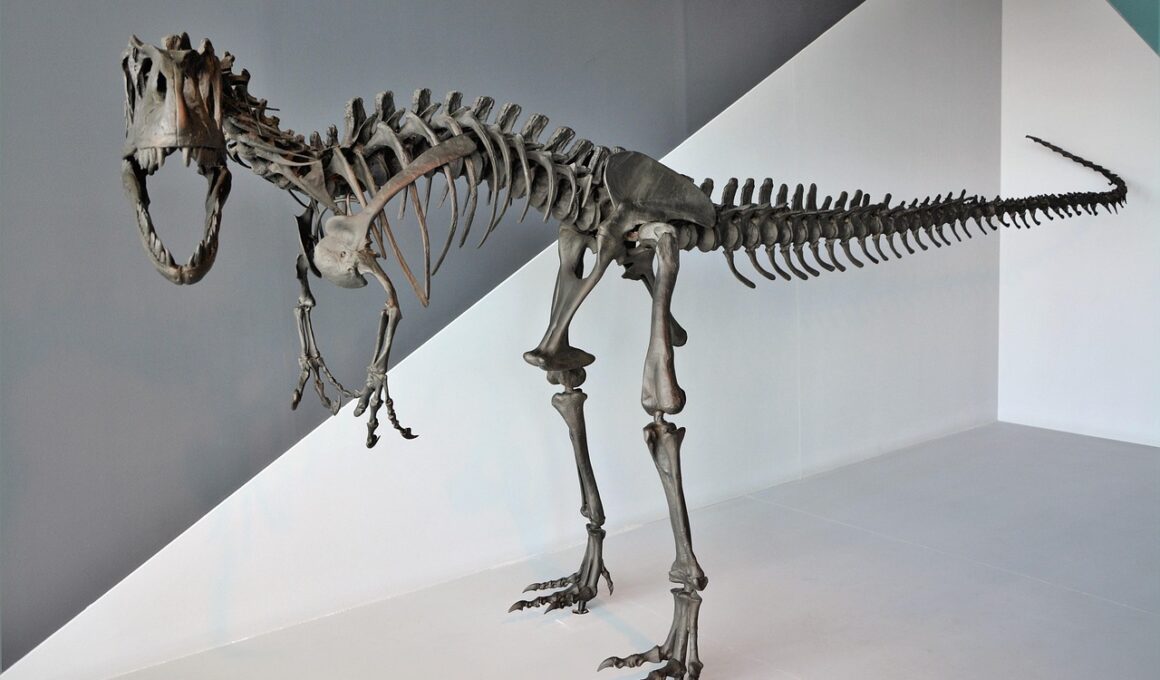
Differences Between Juvenile and Adult Dinosaur Anatomy
Understanding the anatomical differences between juvenile and adult dinosaurs is crucial for paleontologists studying dinosaur growth and evolution. Juvenile dinosaurs exhibited distinct physical characteristics compared to their adult counterparts. For instance, many juvenile dinosaurs were proportionately smaller, with relatively larger heads compared to their bodies. This anatomical trait is often observed in many species. An example includes the well-known Tyrannosaurus rex, where the juvenile had a large skull in relation to its smaller body, facilitating various growth stages. Additionally, their limb proportions also underwent significant changes as they matured. Juveniles had shorter limbs that eventually grew longer and more powerful in adults, which is particularly notable in theropods. Another crucial difference is found in bone structure and density. Juvenile bones were less dense, indicating rapid growth phases that required a different skeletal structure than adults. Furthermore, soft tissue compositions, like muscles and fat deposits, differed significantly. This influenced their movement, behavior, and survival strategies. Overall, understanding these differences sheds light on how dinosaurs adapted to their environments during different life stages.
The evolutionary implications of juvenile versus adult dinosaur anatomy are significant. This understanding provides insights into how dinosaurs evolved over millions of years, particularly regarding their development and lifestyle changes between life stages. By examining fossil records, scientists can discern various growth patterns that existed in prehistoric creatures. For example, in some species, juveniles had unique adaptations for survival, including different dietary needs and behavioral patterns. Juvenile dinosaurs often occupied different ecological niches than adults. They might have been preyed upon more frequently, which necessitated a different approach to adaptation. Another essential aspect involves the transition in body size. Adult dinosaurs could reach massive sizes, which would require profound adaptations for locomotion and resource acquisition. Furthermore, examining the differences in body structure helps clarify the role of sexual dimorphism among certain groups of dinosaurs. This identifies how male and female anatomy may vary, providing clues about their reproductive strategies and social behavior. Recently discovered fossils illustrate these growth patterns, reinforcing the understanding of the complex biology of dinosaurs, demonstrating how juvenile forms laid the foundation for adult characteristics and survival efficiency.
