The Contribution of Ichnology to Dinosaur Studies
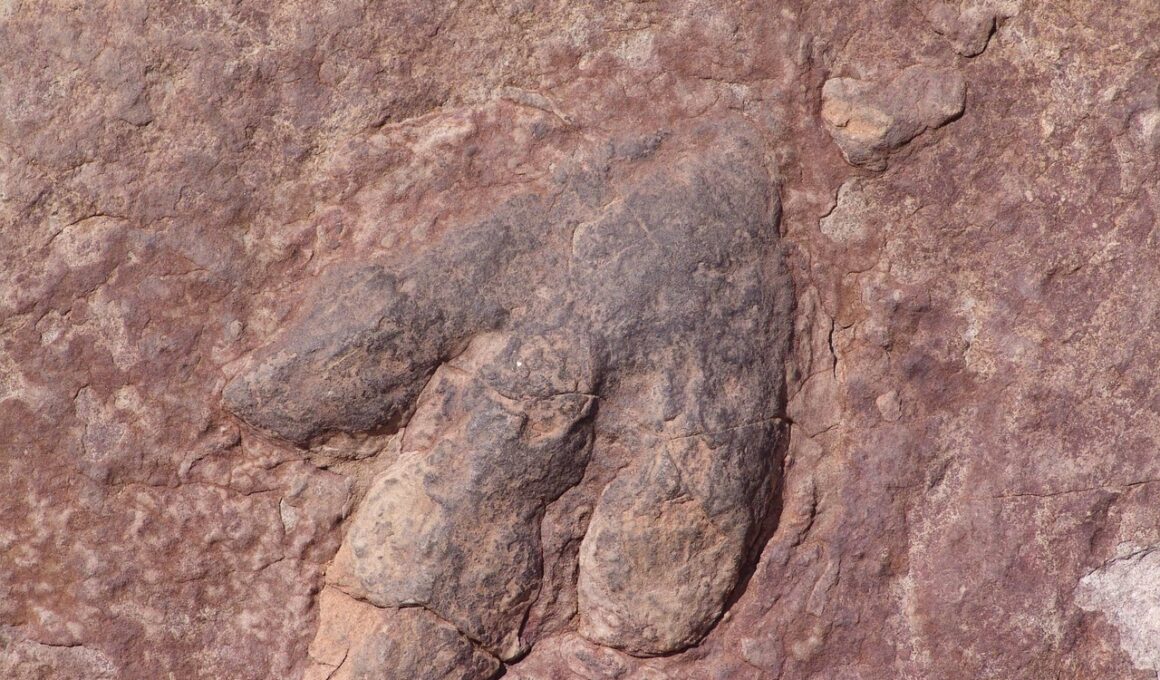
Ichnology plays a pivotal role in understanding dinosaur behaviors and movements through the study of fossilized tracks and footprints. By analyzing these imprints, researchers can glean important insights about how dinosaurs interacted with their environment. Tracks can reveal information regarding the speed, size, and locomotion patterns of different dinosaur species. Paleontologists rely heavily on ichnology to reconstruct the daily lives of these prehistoric creatures. The global distribution of dinosaur footprints offers clues regarding migration routes and habitat preferences. Detailed analysis allows scientists to identify the abilities and constraints of various dinosaur species. Furthermore, each fossilized track provides a unique glimpse into social behaviors, such as herd dynamics and parental care. The study of ichnology has enhanced our understanding of the biodiversity and evolutionary pathways of dinosaurs. Moreover, ichnological evidence contributes to broader ecological models of prehistoric ecosystems. Ultimately, ichnology acts as a critical tool in decoding the complex biological narratives left behind by dinosaurs, shedding light on their lifestyles and interactions. The continued exploration of these fossilized traces promises to unearth further mysteries of the age of dinosaurs, expanding our knowledge about these magnificent reptiles.
In addition to their scientific significance, dinosaur tracks have cultural and educational importance. These footprints draw visitors to museums and natural parks worldwide, acting as a bridge connecting people to paleontology. The allure of encountering real dinosaur footprints captivates the imagination of children and adults alike. Many sites have become renowned tourist attractions, stimulating interest in earth sciences. Educational programs centered around ichnology encourage young minds to explore the natural world, sparking curiosity about dinosaurs and their habitats. This public interest often promotes funding for paleontological research and conservation of significant fossil sites. Additionally, community engagement fosters environmental awareness and appreciation for geological history. Local museums often collaborate with researchers to offer workshops, lectures, and interactive exhibits about dinosaur ichnology, enhancing public understanding of fossil evidence. By disseminating knowledge of ichnology, researchers contribute to the sustainability of scientific inquiry. Therefore, the interplay between scientific research and public interest in ichnology significantly enhances the importance of dinosaur studies. Overall, the field of ichnology not only advances paleontological science but also enriches educational experiences addressing our planet’s ancient past, promoting ongoing engagement with both science and history.
Understanding Dinosaur Movement Through Tracks
Dinosaur tracks provide a roadmap to understanding their movements and behaviors. Each footprint tells a story, revealing how these magnificent creatures traversed their environments. The size, depth, and spacing of tracks allow scientists to make educated guesses about the speed and size of the dinosaurs that made them. For instance, larger footprints often indicate heavier dinosaurs, while the spacing of prints can suggest walking, running, or even social interactions among species. Moreover, recognizing and categorizing different types of tracks has been essential in identifying various dinosaur species. Such identification has led to new insights about the relationships between different dinosaurs, as trackways indicate their social structures and interactions. Additionally, the preservation of these tracks in sedimentary rock layers offers a glimpse into the landscapes of the past, revealing ecological conditions. By studying the context of footprints, researchers can piece together a more complete picture of dinosaur habitats and migration patterns. Ultimately, ichnology serves as a vital tool in paleoecology, offering a dynamic view into the lives of dinosaurs and their environmental adaptations. Through rigorous analysis of these traces, scientists can continue to unravel the complexities of dinosaur locomotion.
