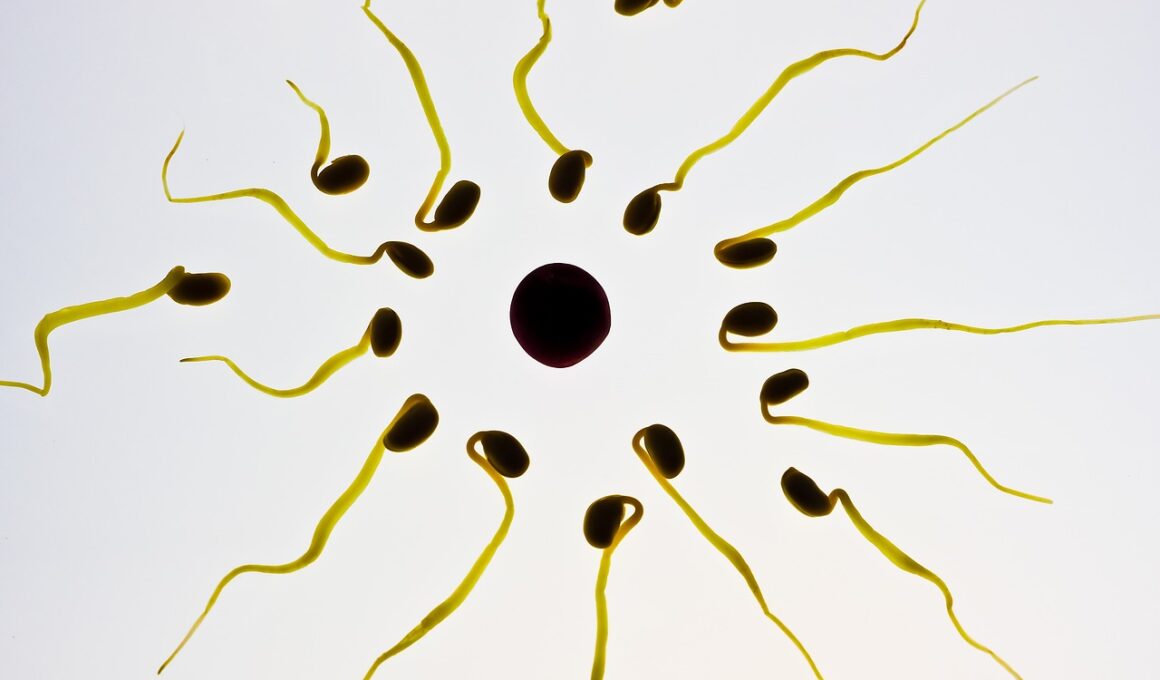
The Influence of Sperm Morphology on Fertilization Success
Sperm morphology is a critical factor in the fertilization process, encompassing the size, shape, and structure of sperm cells. The effectiveness of sperm in achieving successful fertilization directly correlates with these morphological features. Research indicates that sperm with an optimal shape, including a streamlined head and elongated tail, demonstrate superior motility compared to those with abnormal forms. Abnormal morphology can hinder sperm movement, reducing the chances of successfully reaching the egg for fertilization. Studies highlight the need to assess not just sperm count but also morphology when evaluating male fertility. Furthermore, the variation in morphology amongst sperm from different species highlights the adaptive strategies each has developed for fertilization. For example, some species produce numerous sperm with varying shapes, while others produce fewer but genetically superior sperm. The evolutionary significance of sperm morphology illustrates its role in reproductive success and species diversity. Additionally, environmental and health factors, like nutrient availability and exposure to toxins, can significantly influence sperm morphology in male animals. Thus, understanding these impacts is essential for improving reproductive health in various species.
Sperm Competition and Morphology
Sperm competition occurs when the sperm of multiple males simultaneously competing to fertilize an egg leads to the evolution of various sperm morphologies within species. In many animal species, males develop distinct sperm shapes as a strategy to increase their chances of fertilizing eggs successfully. For example, some species feature larger sperm that can swim faster and more effectively, ensuring that the sperm reaches the egg before those from rival males. In contrast, other species produce a higher quantity of smaller sperm, creating a competitive swarm effect that increases fertilization likelihood. The morphology of sperm can influence its penetrative ability, which is crucial when navigating the female reproductive tract. The factors influencing sperm competition and morphology are complex, intertwining genetics, environmental conditions, and behavioral dynamics. These interactions shape the reproductive strategies employed by various species, illustrating an evolutionary arms race. In studies, researchers utilize advanced imaging technology to analyze sperm morphology, providing insight into how these factors maintain biodiversity. Sperm morphology thus serves as a fascinating example of evolutionary biology, demonstrating the intricate balance between physical design and reproductive success.
