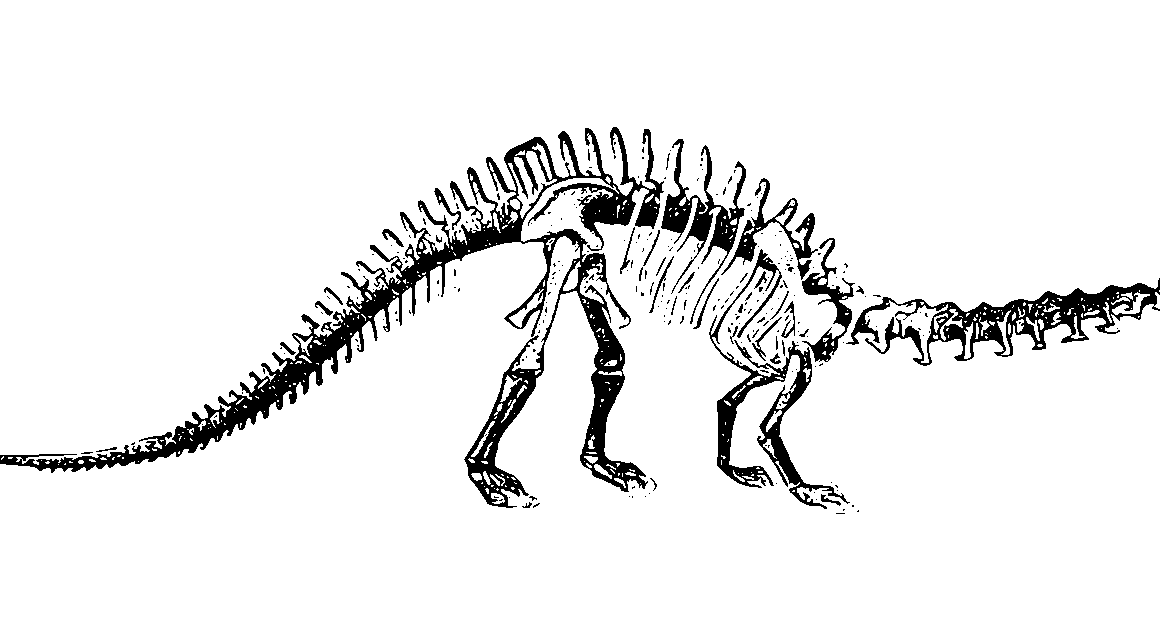
Uncovering the Diversity of Prehistoric Reptiles through Fossils
Fossils serve as vital records of the past, revealing the intricate diversity of prehistoric reptiles that roamed the Earth millions of years ago. Each fossil, from the tiniest fragment to the most complete skeleton, provides insight into the evolutionary pathways these creatures took. The significance of reptile fossils cannot be overstated, as they contribute to our understanding of ancient ecosystems and climatic conditions. Reptilian fossils are typically discovered in sedimentary rock formations, which preserve the organic material over epochs. Researchers meticulously excavate these sites to uncover not just the bones, but also traces of their behavior and habitats. Remarkably, some fossils are so well-preserved that they offer molecular evidence, allowing scientists to study genetic relationships among species. The study of these fossils implicates various factors such as geography, climate, and extinction events in shaping their evolution. Through ongoing advancements in paleontology, new methodologies are constantly developing, enhancing our ability to analyze fossilized remains. Ultimately, these discoveries inform our understanding of biodiversity and the ecological roles reptiles played in their respective environments during the Mesozoic era and beyond.
One of the remarkable aspects of reptile fossils is the vast range of species they represent. Fossils can be categorized into several groups, each illustrating unique adaptive strategies. Among these groups, dinosaurs dominated the era, showcasing immense diversity. Other significant reptilian groups include marine reptiles, such as various plesiosaurs and ichthyosaurs that thrived in ancient oceans. Additionally, there were flying reptiles known as pterosaurs, which possessed adaptations allowing them to soar through the skies. Furthermore, tortoises and crocodilians share lineages that date back to the age of dinosaurs, giving insight into the evolutionary development of these groups. Fossils also depict reptiles with striking features, such as the armored ankylosaurs and the fierce theropods. The variations in size, shape, and morphology are telling of life in prehistoric environments, where predation and survival strategies were crucial for success. These adaptations offer clues about the climate, vegetation, and even the interspecies relationships of the time. As new fossils are unearthed, the catalog of known reptilian diversity continues to expand, enriching our understanding of evolution across geologic time scales.
Significance of Fossils in Reptilian Evolution
The study of reptile fossils plays a crucial role in deciphering the evolutionary history of these remarkable creatures. By analyzing the fossilized remains, paleontologists can reconstruct not only the physical traits of reptiles but also their behavioral patterns and ecological roles. The transition from land-dwelling dinosaurs to the modern reptiles we see today is a fascinating journey shaped by environmental pressures and adaptations. Fossils help illustrate these transitions, showcasing gradual changes in morphology and size over time. For instance, the evolution of birds from theropod dinosaurs was revealed through numerous fossil findings, highlighting the shared characteristics. Additionally, fossils provide critical data on extinction events, revealing how some species vanished while others survived. Mass extinction events and climatic shifts drastically impacted reptilian diversity, showcasing how resilient certain lineages were. As fossils continue to be discovered, newer species are classified, allowing a reevaluation of historical timelines. Furthermore, advanced imaging techniques now enable scientists to study the internal structures of fossils, yielding further details about physiology and growth. This growing understanding helps frame reptiles within the broader scope of Earth’s biological history.
