Ant Conservation Efforts: Protecting Essential Insect Populations
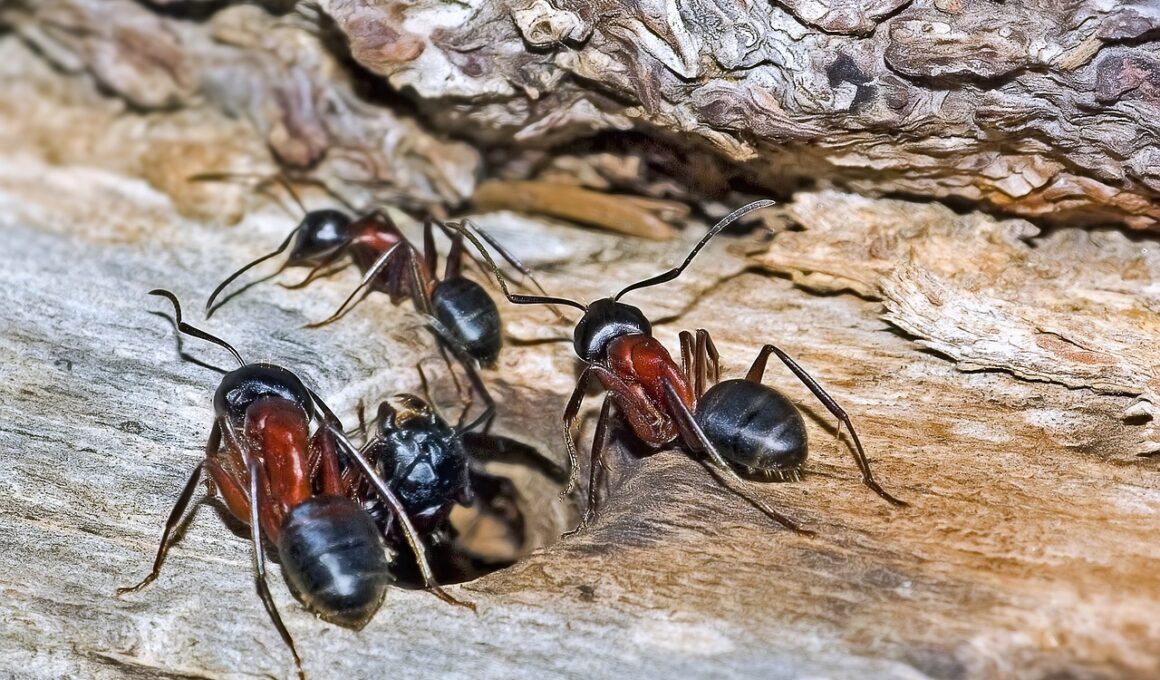
Ants play a crucial role in our ecosystems by aiding in soil aeration, nutrient cycling, and seed dispersal. Unfortunately, urbanization, agricultural practices, and climate change threaten ant populations significantly. Conservation efforts for ants are increasingly necessary to maintain biodiversity and ecological balance. Strategies include habitat restoration, creating ant-friendly environments, and public education campaigns. These measures are essential not only for ant survival but also for overall ecosystem health. Implementing these strategies requires collaboration between scientists, conservationists, and local communities. Involving residents in ant observation projects can foster a greater appreciation of these small but mighty creatures. Teaching the importance of ants affects their well-being, leading to more public interest in supporting ant conservation initiatives. Furthermore, promoting the use of native plants in gardens and parks can create ideal habitats for various ant species. Collaborating with local governments to incorporate these plants into urban planning can yield significant results. Public awareness can effectively fortify the efforts of ant conservationists. By emphasizing the relationships between ants and various natural processes, communities can gain a deeper understanding of their role in environmental stewardship.
Many ant species enrich soil quality through their tunneling activities, allowing air and water to penetrate deeper layers. The mobility of ants also contributes to the spread of various plant species, which benefits whole ecosystems. Ants impact the food web significantly, serving as prey for many organisms. Because of their essential roles, any decline in their populations can have far-reaching consequences. Current research on ant populations indicates a trend of decreasing numbers across various regions globally. This decline demands immediate attention to ensure that existing ecosystems remain intact. The identification of threatened ant species allows for targeted conservation strategies. In some areas, habitat destruction due to agriculture and urban sprawl has led to a decline in vital ant habitats. Innovative techniques in agricultural management can provide solutions that allow farmers to coexist with ant populations. Practices such as maintaining buffer zones and avoiding chemical pesticides help protect these indispensable insects. Increased collaboration between environmental organizations and agricultural stakeholders is necessary to implement sustainable practices effectively. The future of many ecosystems may depend on successful ant conservation.
