How Seals Use Echolocation and Other Senses
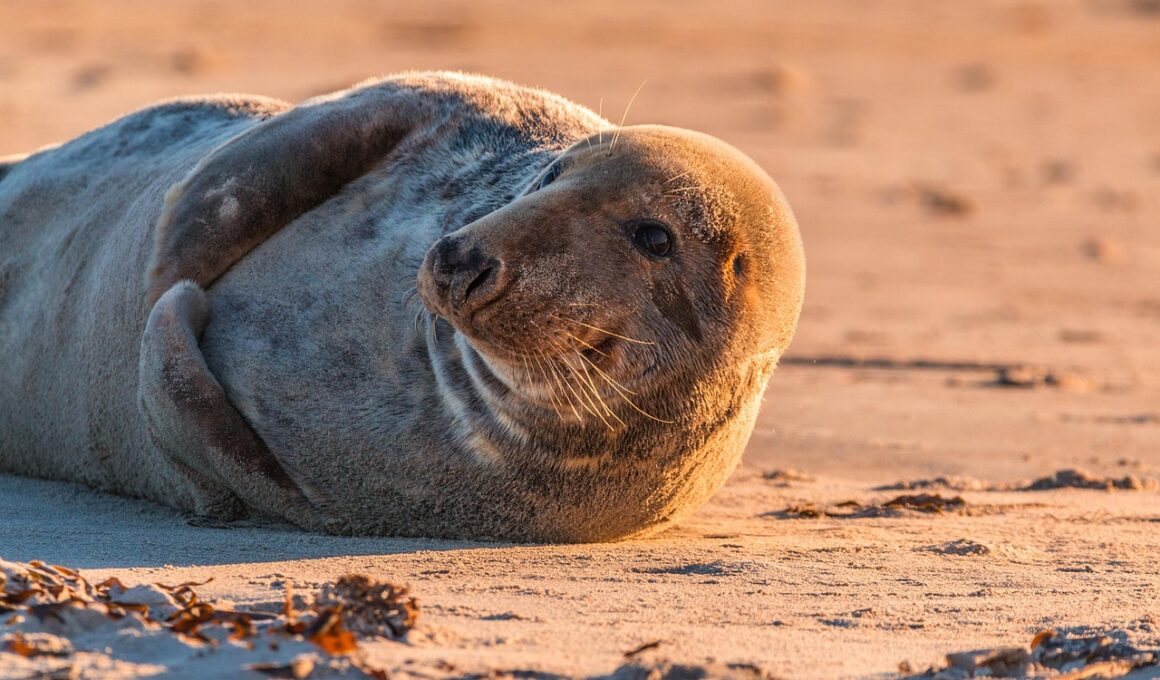
Seals are remarkable marine mammals that possess unique adaptations allowing them to thrive in diverse environments. While commonly known for their agility in water and adorable appearances, their sensory systems are remarkably advanced. For seals, sound plays a crucial role in their everyday navigation. In the deep, dark waters they inhabit, sight may not be as effective, which is why seals utilize echolocation to locate prey and even communicate with each other. By emitting vocalizations that travel through water and return as echoes, seals can ascertain the distances and sizes of objects. Their hearing is so precise that it can distinguish between echoes from various angles, enabling efficient hunting. They rely on complex vocalizations, producing a range of sounds to convey messages within their pods. Additionally, seals possess sensitive whiskers or vibrissae, which enhance their tactile perception. These specialized hairs can detect minute changes in water currents, indicating the presence of fish or other marine life nearby. The combination of echolocation and other heightened senses illustrates how seals have evolved into adept hunters in their underwater domain.
Among pinnipeds, seals exhibit unique adaptations that enhance their ability to hunt effectively. Echolocation is crucial for many species as they navigate through murky waters. The speed at which sound travels underwater is faster than in air, which allows seals to pick up on auditory cues more efficiently. By making sounds and interpreting returning echoes, seals can create mental maps of their surroundings. This ability to perceive their environment through sound is critical for locating prey like fish or squid. Their acute auditory capabilities help them detect not only nearby food sources but also potential threats. Another fascinating aspect of seals is their keen vision, especially in low-light conditions. Their eyes are adapted for excellent underwater visibility. The lens of a seal’s eye is highly flexible, allowing them to focus on objects both near and far without difficulty. Additionally, seals can perceive colors within the underwater spectrum, enhancing their hunting efficiency. This vision, combined with their echolocation skills, positions seals as highly proficient predators in their ecosystems. Their survival in the wild heavily depends on these remarkable sensory adaptations, showcasing nature’s ingenuity.
Seals also rely heavily on other senses, such as smell, to navigate their environments. Although primarily aquatic animals, they need to come ashore to breed and rest, which is when their sense of smell becomes especially important. Their olfactory senses aid in detecting predators, locating mates, and identifying social signals from fellow seals. When seals haul out onto land, they often do so in large groups, creating a lively environment filled with various scents. This olfactory data allows them to communicate effectively. Mother seals can recognize their pups through scent, which is crucial for nurturing. Behavioral studies show that seals may even use smell to detect food sources from afar. Moreover, their tactile sense is exceptional, with sensitive lips and whiskers finely tuned to detect vibrations and movements in the water. This capability assists them in sensing when prey is nearby, such as a school of fish swimming through the currents. The interplay of all these senses contributes to the seal’s survival. By combining echolocation, acute vision, and enhanced smell, seals adapt seamlessly to their environments. Their multifaceted sensory tools allow for successful hunting and social interaction.
