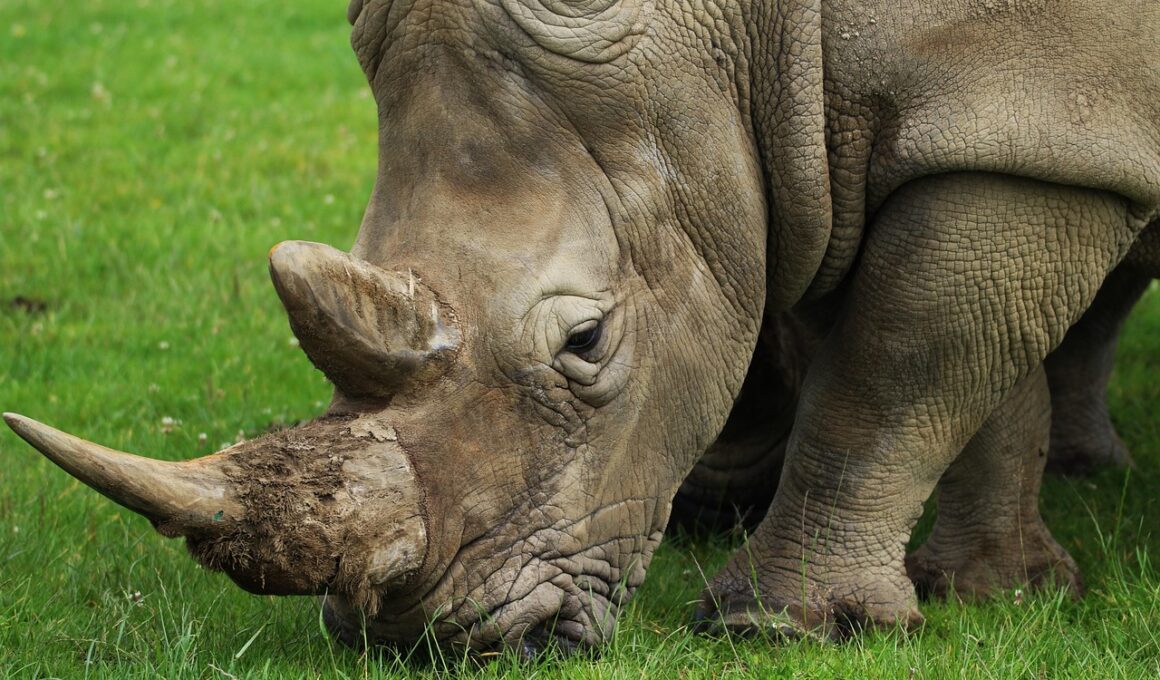
The Impact of Poaching on Endangered Species
Poaching and illegal trade represent some of the most significant threats to endangered species worldwide. Various animals, including elephants, rhinos, and tigers, are being targeted for their body parts like ivory and horns. The methodical hunt for these animals severely impacts their populations, with often dire consequences for ecosystem balance. Poaching results in significant population declines, pushing several species closer to extinction. Beyond individual species, entire ecosystems suffer. As apex predators and keystone species disappear, the delicate interplay between numerous organisms falters, fundamentally altering habitats. The repercussions of these declining populations extend beyond animals; entire communities reliant on healthy ecosystems often face economic hardships as wildlife tourism dwindles. Additionally, the illegal trade of these animals promotes organized crime and corruption, further destabilizing regions. Governments and conservation organizations are taking steps to combat this crisis through various strategies, including increased patrolling, stricter laws, and international collaboration. Public awareness campaigns aiming to educate people about the importance of these species are also crucial. Protecting endangered species requires global attention and action to preserve biodiversity for future generations.
Economic Consequences of Poaching
The economic ramifications of poaching are multifaceted and severe. Countries that lose their wildlife to poaching and illegal trade often face declining tourism revenues. Wildlife tourism is a substantial financial segment for many nations, supporting jobs and local economies. When iconic species, such as elephants, are poached, the draw for tourists diminishes, leading to economic instability. Moreover, local communities that benefit from conservation efforts may experience significant loss. Residents who engage in eco-tourism, wildlife photography, and other conservation-linked activities find themselves at a disadvantage when poaching results decline. The illegal trade of wildlife also siphons resources from legitimate economies. Criminal networks involved in poaching often funnel profits into illicit activities that harm communities. Conversely, investments in wildlife conservation can provide sustainable economic benefits. Conservation initiatives can improve local livelihoods, offering alternative income sources. Educating communities about the value of preserving wildlife for future generations is vital. Programs that combine conservation with community development foster a sense of stewardship, encouraging locals to protect endangered species instead of participating in poaching. Economic incentives align conservation objectives with community priorities for a sustainable future.
One major impediment to combating poaching is the persistence of demand for wildlife products. In many regions, cultural beliefs and traditional practices contribute to the demand for items such as tiger bones, rhino horns, and elephant tusks. These beliefs often arise from misconceptions about their medicinal properties or perceived social status linked to ownership. Addressing this demand involves comprehensive education and cultural engagement strategies. Informing consumers about the impact of their purchases can foster change. Campaigns aimed at reducing demand for illegal wildlife products have shown effectiveness in various contexts. They focus on creating awareness about the plight of endangered species and promoting alternatives. Collaboration with local leaders and influencers can shift perceptions, leading to changes in cultural practices that support conservation efforts. Additionally, international cooperation is crucial for dismantling trafficking networks that exploit wildlife. Efforts to implement stricter regulations regarding wildlife trade, alongside penalties for offenders, can help curb poaching. Global partnerships unite governments, NGOs, and communities in a shared goal of protecting wildlife. By reducing demand for poached products, the driving force behind illegal trade can be diminished, allowing endangered species to recover.
