter can significantly reduce arachnid presence without harming the environment. If chemical treatments become necessary, they must be applied judiciously and selectively. Research options for less toxic substances that target specific pests while preserving beneficial species. Additionally, creating an ecological balance can reduce pest populations naturally. For instance, fostering birds and other natural predators can help control arachnid numbers. Educating yourself and your community about the biology of these pests empowers effective management strategies.
Common Arachnid Pests
The most common arachnid pests include spiders, ticks, and scorpions. Each poses different health risks and requires unique control strategies. Spiders, though generally harmless, can cause fear and anxiety in some individuals. Identifying spider species is vital for understanding their behavior and control. For instance, a wolf spider may control insect populations, while a dangerous black widow requires immediate attention. Ticks, on the other hand, pose significant health risks as they transmit diseases like Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Prompt removal of ticks from the skin is essential to reduce the risk of transmission. Scorpions are often feared for their sting, which can cause serious reactions in sensitive individuals. Effective management of scorpions involves habitat modification to make areas less appealing. Removal of debris and landscaping can help lessen scorpion encounters. Each pest requires specific preventive measures, including regular inspections. Furthermore, education on the behavior of these pests can assist in alleviating concerns regarding their presence. In summary, understanding common arachnid pests helps formulate effective control strategies.
Habitat modification plays a crucial role in controlling arachnid pest populations. By altering the environment, you can make it less conducive for them to thrive. For spiders and scorpions, removing clutter around the home and yard can significantly reduce the spaces they inhabit. This includes eliminating webs and debris, as well as trimming back overgrown vegetation. For ticks, managing grass and leaf litter around properties is particularly important. Regular lawn maintenance can deter tick populations from establishing. Ensuring proper drainage in areas prone to water accumulation helps mitigate moisture, an attractive factor for many arachnids. Additionally, using landscaping to your advantage can offer natural barriers. Certain plants may repel arachnids while attracting insects that serve as natural pest control. Implementing these strategies may take time, but the long-term benefits are substantial. A well-maintained environment reduces the likelihood of infestations, which is more effective than reactive measures. Moreover, such practices enhance the overall aesthetics of your outdoor spaces. Educational outreach and community initiatives foster collective effort towards these modifications, underscoring the importance of a unified approach in arachnid pest management.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Techniques
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) combines various management strategies to ensure effective control of arachnid pests. This approach is holistic, taking into consideration ecological balance and pest biology. IPM starts with thorough monitoring to identify pest populations and inform decisions. By understanding when arachnid populations increase, pest control efforts can be timed for maximum effectiveness. Additionally, utilizing non-chemical methods forms the foundation of IPM. Habitat modification, biological controls, and cultural practices can be prioritized to minimize chemical usage. When necessary, targeted chemical treatments can be employed as a last resort. Education plays a key role in IPM, equipping individuals and communities to understand the importance of each component. Collaboration among homeowners, pest professionals, and local authorities enhances results and fosters sustainable practices. Moreover, raising awareness about the potential benefits of a balanced ecosystem can enrich community engagement in pest management. Ultimately, IPM aims to reduce pest populations while safeguarding human health and the environment. This comprehensive approach means that despite the challenges posed by arachnids, effective control remains achievable through informed decision-making.
Preventative measures are crucial in maintaining control over arachnid populations. Awareness of risks associated with arachnids plays a significant role in community safety. For instance, understanding how ticks latch onto hosts can guide individuals in taking precautions during outdoor activities. Wearing protective clothing and applying repellents can help deter tick bites during hikes or picnics. Furthermore, educational programs about identifying local spider species can diminish unnecessary fears and promote coexistence. Emphasizing that most spiders help regulate pest insects is essential in shifting public perception. Utilizing resources, such as informative websites and community workshops, can help disseminate knowledge about effective preventative strategies. For outdoor enthusiasts and gardeners, using barriers like mulch around plants can reduce tick habitats effectively. Encouraging community collaboration in monitoring arachnid presence also strengthens preventative efforts. Neighborhood watch programs can share information on spider or tick sightings, promoting collective understanding. In conclusion, preventative measures are paramount for maintaining low arachnid populations. Emphasizing awareness and community engagement can significantly impact pest management success.
Conclusion
Understanding the lifecycle of arachnid pests enables better approaches to their management. By knowing how arachnids reproduce and develop, targeted control methods can be implemented effectively. Through habitat modification, IPM strategies, and preventative measures, communities can work toward minimizing the impact of arachnids on health and safety. Education plays a pivotal role in transforming fear into understanding, further supporting effective controls. Familial and community involvement fosters collaborative strategies that ensure a comprehensive approach. In this way, arachnid pest management is no longer solely reactive but anticipatory, reducing infestations before they escalate. Encouraging ongoing awareness helps ensure that environments remain both functional and eco-friendly. Moreover, integrating pest management fosters sustainable practices, allowing for balanced ecosystems. Finally, less reliance on harsh chemicals in favor of eco-friendly techniques contributes positively to public health and environment. In conclusion, by combining knowledge about arachnid lifecycles with effective control measures, it is possible to maintain a harmonious relationship with these vital creatures.
By understanding the lifecycle of arachnids, we foster effective management strategies. Regular inspections and timely responses form the cornerstone of successful control. Exploring natural solutions should always be prioritized, thereby minimizing impacts on non-target species. Utilizing biological controls and encouraging natural predators create a balanced approach. Moreover, educating the community about risks associated with arachnids enhances proactive measures. The implementation of habitat modifications ensures reduced populations, showcasing the impact of preventive actions. Additionally, exploring various non-chemical treatments renders significant benefits for those concerned with toxicity. Through research and adaptation, new methods continue to emerge, complementing existing strategies. Ultimately, applying knowledge and awareness will empower communities to coexist harmoniously with arachnids. By integrating pest management practices, we create safer environments, paving the way for healthy ecosystems. Transitioning from reactive to proactive management approaches leads to positive outcomes. Communities committed to responsible pest management recognize the importance of education and collaboration. Thus, a united effort guarantees success in tackling arachnid pests effectively.