The field of paleontology has drastically evolved, with new technologies significantly aiding fossil discoveries and analyses. For example, the advent of 3D scanning and digital modeling enhances the way researchers visualize and study fossil structures without causing damage. These technologies facilitate detailed examinations of intricate features, such as teeth, bones, and even skin imprints, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of reptilian physiology. Moreover, isotopic analysis provides insights into the diets and habitats of various reptiles, often revealing subtle shifts in their lifestyles over time. As techniques improve, researchers can also delve into behavioral studies using fossil evidence to infer social interactions and nesting habits. This fusion of technology with traditional paleontological methods fosters innovative approaches in understanding ecosystems of the past and the contributions of reptiles to them. Fossil discoveries are reported occasionally, generating excitement and reassessing existing theories about reptilian evolution. Social media plays an important role in disseminating these findings rapidly, connecting communities interested in paleontology. It encourages collaboration among scientists, enthusiasts, and institutions, further enriching this dynamic field of study.
Discovering Fossil Localities
Fossil localities worldwide present unparalleled opportunities for studying prehistoric reptiles. These sites often vary in age, preservation quality, and fossil abundance, making unique contributions to our understanding. Some notable fossil hotspots include the Hell Creek Formation in Montana, which has yielded countless dinosaur fossils, including those of incredible theropods like Tyrannosaurus rex. Similarly, the Solnhofen Limestone in Germany is famed for exceptional specimens of pterosaurs and early bird-like dinosaurs, known for their stunning preservation. Additional well-known localities include the La Brea Tar Pits in California, where numerous reptiles were trapped in asphalt, resulting in perfectly preserved remains offering extensive paleoecological insights. Fossil-rich areas also exist in China, providing evidence of significant transitional forms that support evolutionary theories. Surveying these localities requires careful planning and permits, considering legal and ethical aspects of excavation. Researchers often collaborate with local institutions to ensure responsible study and conservation of these invaluable sites. As new fossil-rich regions are discovered, the quest to uncover the mysteries surrounding prehistoric reptiles continues, inviting questions about their life histories and eventual fates in the grand tapestry of evolutionary history.
Additionally, the examination of paleobiogeography sheds light on how prehistoric reptiles spread across different regions. Fossil evidence highlights unique adaptations that arose in various environments, influencing evolutionary trajectories. Certain reptiles demonstrate remarkable geographic isolation, leading to endemic species that evolved in response to localized conditions. For example, the discovery of marine reptile fossils in non-marine settings suggests complex migration patterns and habitat shifts. Analyzing these patterns assists researchers in understanding climate impacts on reptilian distribution and diversification. Moreover, plate tectonics played a significant role, facilitating land connections or separations, affecting the biodiversity witnessed today. The explorations of former continents that have since drifted apart continue to reveal insights about ancient ecosystems where reptiles thrived. Importantly, combining fossil data with geological changes creates a fuller picture of the ecological dynamics at play during periods of reptilian dominance. This multidisciplinary approach enhances the narrative of reptilian evolution, linking geological events with biological outcomes. As research progresses, the reptile fossil record gains depth, highlighting intricate histories interwoven through millions of years of Earth’s evolving landscape.
Challenges in Reptile Fossil Research
Despite significant advancements in paleontological methods, challenges remain when studying reptile fossils. Environmental factors, such as erosion and weathering, can hamper discoveries and threaten fossil integrity. Many geological formations are inaccessible, complicating excavation efforts for researchers. Furthermore, political and social issues in certain regions might restrict access to vital fossil sites, complicating global collaboration. Ethical practices must also be maintained, balancing the interests of scientific inquiry with the preservation of cultural heritage sites. There is an increasing demand for training young paleontologists who can carry forward research in a responsible and informed manner. Additionally, funding limitations often hinder fieldwork and laboratory analyses crucial for advancing knowledge. Collaborative research efforts can sometimes bridge these gaps, pooling resources to maximize discoveries. Yet, the ongoing preservation of fossil sites remains paramount to ensure future generations have access to these valuable resources. As technology improves, geolocalization and analysis can streamline the identification of both known and unknown fossil sites, presenting more opportunities for research. Thus, overcoming these challenges is essential for progressing our understanding of prehistoric reptiles through fossil evidence, ensuring that the wealth of knowledge is not lost to time.
In conclusion, the study of reptile fossils continues to unveil amazing discoveries that shape our understanding of the evolutionary history and diversity of reptiles. Every fossil, with its unique features and contexts, contributes to our knowledge about how these ancient creatures adapted over time. Insights gained from fossils reveal not just diverse species, but also ecological dynamics, behaviors, and responses to environmental changes. Further research thrives on technological advancements, collaborative efforts, and a deep commitment to preserve fossil sites and data. The ongoing exploration of fossil-rich areas worldwide promises new revelations and the potential to reassess long-held theories. Moreover, awareness and appreciation for the delicate balance of Earth’s ecosystems is essential as we reflect on the histories told through reptile fossils. This knowledge aids science and informs conservation efforts for modern reptiles still inhabiting our world. As we move forward, the integration of various disciplines will continue to enhance the study of ancient life forms, guiding the next generation of scientists. Future fossil discoveries may lead to profound implications on how we understand life on Earth, making the quest to uncover the richness of prehistoric reptiles even more intriguing and vital.