Impact of Environmental Factors on Sperm Morphology
Environmental factors critically influence sperm morphology, affecting fertility and reproductive success in animals. Various studies indicate that factors like temperature, pollution, and dietary conditions can lead to marked changes in sperm structure. Increased exposure to environmental pollutants has been linked to significant rates of abnormal sperm morphology in several animal populations. For example, wildlife living in contaminated waters often exhibit reduced sperm quality, impairing their reproductive capabilities. Additionally, fluctuations in temperature can disrupt sperm production, especially in species that utilize external fertilization, like many fish. Nutritional deficits also compromise sperm morphology; animals lacking key vitamins and minerals exhibit higher incidences of abnormal sperm shapes. Understanding these environmental impacts is essential for conservation and reproductive health strategies, particularly for endangered species. Research has led to initiatives focusing on habitat restoration to improve reproductive outcomes. Furthermore, it emphasizes the importance of monitoring environmental health for biodiversity. Academic and applied studies examine these myriad factors, correlating findings to aid in the design of health policies for wildlife management. Future studies focusing on interventions that can mitigate these environmental effects will be vital for species conservation.
Sperm Morphology and Assisted Reproductive Technologies
Advances in assisted reproductive technologies (ART) have highlighted the critical role of sperm morphology in enhancing fertilization success rates. Techniques like intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) specifically target sperm with optimal morphological characteristics for egg fertilization, greatly improving outcomes for couples facing infertility. Determining sperm morphology before initiating ART is paramount for selecting healthy sperm that are more likely to succeed in fertilization. Comprehensive assessments using microscopy and sperm sorting methods enable clinicians to identify morphologically normal sperm for these procedures. Moreover, incorporating sperm morphology assessments into standard fertility evaluations could lead to more personalized treatment options for those experiencing fertility challenges. Success rates for ART can be significantly affected by sperm quality, directly linking morphology with reproductive outcomes. Not only does morphology provide insight into sperm function, but it also serves as a predictive tool for potential fertility issues. This approach underscores the importance of biology in developing successful ART applications. In understanding the relationship between sperm morphology and fertilization, we enhance our ability to provide effective fertility solutions. Ongoing research in morphology’s influence on ART will continue to pave the way for improved reproductive technologies.
Conclusion: The Importance of Sperm Morphology
In conclusion, sperm morphology plays an integral role in the fertilization process across various species. Its importance is underscored by its influence on sperm motility, success rates of fertilization, and overall reproductive strategies. Factors influencing morphology, such as environmental conditions and assisted reproductive technology applications, continue to shape our understanding of fertilization dynamics. A deep appreciation for the complexities of sperm morphology highlights its evolutionary significance and its impact on reproductive health. As researchers delve deeper into the intricacies of sperm function and morphology, more effective conservation strategies and interventions can emerge. By prioritizing sperm morphology in studies, we can enhance our understanding of animal reproductive behaviors and improve fertility treatments for species facing challenges. The health of animal populations and their ability to reproduce successfully depends upon well-functioning morphologies. Thus, addressing issues relating to sperm form and quality must be prioritized. Promoting education and awareness regarding sperm morphology, its implications for fertility, and environmental impacts can help bolster successful reproductive outcomes. Finally, fostering interdisciplinary collaboration will enrich research and practice, enhancing reproductive success globally.
Future Research and Developments in Sperm Morphology
Future research efforts must focus on expanding our understanding of sperm morphology and its influence on fertilization across various species. Innovative approaches that incorporate genetic, environmental, and behavioral analyses will be essential to uncover the multifaceted relationships governing sperm success. Developing advanced imaging techniques and analytical methods that improve assessments of sperm morphology can significantly aid in evaluating fertility. Studies that explore the genetic basis of sperm morphology can reveal how traits are inherited and help elucidate patterns of variation within and between species. Moreover, interdisciplinary collaborations among ecologists, reproductive biologists, and environmental scientists can yield holistic perspectives on animal reproduction, gestation, and health. By emphasizing the effects of changing environments on sperm quality and morphology, researchers can provide critical insights into addressing reproduction challenges driven by climate change and habitat destruction. The integration of technology and artificial intelligence into morphology studies may lead to enhanced predictive capabilities for assessing sperm health. Ultimately, sustained collaboration and knowledge-sharing among scientists will pave the way for breakthroughs in reproductive health, conservation biology, and species longevity.
Call to Action on Sperm Morphology Studies
In light of the evidence supporting the pivotal role of sperm morphology in fertilization, a call to action is warranted within the scientific community to prioritize studies in this vital field. Emphasizing research related to sperm morphology will enhance fertility assessments and promote interventions that safeguard reproductive efficacy across animal populations. Knowledge-sharing initiatives among researchers, clinicians, and conservationists can facilitate awareness of morphological impacts on fertility. Collaborative efforts can lead to improved education efforts surrounding wildlife and domestic animal reproductive health. Increased funding for research examining environmental influences on sperm quality and morphology will yield critical insights into reproductive challenges facing many species today. As we strive to mitigate environmental damages and promote conservation, understanding sperm morphology’s role becomes essential to preserving biodiversity. Encouraging students and early-career scientists to engage in this research area will foster innovative ideas that may lead to groundbreaking developments. Collectively, these efforts contribute to a deeper understanding of reproductive health, ensuring cleaner ecosystems for future generations and sustaining diverse animal populations globally.