The Role of Ecotourism in Promoting Habitat Conservation
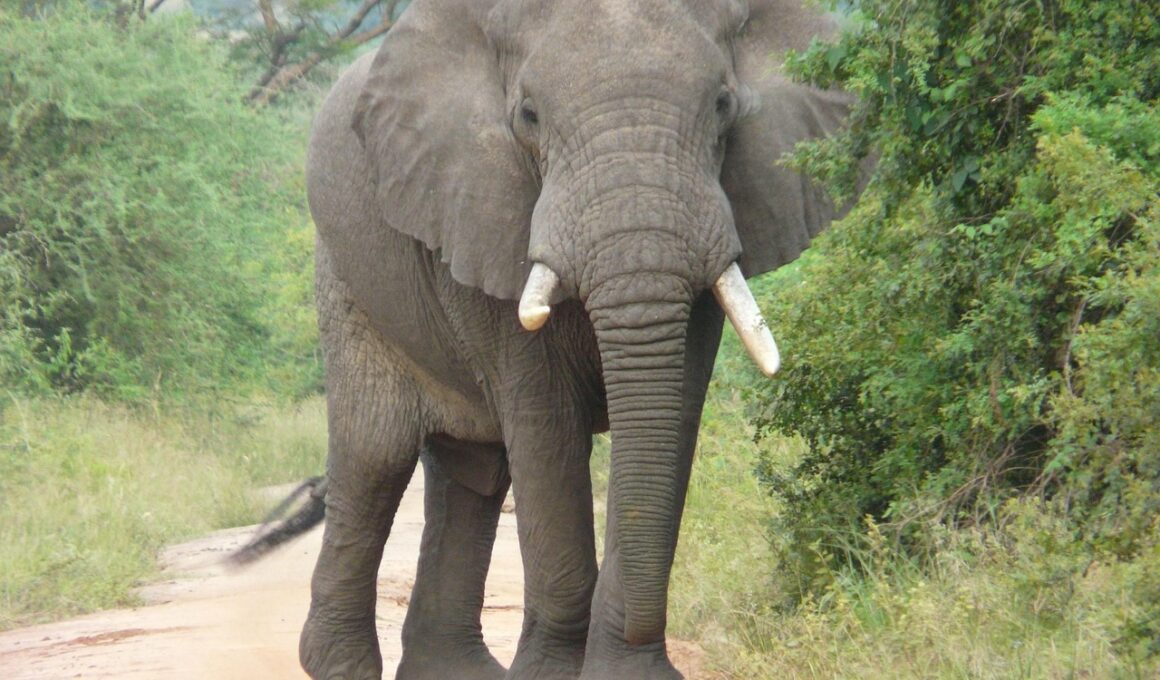
Ecotourism is more than just a travel trend; it represents a vital approach to conservation that benefits both nature and local communities. By emphasizing sustainable travel practices, ecotourism encourages visitors to appreciate natural habitats while fostering environmental respect. Conserving regions at risk, ecotourism creates an economic incentive to preserve endangered ecosystems. Tourists engage with wildlife and explore diverse landscapes, which can include tropical rainforests, coral reefs, and savannas—habitats that provide essential services. This engagement translates into financial support for local conservation efforts while raising awareness of the environmental challenges these areas face. Moreover, ecotourism promotes responsible travel behaviors, such as minimizing waste and respecting wildlife. In doing so, it instills in individuals an appreciation for preservation and sustainability as a collective responsibility. Over time, these visits can lead to public pressure on governments to protect at-risk habitats and implement conservation policies. This relationship fortifies the commitment to habitat preservation and amplifies the voice of local communities who often serve as guardians of their environmental resources. Ultimately, ecotourism can be harnessed as a powerful tool in the fight against habitat destruction worldwide.
Ecotourism offers significant economic opportunities to communities living in or around threatened habitats. When these communities witness the financial benefits of preserving their natural environment, they are more likely to protect the ecosystems that sustain them. Local businesses flourish with responsible tourism, creating jobs that revolve around conservation. Potential employment avenues are guided tours, wildlife tracking, and educational workshops. By establishing a link between tourism and conservation efforts, communities can cultivate sustainable income sources. Tourists are increasingly drawn to experiences that blend adventure with educational components, allowing them to better understand the value of biodiversity. Efforts are often made to ensure that proceeds directly support conservation projects, thereby reinforcing local engagement in sustainability. As conservation funding can be directed toward protecting natural habitats, ecotourism brings communities into the fold of ecological preservation. Furthermore, educational programs can empower locals to become effective stewards of their environments. This not only benefits biodiversity but also ensures that future generations will live in vibrant ecosystems. This comprehensive approach ensures a harmonious relationship between human activities and ecological balance, paving the way for sustainable development opportunities that resonate throughout society.
Awareness and Education Through Ecotourism
One of the primary advantages of ecotourism is its ability to raise awareness and educate the public about environmental issues. Tourists who participate in ecotourism activities—such as guided wildlife tours or conservation volunteer projects—become more informed about the threats facing various habitats. Education is a crucial aspect of fostering a strong conservation ethic, as it empowers individuals to make sustainable choices in their daily lives. Additionally, education through ecotourism encourages tourists to recognize their impact on ecosystems, highlighting concepts like carbon footprints, overconsumption, and habitat loss. Oftentimes, tour operators integrate educational resources—including brochures, workshops, and talks—into their offerings. These educational components help bridge the gap between local communities and tourists, fostering cultural exchange. Furthermore, they help visitors understand their role in supporting conservation initiatives. As tourists educate themselves regarding the specific issues facing a location, they are more likely to advocate for conservation efforts once they return home. Advocacy can extend beyond monetary support to include lifestyle changes, encouraging responsible consumption patterns and sustainable travel practices that protect ecosystems worldwide.
