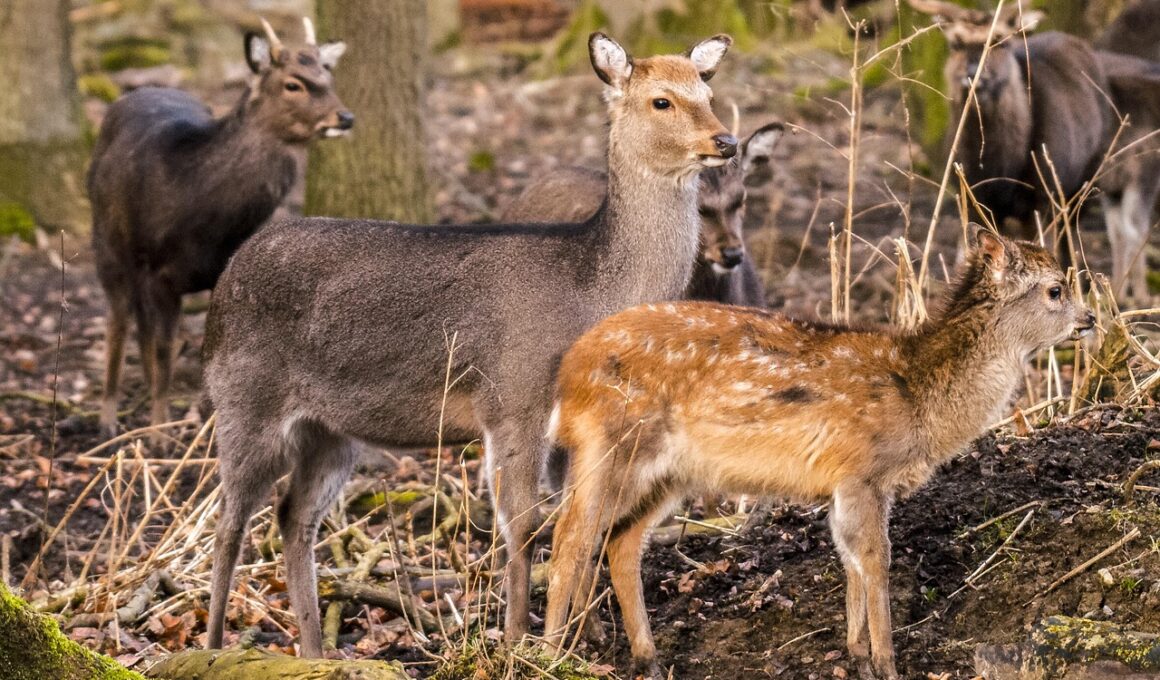
Long-term Studies on Ungulate Population Trends
Ungulate population dynamics are critical for understanding ecosystems and wildlife management. Long-term studies allow researchers to track changes over time, providing insights into species health and ecosystem balance. Such research often focuses on how environmental changes affect population numbers and behaviors. By analyzing historical data, scientists can discern patterns and predict future trends in ungulate populations. This can help in planning conservation efforts and managing hunting activities more sustainably. Key parameters measured include birth rates, death rates, and migration patterns. Moreover, issues like habitat loss, climate change, and disease outbreaks significantly impact these dynamics. Utilization of technology in monitoring, such as GPS collars or remote sensing, has revolutionized data collection. These methods provide real-time insights that were not possible earlier. The results then contribute to models that help wildlife managers make informed decisions. Engaging stakeholders is crucial, as local communities often hold valuable knowledge about species behavior. Thus, integrating scientific and traditional knowledge can lead to more effective management strategies for ungulate populations in diverse environments.
Factors Influencing Ungulate Populations
Understanding what influences ungulate populations is vital for effective management and conservation. Various factors, including predation, food availability, and habitat quality, have direct effects on population dynamics. Predation is one of the most significant factors, affecting young and vulnerable ungulates. Natural predators such as wolves and humans often regulate ungulate numbers through hunting and predation pressures. Additionally, availability of quality forage impacts health and reproduction rates among ungulates. Poor food sources can lead to malnutrition, ultimately affecting population sustainability over time. Furthermore, habitat loss due to urbanization and logging reduces living spaces for these animals. Climate change also poses a growing threat, altering migration patterns and seasonal behaviors. As temperatures rise, ungulates might have to shift their ranges to find suitable climates. This results in interactions with human infrastructures and other species, complicating conservation efforts. Understanding these interrelated factors is essential for developing adaptive management strategies. Research studies emphasize tracking long-term trends in population health. Collaboration among researchers, local governments, and conservation organizations can enhance ungulate management efforts and ensure ecological balance.