In addition to economic effects, poaching poses significant ecological threats. The loss of species disrupts food chains and biodiversity. For example, when herbivores are depleted, plant life suffers, affecting entire ecosystems reliant on these species for balance. Apex predators, like lions and tigers, control prey populations. When they are removed through poaching, overpopulation can ensue, leading to habitat degradation and diminished biodiversity. Ecosystems depend on every species having its role, creating complex interdependencies. The extinction of a single species impacts not just fellow species but entire ecosystems. This alteration can have long-term, irreversible impacts on the environment. Biodiversity loss may also impact human communities, as ecosystems provide vital services such as clean water and fertile land. Furthermore, invasive species may thrive in altered habitats, leading to further challenges as they outcompete native species. Restoration of these systems is complex and often involves considerable resources. To combat this crisis, preserving habitats and protecting diverse species is essential. Conservation strategies should focus on safeguarding entire ecosystems, not just single species, ensuring sustainable coexistence with humans.
Combating the poaching crisis requires a comprehensive approach that includes innovation in enforcement tactics. Technology plays a pivotal role in modern conservation efforts. Drones, camera traps, and satellite imaging are cutting-edge tools used to monitor wildlife and poacher movements in real time. These technologies enhance surveillance capabilities, allowing rangers to cover extensive areas efficiently. Advanced tracking methods enable detection of poaching hotspots, focusing resources where they are most needed, thereby maximizing the impact of conservation efforts. Data analytics can provide invaluable insights, predicting trends in poaching activities and assisting in resource allocation. Educating local communities on these technologies fosters collaboration, empowering residents to take part in conservation efforts actively. Moreover, the integration of technology provides a robust deterrent to would-be poachers. Equip local law enforcement agencies with these innovative tools enhances their ability to combat illegal activities effectively. The implementation of such strategies should focus on accessibility, ensuring that local stakeholders can utilize technology. By embracing modern approaches, the fight against poaching can advance, offering hope for endangered species at risk of extinction.
International cooperation is a cornerstone of effective wildlife conservation. Poaching and the illegal wildlife trade cross national boundaries, necessitating a coordinated global response. Countries must collaborate to strengthen laws, share intelligence, and implement joint enforcement strategies. Treaties such as the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES) play a vital role in regulating and monitoring international trade in wildlife. These agreements establish guidelines that countries must adhere to ensure the protection of endangered species. However, enforcement of these laws remains challenging, particularly in regions with weak governance. Strengthening legal frameworks and investing in local law enforcement are crucial. International partnerships can provide the necessary resources and training to improve local capacities. Public awareness initiatives foster a global community committed to wildlife protection. Educating the public about the implications of poaching creates a sense of global responsibility. Additionally, cultivating strong relationships among governments, NGOs, and communities is essential. Through fostering collaboration, countries can address the root causes of poaching and illegal trade, working towards comprehensive solutions aimed at conserving biodiversity.
To ensure a sustainable future for endangered species, proactive conservation methods are essential. Strategies like habitat restoration, community engagement, and viable conservation funding are critical. Habitat restoration involves rehabilitating degraded ecosystems, providing wildlife with safe spaces to thrive. Community engagement encourages local populations to actively participate in conservation efforts. Offering economic incentives for wildlife protection fosters a culture that values biodiversity. Viable funding models are necessary to support ongoing conservation initiatives. Developing partnerships with private sectors, governments, and NGOs can provide the needed resources for these efforts. Additionally, education and awareness can transform societal attitudes toward wildlife. Engaging youth through educational programs inspires the next generation of conservationists. These programs highlight the importance of preserving endangered species, encouraging stewardship. Innovations in conservation financing, such as ecotourism, can create sustainable income sources for communities while promoting wildlife protection. Ultimately, a dedicated, multidisciplinary approach is crucial to tackle poaching effectively. Collective efforts from individuals, communities, governments, and international organizations are essential. By working together, we can protect endangered species and create an environment where both wildlife and human populations coexist sustainably.
The effect of poaching, emphasized through research and on-the-ground experience, reveals critical insights into a crisis needing dedicated action. Reducing poaching requires an understanding of the social, economic, and environmental factors that fuel these activities. Sustainable interventions must focus not just on protecting individual species but also on ensuring that entire ecosystems remain intact. The challenge lies not only in developing effective laws but also in enforcing them through robust systems. As the interconnectedness between humans and wildlife grows, appreciating our role in conservation is essential. In addition, collaborative efforts across borders significantly enhance conservation potential. Global awareness and local action can drive real change, as communities become central to conservation efforts. Educating the public about the interconnectedness of ecosystems can foster deeper appreciation for wildlife. Furthermore, cultural shifts supporting wildlife conservation render real successes. These changes often evolve slowly but can lead to transformative outcomes. Protecting endangered species must be a shared responsibility among all people. Through such collective dedication and global cooperation, we can forge a path towards a future that honors wildlife, ensuring its thriving for generations to come.