Preserving animal species that inhabit fragile ecosystems is another vital contribution of ecotourism. As the focus on wildlife conservation grows, more travelers seek experiences that highlight endangered species. Ecotourism thrives on wildlife observation, where educated visitors can witness animals in their natural habitats. Observing endangered species in the wild creates an emotional connection, prompting individuals to become advocates for their protection. Additionally, ecotourism can support breeding programs and habitat restoration efforts aimed at species recovery. Tourists can contribute to funding these programs through entry fees or donations. Conservation organizations collaborate with ecotourism operators to ensure that best practices are employed. This collaboration not only enhances visitor experiences but solidifies critical research partnerships necessary for species study. Tourists also gather data during their visits, aiding conservation scientists in understanding animal behavior and habitat needs. Lastly, the influx of tourism can serve as a catalyst for government intervention. When endangered species attract attention and concern, it can motivate policymakers to enact stricter regulatory measures to ensure their safety. In this way, the role of ecotourism continues to evolve, forming a sustainable bridge between environmental stewardship and economic growth.
Local Community Engagement
Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is essential for sustainable ecotourism. Respecting the voices and needs of local populations not only enhances authenticity but also fosters shared ownership of natural resources. Communities often possess invaluable traditional knowledge on local ecosystems, contributing to enhanced conservation strategies. By including them in design and implementation, ecotourism can create programs and services that cater specifically to local and traveler needs. Local guides, for example, can offer unique insights into biodiversity while creating immersive experiences for tourists. This deeper engagement elevates the visitor experience and cultivates meaningful connections with nature. Furthermore, community-based ecotourism empowers residents by distributing the economic benefits of tourism equitably. Consequently, individuals are more likely to invest in their ecosystems’ health. Taking part in conservation initiatives can also serve as an important avenue for skill development. By providing training, local residents can acquire skills necessary for sustainable tourism practices. Building these capacities ensures that communities can thrive environmentally and economically, creating a sustainable legacy that benefits all parties involved. This convergence of interests solidifies the foundation of ecotourism as a driving force for conservation, linking the future of local cultures and ecosystems together.
Ecotourism also plays a crucial role in funding conservation projects, which provide resources for protecting threatened habitats. Many ecotourism operations allocate a portion of their profits directly toward local conservation initiatives. These funds can be utilized for habitat restoration, anti-poaching efforts, or scientific research. This financial support becomes vital in areas where government resources may be limited. By engaging with tourists who contribute financially, ecotourism amplifies the potential for long-lasting positive change in vulnerable habitats. These conservation projects typically involve a multifaceted approach that combines ecological restoration with community involvement. For instance, local stakeholders may collaborate to create incentives for landowners to engage in conservation. Moreover, ecotourism can stimulate broader interest in ecological studies, attracting researchers and scientists from various fields. Funding derived from tourism grants organizations the ability to study how endangered species interact with their habitats. These empirical findings yield transformative insights, leading to well-informed conservation strategies. Therefore, ecotourism serves as a critical mechanism to promote not only the preservation of endangered habitats but also the progression of scientific knowledge—an essential stepping stone toward sustainable environmental management.
Challenges and Future Direction
Despite its numerous benefits, ecotourism also faces challenges that can hinder its potential to contribute to habitat conservation effectively. Over-tourism, for instance, can lead to environmental degradation and strain local ecosystems, ultimately countering conservation efforts. Managing visitor numbers is essential to mitigate the environmental footprint that travel can produce. Developing policies that promote responsible tourism while protecting the sanctity of habitats is crucial. Furthermore, educating tourists about their impact and promoting sustainable choices can enhance the overall effectiveness of ecotourism initiatives. Balancing economic gain with environmental responsibility remains a central concern. Lastly, fostering collaborations among stakeholders—including governments, NGOs, and local communities—ensures that ecotourism aligns with broader conservation goals. Monitoring the effectiveness of ecotourism programs is another crucial element; ongoing assessment enables adaptations to meet environmental and social needs. By openly addressing challenges and continuously improving practices, ecotourism can play a pivotal role in promoting habitat conservation. Moving forward, the integration of technology to track environmental impacts and visitor behaviors further positions ecotourism as a viable, sustainable solution toward safeguarding endangered habitats worldwide.
In conclusion, the intersection of ecotourism and habitat conservation presents numerous opportunities for the protection of threatened ecosystems. Through economic incentives, awareness-building, and local community engagement, sustainable travel practices can create a significant positive impact on biodiversity preservation. The collaborative efforts of ecotourism operators, local communities, and conservation organizations synergize to champion the protection of endangered habitats. Moreover, tourists themselves have a role to play by making conscious travel choices that prioritize conservation. Together, these collaborative efforts cultivate a brighter future for wildlife and their habitats while establishing sustainable livelihoods for local communities. Building on these achievements, it remains vital to address challenges that could undermine ecotourism’s effectiveness. Continuous engagement with stakeholders, ongoing education, and the integration of sustainable practices will pave the way for a more effective ecotourism model. The future of habitat conservation relies on collective action and a shared vision towards the sustainable interaction of humans and nature. As ecotourism evolves, its potential as a transformative force for ecological preservation is undeniable and essential for the survival of our planet’s vanishing natural habitats.