Furthermore, the discovery of dinosaur tracks has profound implications for understanding dinosaur behavior. For example, trackways with multiple footprints suggest social interactions, such as herding behavior or parental paths where adults accompanied juveniles. Analyzing these patterns helps scientists infer the social structures and parenting habits of various species. Ichnology can also reveal instances of predation or competition, as overlapping tracks may indicate encounters between rival dinosaurs. This insight contributes to a broader understanding of ancient ecosystems, illustrating how different species coexisted. Additionally, the investigation of ichnofossils—fossilized evidence of animals’ activities—provides insights into the environmental conditions in which these dinosaurs lived. Such studies often reveal the influence of climate, geography, and vegetation on dinosaur behavior. Understanding how dinosaurs responded to their environments significantly contributes to our knowledge of their evolution over millions of years. By integrating ichnology with other paleontological methods, researchers create a comprehensive narrative of life during the Mesozoic era. This interdisciplinary approach fosters collaboration among scientists and enriches the overall understanding of dinosaur ecology and behavior further. The significance of ichnology extends beyond mere footprints, enhancing our grasp of dinosaur lifestyles within their unique ecosystems.
The Role of Technology in Ichnoanalysis
Modern technology has revolutionized the field of ichnology, providing researchers with powerful tools to analyze dinosaur tracks more effectively. 3D imaging and modeling techniques allow scientists to create detailed digital representations of footprints, enabling precise measurements and analyses. With advanced imaging, researchers can examine subtle details that are unreachable or invisible to the naked eye. These methods facilitate the comparison of different track types and sizes, contributing to more nuanced categorizations. Additionally, geographic information systems (GIS) empower researchers to map the distribution of dinosaur footprints across various landscapes. This spatial analysis offers insights into potential migration routes and ecological patterns, enhancing our understanding of the interactions between dinosaurs and their environments. Furthermore, technologies like ground-penetrating radar (GPR) reveal the geological context of tracks, allowing for the exploration of sediment characteristics and preservation conditions. Such technological advancements are essential for enriching the context in which tracks are discovered, yielding rich data sets for paleontologists. As a result, the integration of technology in ichnology not only advances research methodologies but also deepens our understanding of dinosaur behavior, ecology, and evolutionary history.
Moreover, studying dinosaur footprints extends to evaluating the environmental shifts that occurred during their time on Earth. Ichnological evidence provides data on the terrestrial ecosystems and climate changes that influenced the habitats of dinosaurs. The study of sedimentary deposits accompanying tracks can reveal information about ancient weather patterns, flora, and fauna. For instance, research identifying variations in track density and footprints types correlates with changes in vegetation and climate over time. Consequently, ichnology serves as a form of ecological documentation, illustrating how dinosaur communities adapted to shifting conditions. This knowledge further contributes to our understanding of extinction events and subsequent recoveries within ecosystems. By examining how dinosaurs responded to various environmental challenges, ichnologists can piece together the narrative of survival amidst change. Such insights provide valuable parallels to modern ecological studies, offering guidance on species adaptation in the face of current environmental crises. Thus, ichnology not only enriches our comprehension of the past but also serves as a contemporary reference for understanding ecological resilience. As scientists continue to analyze these fossilized traces, they deepen their exploration of the complex interplay between dinosaurs and their ancient habitats.
Future Directions in Ichnological Research
The future of ichnology promises exciting developments as researchers continue to uncover dinosaur tracks across the globe. With advancements in excavation techniques and technologies, new footprints are being discovered with increasing regularity. This will enhance the understanding of dinosaur diversity and behavior significantly. Exploring remote areas where previous research has been scarce may uncover untapped regions rich in ichnological data. Collaborative projects utilizing international expertise can facilitate data sharing and innovative approaches to study these footprints. Additionally, interdisciplinary approaches involving archaeology, geology, and ecology are likely to yield new perspectives on ichnological research. The integration of diverse scientific perspectives can lead to refined methodologies and fresh interpretations. As climate change and environmental impacts become urgent global topics, ichnological research may also provide crucial lessons on adaptability and survival strategies from millions of years ago. Engaging citizen scientists and amateur paleontologists through workshops and community programs can broaden public interest in ichnology, inspiring the next generation of researchers. Ultimately, the field of ichnology is poised for remarkable growth and will continue to play a vital role in decoding the prehistoric world of dinosaurs through their tracks and footprints.
In conclusion, ichnology significantly contributes to our understanding of dinosaurs and their ecosystems. Through detailed analyses of tracks and footprints, researchers unravel the complexities of dinosaur life, revealing insights into behaviors, movement, and interactions with their environments. The integration of technology further enhances these studies, allowing for precise measurements and comprehensive mapping of tracks worldwide. Moreover, ichnology fosters public engagement through educational programs, bridging the gap between science and community interest. The intrinsic value of studying footprints transcends academic research, as they hold cultural significance and spark the curiosity of people across generations. Future ichnological research will undoubtedly lead to new discoveries, enriching paleontological narratives and enlightening current ecological challenges. As scientists continue to investigate these fossilized traces, they will deepen our understanding of the magnificent dinosaurs that once roamed the Earth. The stories embedded in these footprints invite ongoing inquiry and exploration, igniting passion for paleontology and the natural world. Ichnology represents a vibrant, evolving field with unlimited potential, continuously offering fresh perspectives on the ancient animals that shaped our planet. The role of ichnology in dinosaur studies is invaluable and will remain integral to advancing our knowledge about prehistoric life.