One critical aspect of ungulate population dynamics is their social structure and behavior. Many ungulate species exhibit complex social hierarchies, impacting their reproductive success and survival rates. For instance, species like deer often form herds that provide protection from predators and environmental stresses. Family groups can share knowledge about foraging areas and avoid dangers, thus increasing their chances of survival. On the contrary, lone individuals might struggle to find adequate food sources or face higher predation risks. Seasonal migrations also play a crucial role in population dynamics, where ungulates move to follow food availability and suitable climates. Migration routes can lead to conflicts with human activities or barriers, such as roads. Furthermore, breeding behaviors often adapt according to population density and environmental cues. When population numbers rise beyond the carrying capacity of their habitat, reproductive rates tend to decrease as competition for resources intensifies. Effective population monitoring must consider social behaviors and seasonal changes in dynamics, as these factors significantly influence long-term survival. By applying comprehensive research methodologies, managers can ensure the stability and growth of ungulate populations.
The Role of Habitat Conservation
Habitat conservation is paramount for supporting stable ungulate populations and ensuring their long-term survival. The natural habitats of ungulates serve as crucial components of the ecosystems they inhabit. When these habitats undergo fragmentation or degradation, it results in decreased food resources and breeding grounds. Conservation strategies must prioritize preserving essential habitats. This includes implementing protected areas and wildlife corridors that facilitate migration and movement between populations. Such efforts help maintain genetic diversity, which is critical for adaptability in changing environments. Additionally, managing human activities near these habitats is vital. This can involve regulating land use and promoting sustainable practices in agriculture and forestry. Restoration projects can also revitalize degraded areas, making them suitable for ungulate habitation again. Engaging local communities is crucial; they play a significant role in habitat stewardship and conservation initiatives. Education programs about the ecological importance of ungulates can foster appreciation and support. Effective habitat conservation can lead to increases in ungulate populations. By maintaining healthy ecosystems, we ensure not only the survival of ungulates but overall biodiversity.
Climate change significantly impacts ungulate populations, causing shifts in distribution and abundance. Altered weather patterns can affect food availability, reproductive cycles, and migration timings. For instance, many ungulates depend on seasonal forage; climate-induced changes can lead to mismatches between food availability and life cycle events. Additionally, extreme weather events can result in habitat destruction and increased mortality rates for vulnerable species. Research indicates that rising temperatures may force ungulates to seek cooler areas, leading to habitat compression. This results in increased competition for resources among the species, potentially disrupting social structures. Furthermore, climate change can also exacerbate existing threats, such as disease outbreaks. Changes in ecosystems can alter pathogen dynamics, making populations more susceptible to illness. Thus, studying these relationships is crucial for developing adaptive management approaches. Monitoring the impacts of climate change on ungulate populations can inform conservation strategies. It allows wildlife managers to create more resilient populations. Initiatives such as habitat monitoring and species tracking contribute significantly to understanding these dynamics. Ultimately, integrating climate considerations into ungulate management is increasingly necessary for ensuring species persistence.
Importance of Research Collaboration
Collaboration among researchers, conservationists, and local communities is paramount in ungulate population studies. Such partnerships enhance the understanding of population dynamics and promote effective management strategies. By combining expertise from various fields, it’s possible to develop comprehensive approaches to address the complexities of ungulate populations. Interdisciplinary teams can incorporate biological data with socio-economic factors, thus achieving more effective conservation outcomes. Furthermore, engaging local communities ensures that traditional ecological knowledge complements scientific research. This can result in better-targeted management plans that resonate with community values. Community-based monitoring programs empower individuals to participate actively in the conservation efforts, leading to sustainable practices. Capacity building within local populations increases awareness about the importance of ungulate species and their habitats. Researchers must also share findings with stakeholders to inform policy decisions and foster adaptive management. Disseminating research contributes to a greater understanding of conservation challenges. Moreover, collaboration can lead to increased funding opportunities for joint projects. By creating networks among various stakeholders, research initiatives can have a more significant impact on ungulate populations, leading to improved conservation practices.
Long-term studies on ungulate populations are essential for effective wildlife management and conservation. These studies offer valuable insights into population trends, which can help anticipate challenges posed by environmental changes. Identifying population declines early can facilitate timely interventions, ensuring the survival of at-risk species. Additionally, rigorous data collection methods increase the reliability of research outcomes. Analytical models derived from long-term datasets allow for predictions regarding future population dynamics. Managers can use this information to schedule hunting seasons or make regulations regarding land-use practices. Integrating adaptive management strategies allows for adjustments based on ongoing research findings. Moreover, public awareness and understanding of ungulate dynamics can lead to supportive policies. Educating the public about the importance of these animals fosters community involvement in conservation efforts. It also galvanizes public support for necessary funding. Consequently, sustainable practices can be adopted within local communities, benefiting both ungulates and people. By prioritizing comprehensive, long-term research on ungulate populations, we ensure improved management strategies and the resilience of ecosystems. Long-term monitoring ultimately confirms the significance of collaboration, science, and community engagement in conservation efforts.