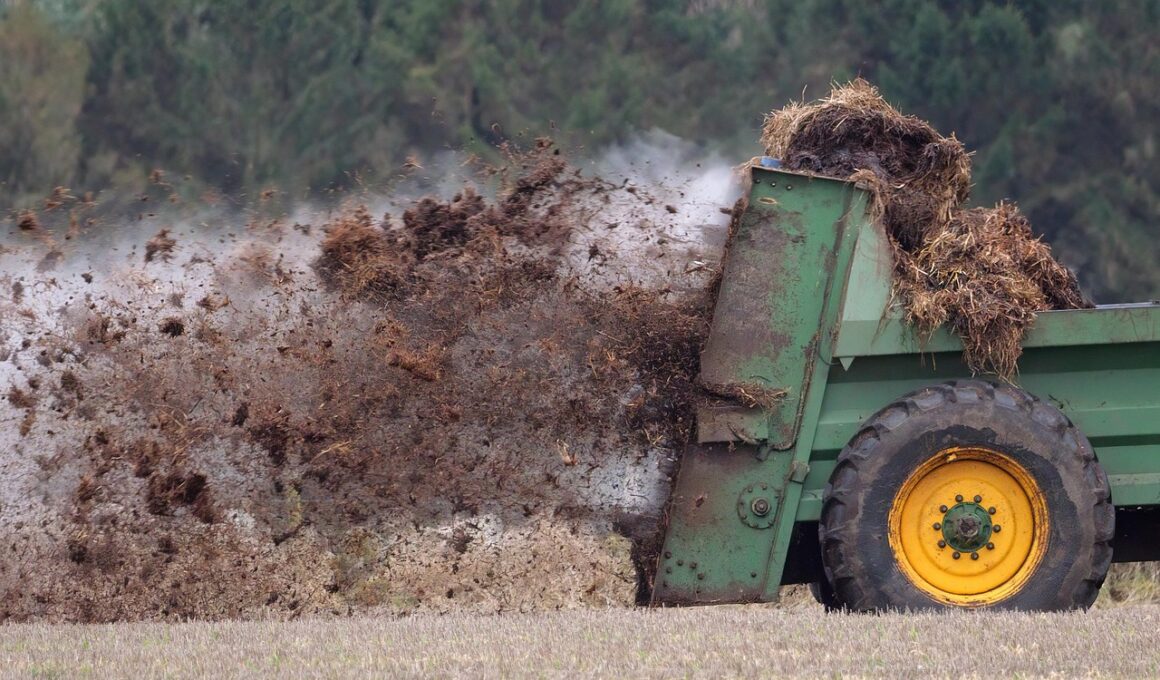
Nutrient Recycling: Using Manure as Organic Fertilizer
Manure management is a crucial aspect of sustainable agricultural practices. The use of manure as organic fertilizer promotes nutrient recycling and minimizes environmental harm. Manure contains essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are necessary for plant growth. However, effective manure management involves the proper collection, storage, and application to avoid nutrient runoff into water bodies. Farmers can benefit significantly from using manure as fertilizer by enhancing soil fertility, promoting healthier crops, and improving yield quality. In addition, manure management reduces reliance on chemical fertilizers, which can harm soil health over time. It is essential to understand the right application rates and timings for manure to maximize its benefits and minimize potential negative impacts. Implementing composting practices can also help in reducing pathogens in manure while creating a balanced organic fertilizer. Moreover, educating farmers on the best manure management techniques is vital to promote sustainable agriculture. Increased awareness and proper training will lead to better practices and improved environmental outcomes. Overall, nutrient recycling through manure management supports both agricultural sustainability and environmental stewardship, ensuring a healthier planet for future generations.
To apply manure effectively, farmers must consider several factors including type, soil condition, crop type, and application timing. Different animals produce various types of manure, each with unique nutrient content. For example, poultry manure is rich in nitrogen, while cow manure provides a balanced nutrient profile. Testing manure before application can accurately determine nutrient concentrations, allowing for more informed decisions regarding application rates. Additionally, incorporating manure into the soil rather than spreading it on the surface can enhance nutrient absorption by plants. It is recommended to apply manure during specific growth stages of crops to ensure maximum uptake of nutrients. This optimizes both crop yields and nutrient efficiency, while minimizing leaching losses during rainfall events. Waterlogged soils can exacerbate nutrient runoff, thus creating the need for strategic planning when managing manure. In regions where rainfall is high, scheduling manure applications to occur during dryer periods can prevent nutrient loss. Adopting cover cropping systems may also alleviate runoff issues by improving soil structure and increasing organic matter. It is essential for farmers to take proactive measures in manure management to maintain soil fertility and promote sustainable agriculture.
The Benefits of Using Manure
Using manure as organic fertilizer offers numerous benefits to farmers and the environment. Firstly, manure enhances soil structure and fertility through the addition of organic matter. Healthy soil supports microbial communities that aid in nutrient cycling, improving overall soil health. Additionally, the use of manure as fertilizer can decrease the need for chemical fertilizers, reducing financial input costs for farmers. This eco-friendly approach not only benefits the farm’s economy but also enhances the sustainability of agricultural practices. Secondly, proper manure management can contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. By means of composting and careful application, methane emissions associated with manure decomposition can be minimized. Furthermore, manure can act as a carbon source for improving soil organic carbon levels, leading to increased carbon sequestration. This has positive implications for mitigating climate change impacts. Moreover, farmers can unlock additional revenue streams through nutrient credits from utilizing manure effectively. Well-managed manure systems can produce high-quality organic fertilizers that can be sold or traded. Lastly, leveraging manure as an organic fertilizer fosters a healthier ecosystem by promoting biodiversity and improving habitat quality.