The Role of Education in Ant Conservation
Educational initiatives play an important part in promoting ant conservation efforts. Schools and community programs focusing on biodiversity enhance awareness regarding the significance of ant populations. Engaging students in conservation projects fosters a sense of responsibility for their environment. By helping young individuals learn encounters with nature, we can encourage lifelong stewardship. Schools could incorporate field trips to local nature reserves or parks where students can observe ants in their natural habitat. Hands-on learning experiences create lasting impressions and encourage discussions about various insect roles. Additionally, workshops aimed at adults emphasize sustainable gardening practices that support ants. Providing local residents with knowledge of beneficial insects like ants can help them rethink their gardening strategies. Effective education strategies can lead to increased participation in ant conservation activities. Disseminating informative materials through social media platforms further spreads awareness in communities. Videos, articles, and interactive content make the learning process more engaging and relevant. By sharing success stories, we can inspire others to take part in conservation initiatives. Cultivating a knowledge base around ants and their ecological roles will ultimately lead to greater advocacy for their protection.
Community involvement is pivotal for the success of ant conservation efforts. Local conservation groups often organize surveys and monitoring activities to gauge ant populations accurately. Volunteers from the community can contribute significantly to data collection and analysis. Citizen science encourages members to participate in scientific endeavors while promoting awareness about ant issues. By aligning community goals with scientific research, synergies can emerge to bolster ant conservation. Organizing events like ‘Ant Days’ fosters public interest and encourages learning about local species. Such occasions can feature expert talks, workshops, and information booths focused on the importance of ants. Encouraging neighborhood competitions for ant-friendly gardens can further elevate awareness. These initiatives create a collaborative environment where conservation becomes a community effort. Upgrading public green spaces can also include planting native vegetation and reducing chemical use that negatively affects ant populations. Community-led initiatives designed with inclusivity can ensure long-term dedication to conservation efforts. This camaraderie promotes a deeper understanding of local ecosystems, including the vital roles ants play within them. Dedicated communities contribute to better monitoring and enhanced efforts to protect critical insect populations.
Research and Development in Ant Conservation
Research fosters a deeper understanding of ant behavior, population dynamics, and ecological relationships. Such insights are essential for formulating effective conservation strategies. Scientific studies contribute to identifying threatened ant species and understanding their habitat requirements. This knowledge assists in designing conservation programs tailored to specific species. Collaborations between universities, government agencies, and NGOs play a vital role in advancing research efforts. Increased funding for ant conservation research enables more extensive studies, leading to substantial ecological insights. Practical applications of research findings can guide policy-makers in creating protective regulations for endangered species. Knowledge-sharing through academic journals plays a crucial role in providing resources for conservationists. Enhancing research publications to include suggestions for amateur ecologists increases public engagement in ant conservation. Researchers also have an important instructional role, mentoring the next generation of ecologists. Creating opportunities for students to participate in field research cultivates skills and passion for eco-studies. Furthermore, designing citizen science programs that appeal to broader audiences can enhance community participation. Monitoring local ant populations allows the public to contribute to vital ecological data.
One of the greatest challenges in ant conservation is the impact of invasive species. These species often disrupt local ecosystems, outcompeting native ants for resources such as food and habitat. To address this threat, it is crucial to monitor the introduction of invasive ants and mitigate their spread. Establishing protocols for early detection can help manage invasive populations effectively. Community involvement in reporting sightings of invasive species can significantly aid in these efforts. Educational programs that inform the public about the risks of invasive ants are necessary. Appropriate management techniques reduce their environmental impact and protect local ants from being displaced. In certain regions, managing invasive species can involve diverse strategies, including physical removal or biological control methods. Successful experiences with invasive ant management highlight the importance of vigilance in conservation efforts. Developing partnerships with ecological organizations can enhance the effectiveness of these strategies. By creating the necessary infrastructures for early detection and active management, we can safeguard local ant populations. Promoting awareness around the issue of invasive species expands the commitment to preserving native ant species in natural habitats.
Conclusion: The Way Forward for Ant Conservation
Ant conservation efforts are vital for sustaining healthy ecosystems worldwide. Grassroots initiatives coupled with educational campaigns contribute significantly to public awareness. As communities unite for action, successful conservation outcomes become more feasible. Research and collaboration create informative frameworks that strengthen conservation strategies. Adopting a multi-faceted approach can protect ant populations effectively. Long-term commitment from individuals, organizations, and local governments is essential. Promoting policies that favor sustainable practices shows promise in combating threats to ants. Ensuring the protection of habitats and minimizing human-induced pressures is crucial. Engaging younger generations and fostering appreciation for all insects can create potential future champions of conservation. An emphasis on experiential learning will strengthen the connections between people and nature. Empowering local communities to adopt eco-friendly practices creates significant strides in conservation. Active involvement leads to a sense of ownership over local ecosystems. Overall, collaborative efforts hold the key to restoring and maintaining ant populations. Their crucial roles can only be preserved through continued advocacy and action. By implementing comprehensive strategies, we can ensure that ant populations thrive for generations to come.