The Importance of Social Interactions
Social interaction among seals is a vital aspect of their behavior, impacting their hunting efficiency and overall survivability. Through vocalizations, seals engage in a rich social life, fostering connections within their pods. The various sounds produced by seals not only assist in locating each other in dense waters but also maintain group cohesion. This social aspect is especially important during breeding seasons when seals gather in large numbers. Mothers and pups rely on vocalizations for bonding, establishing communication from birth. This foundational connection ensures that pups can find their mothers even in crowded beaches. Furthermore, social learning occurs within these communities. Young seals observe older individuals when they hunt, learning techniques that improve their skills over time. This learning process is crucial for survival, as effective hunting techniques can significantly impact their health and wellbeing. In colder regions, seals often group together for warmth, showcasing another dimension of their social behavior. These interactions not only foster communal bonds but also enhance their chances of survival by leveraging group dynamics. Therefore, social behavior and sensory communication play integral roles in the lives of seals, illustrating the complex nature of their existence.
In addition to social interactions, seals engage in various behaviors that are critical for their survival in the wild. Their strategies include hunting synchronously, allowing them to encircle schools of fish and improve their catch rates. These cooperative techniques exemplify the importance of social bonds. By working together, seals can outmaneuver and capture prey more effectively than when they hunt alone. Observational studies indicate that group hunting is not only a learned behavior but a manifestation of their communication skills. Furthermore, seals utilize their senses while hunting individually using echolocation alongside their vision. They may display behaviors like diving or porpoising to catch fish off-guard. Each technique showcases their adaptability and intelligence as hunters. Additionally, seals engage in play, which is essential for developing social and cognitive skills. Young seals often frolic in the surf, honing their swimming abilities while also learning necessary social cues. Play behaviors are critical for pups, serving as the foundation for future hunting techniques. Through these diverse behaviors and social structures, seals demonstrate the remarkable complexity within their species, revealing the intricacies involved in maintaining their ecological success in marine environments.
The evolutionary journey of seals has led to distinctive adaptations that enable them to thrive as apex predators. As they spend most of their lives in the ocean, seals have evolved streamlined bodies optimal for swimming. Their blubber layer not only aids in buoyancy but also provides insulation against harsh cold waters. This adaptability showcases nature’s response to environmental challenges faced by seals. Their front flippers are highly developed for propulsion, while their hind limbs are modified for steering. This physical anatomy enhances their agility and speed, enabling them to pursue prey efficiently. The advanced echolocation capabilities discussed earlier stem from these evolutionary changes, highlighting their adaptability within aquatic ecosystems. Furthermore, seals have developed social structures that enhance their reproductive success. They often establish territories, engage in courtship behaviors, and vocalize to attract mates. These adaptations, both physical and behavioral, illustrate the evolution of seals as a unique order of marine mammals. By investigating these characteristics, we gain insight into how seals have become specialized hunters in an ever-changing marine environment. This continuous evolution reflects the dynamic relationship between species and their habitats.
Conservation of Pinnipeds
Conservation efforts aimed at preserving seal populations have become increasingly important as marine ecosystems face unprecedented pressures. Climate change, pollution, and overfishing pose significant threats to seals, undermining the delicate balance of their habitats. Effective conservation strategies should focus on protecting breeding sites and maintaining healthy marine environments. Marine protected areas can serve as safe havens, ensuring seals can thrive without human interference. Additionally, reducing pollution levels in oceans will improve marine life quality. Educational campaigns highlighting the importance of seals in maintaining ecosystem balance can help foster awareness among the public. By advocating for sustainable fishing practices, we can ensure adequate prey availability for seals, promoting biodiversity in marine ecosystems. Collaborations between governments, conservation organizations, and local communities are essential to create comprehensive strategies. Research into seal populations, their behaviors, and habitats is also crucial for informed conservation practices. Moreover, monitoring climate impacts enables timely intervention, protecting seals from further decline. Preserving pinnipeds is not just about saving one species; it represents an effort to sustain marine ecosystems and the myriad of life forms they support. Therefore, a holistic approach is essential for seal conservation.
In conclusion, seals embody the remarkable adaptations that allow them to thrive in aquatic environments. Through their ability to utilize echolocation, advanced vision, and keen sense of smell, they navigate their underwater world efficiently. Their social interactions reflect the importance of communication and learning, while their evolutionary traits showcase physical excellence in hunting practices. However, today’s environmental challenges necessitate a strong commitment to conservation efforts to protect these unique mammals. Understanding their sensory adaptations offers critical insights into the dynamics of marine ecosystems. Collaborative conservation programs that emphasize sustainable practices will ensure that seals continue to flourish in their natural habitats. Thus, every initiative aimed at preserving seals also contributes to the protection of their ecosystems. By ensuring the survival of seals, we promote healthy oceans that host a myriad of marine life. As such, the journey towards conserving seals represents a larger narrative about maintaining the balance of our planet’s ecosystems. A united effort can lead to effective measures that address the pressing issues faced by these charismatic marine mammals. Protecting seals is a vital step in nurturing a vibrant marine future for generations to come.