However, challenges do exist with using manure in agriculture. The risk of pathogen contamination is a notable concern, especially in direct applications to crops intended for human consumption. To mitigate such risks, it is crucial to adhere to proper application methods and timing guidelines. Composting manure is one effective strategy to kill pathogens and further improve safety for agricultural use. Secondly, the nutrient imbalance in manure can lead to over-application and subsequent environmental issues, such as water pollution. Farmers need to practice precision agriculture techniques to ensure they apply manure in appropriate amounts that correspond to crop nutrient requirements. Understanding soil nutrient dynamics and conducting regular soil tests can help prevent such challenges. Moreover, heavy rainfall can result in runoff and negative consequences for nearby water bodies. By implementing best management practices, such as buffer strips and controlled application rates, farmers can protect water resources while benefitting from manure applications. Therefore, while there are challenges, proactive management can overcome these obstacles and facilitate the responsible use of manure as a valuable organic fertilizer in sustainable agriculture.
Regulatory Considerations
Farmers utilizing manure as fertilizer must adhere to various regulatory requirements to ensure environmental safety. Federal and state regulations govern manure application practices to protect water quality. Livestock operations are typically required to develop nutrient management plans outlining how manure will be handled, stored, and applied. These plans serve to minimize nutrient runoff and potential contamination of waterways, maintaining compliance with local environmental standards. Understanding these regulations is vital for farmers to operate legally and sustainably, and it often necessitates collaboration with agricultural advisors or agencies. Training programs are available for farmers to enhance their understanding of regulatory obligations, showcasing the significance of education in responsible manure management. By attending workshops and information sessions, farmers can stay informed about updates in regulations and best practices. Furthermore, documentation of manure application records is often required to demonstrate compliance with nutrient management plans. This helps in tracking nutrient contributions to crops and managing potential environmental impacts effectively. Keeping meticulous records also serves as evidence of compliance during inspections by regulatory bodies, reinforcing the importance of accountability in manure management practices.
Engaging in community practices can enhance manure management strategies significantly. Farmers can collaborate on composting efforts or engage in cooperative manure application services that benefit each participant. By pooling resources and sharing equipment, farmers can reduce individual costs associated with manure management, increasing overall efficiency. Furthermore, experimental practices can be tested within the community for improved outcomes in soil health and crop production. Collaborative learning fosters innovation and the exchange of ideas, empowering farmers to adopt best practices from one another. Local agricultural organizations often facilitate these community endeavors, providing valuable resources and support. Demonstration farms can serve as educational platforms where farmers can observe effective manure management techniques in action. Additionally, networking within the agricultural community strengthens social ties and facilitates knowledge sharing that enhances all participants’ sustainable farming efforts. Involving the larger community in discussions around manure management can also raise public awareness regarding the benefits of organic fertilizers and responsible agricultural practices. By working together, farmers can create a more resilient agricultural landscape and foster sustainable practices that benefit both the environment and their livelihoods.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Manure Management
With growing interest in sustainable farming practices, manure management will continue to evolve. Innovations in biotechnology are expected to play a pivotal role in enhancing manure’s value as an organic fertilizer. Researchers are working on developing microbial inoculants that improve nutrient availability and uptake by plants. These advancements could lead to more efficient use of manure in agriculture and greater benefits for soil health. Additionally, precision agriculture technologies promise to revolutionize nutrient management through targeted applications based on real-time data and soil health diagnostics. By utilizing sensors and drones, farmers can apply manure more accurately and mitigate negative impacts associated with over-application. Furthermore, ongoing educational initiatives will promote best practices among farmers, ensuring they stay up-to-date with new findings and regulations surrounding manure management. Policy changes may also be needed to encourage more ecological approaches to nutrient management, fostering an environment where organic fertilizers like manure are embraced. Adopting such innovations can enhance not only the farmer’s productivity but also the environmental sustainability of agricultural systems, showcasing the importance of continually advancing manure management techniques in the quest for sustainable farming solutions.
In conclusion, nutrient recycling through the effective management of manure holds significant potential for constructing a more sustainable agricultural framework. The multifaceted benefits such as enhanced soil fertility, reduced chemical dependency, and improved environmental health underscore the crucial role of manure in achieving sustainable development goals. Farmers must engage with the proper management practices, which include adhering to regulations, utilizing technologies, and accepting community-driven initiatives. By understanding the unique properties of different types of manure and the best ways to apply them, agricultural productivity can be maximized. Furthermore, ongoing education and training offer opportunities for farmers to refine their practices and adapt to evolving challenges. The importance of manure management in mitigating harmful outcomes, such as water runoff and soil degradation, cannot be overstated. As we look ahead, the future of manure as an organic fertilizer appears promising, bolstered by innovation and collaborative efforts among the agricultural community. Committing to these principles can create a circular economy within farming practices, ultimately fostering resilience against changing climatic conditions. Overall, proper manure management is foundational to advancing sustainability and promoting a healthier environment for all.