Bone Structure Differences
Bone structure is one of the most profound differences found between juvenile and adult dinosaurs. Juvenile bones exhibited greater flexibility and resilience, which allowed them to withstand numerous physical activities typical for young animals. In contrast, adult bones were more robust and dense, adapted to support larger body sizes and heavier weights. The intricate details of bone growth, including growth plates in juvenile bones that eventually fuse in adults, highlight these changes. This physiological difference is important for understanding dinosaur longevity and overall health. Additionally, research suggests that the faster metabolism of juveniles contributed to their rapid growth, requiring unique adaptations in their skeletal framework. Another interesting aspect is the directional growth of bones based on environmental factors and behavioral patterns. For adult dinosaurs, bones developed heavy structures necessary for activities like hunting or defending territories. In some cases, the skeletal structure showed modifications beneficial for specific environments, such as aquatic adaptations in certain species. Investigating fossilized bones enables scientists to ascertain the age, health, and gender of dinosaurs, providing further knowledge on their anatomy and various growth stages.
Muscle composition also differed significantly between juvenile and adult dinosaurs, aligning with their differing lifestyles and survival strategies. Juveniles required muscles adapted for quick escapes from predators. This led to a composition favoring speed and agility, which is crucial for young animals that are often more vulnerable. As dinosaurs matured, their muscle structure changed to support the powerful movements characteristic of adults. For instance, adult theropods exhibited strong leg muscles capable of sprinting, allowing them to be proficient hunters. The transition in muscle density and type reflects changes in the dinosaur’s behavior and dietary requirements. Moreover, the development of specialized muscles in certain dinosaurs aligns with their hunting mechanisms and social dynamics. Additionally, the differences in body fat distribution could also impact a dinosaur’s ability to insulate and regulate body temperature as it matured, serving additional survival functions. Overall, understanding muscle composition changes provides insights into how dinosaurs functioned during different life stages, contributing significantly to their overall health and effective mobility within their ecosystems.
Skin and Feathers Variations
Another fascinating aspect of juvenile versus adult dinosaur anatomy involves the variations in skin textures and potential feather development. Many paleontological studies suggest that while juvenile dinosaurs may have had softer, more pliable skin, adults displayed tougher skin capable of withstanding environmental stressors. The presence of feathers, particularly in theropod dinosaurs, potentially reveals critical differences between growth stages. Juvenile theropods possibly exhibited downy feathers that allowed for better temperature regulation while also providing camouflage in their habitats, while adults displayed larger feathers for mating displays or insulation. This feather development paradigm is crucial for survival, providing insights into their growth, behavior, and ecological roles. Moreover, the skin color and patterns could also vary significantly between these stages. Bright colors or patterns could denote sexual maturity in adults, impacting mating behaviors and territorial displays. The study of fossilized skin impressions allows for a more profound understanding of these characteristics. Overall, understanding skin variations in juvenile and adult dinosaurs enriches our knowledge of their survival strategies and environmental adaptations, emphasizing the evolutionary mechanisms at play in these magnificent creatures.
The differences in reproductive anatomy between juvenile and adult dinosaurs also play a pivotal role in understanding their life cycle. Adult dinosaurs were equipped with complex reproductive systems suited for laying eggs or nurturing young, while juveniles exhibited simpler versions. In many species, juvenile dinosaurs may not have possessed the physical adaptations needed for reproduction. This dynamic sheds light on the reproductive strategies employed by different dinosaur species and their ecological significance. It illustrates the gradual transition from juvenile innocence to mature responsibilities within the lifecycle of these prehistoric giants. Paleontological evidence highlights how reproductive anatomy underwent changes parallel to the physical growth of dinosaurs. Such anatomical changes often reflected not just size, but also differences in behavior related to mating and parental care. The reproductive adaptations likely ensured species survival, as they would have dictated mating rituals and parental investment in offspring. Further exploration of these differences will enhance our understanding of the evolutionary pressures that shaped reproductive strategies and the overall life cycles of dinosaurs. This crucial element reflects broader patterns of growth, survival, and evolution through the ages of these magnificent animals.
Conclusion
The examination of anatomical differences between juvenile and adult dinosaurs provides deeper insight into their biology, behaviors, and ecological roles throughout their lifespans. As seen, variations in bone structure, muscle composition, skin textures, and reproductive systems significantly highlight the complexities of growth in these creatures. The juvenile stages often reveal adaptations vital for survival and highlight the evolution and changes necessary as the dinosaurs matured into adults. Understanding how these differences affected their lifestyles is essential for contextualizing the entire species within prehistoric ecosystems. This accumulated knowledge not only enhances our understanding of dinosaurs themselves but also offers clues about their relationships with other species during their time. Fossil evidence continues to play a critical role in shedding light on these differences, as every discovery contributes to a larger narrative of dinosaur evolution. In essence, the differences between juvenile and adult dinosaur anatomy reflect a fascinating interplay of biology and ecology, providing a lens through which to view natural history. Continued research in this area promises to unveil more captivating aspects of dinosaur life, emphasizing the importance of understanding evolutionary pressures and developmental patterns.