Dholes: The Asiatic Wild Dogs
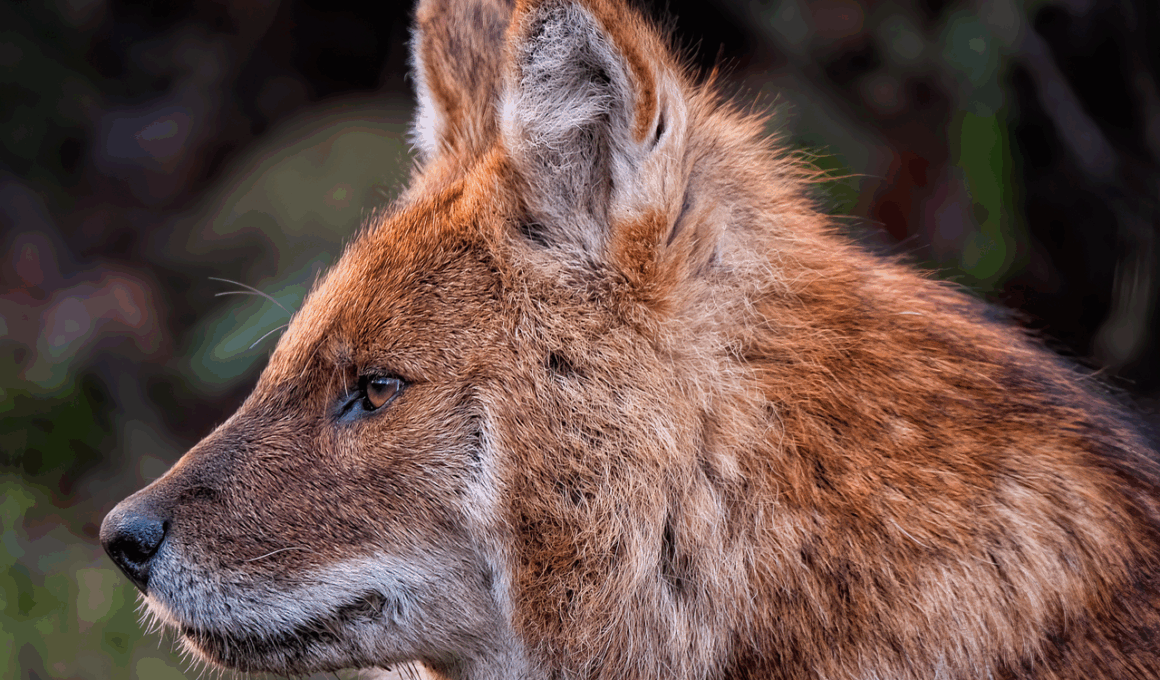
Dholes (Cuon alpinus), often called Asiatic wild dogs, are a captivating species found in specific habitats across Asia. These social animals thrive in packs, typically consisting of five to twelve dogs, embodying an intricate social structure that facilitates hunting and raising the young. Known for their reddish-brown fur and bushy tails, dholes showcase remarkable agility, which aids them in navigating their forests and grasslands, where they hunt primarily for deer, boar, and livestock. With a unique vocalization system, they can communicate effectively within their packs, allowing for coordinated hunts. Dholes can cover great distances, which is critical for chasing prey over varied terrain. Research has indicated that their numbers have declined significantly over recent decades mainly due to habitat loss and competition with other carnivores. Conservation efforts are critical to ensuring that these wild dogs continue to exist in the wild. Unique in behavior and ecology, dholes warrant the attention of both researchers and wildlife enthusiasts. Observing these incredible animals in their natural habitat is a thrilling experience that helps underscore their importance in maintaining ecological balance.
Habitat and Distribution
Primarily found in parts of Southeast Asia, dholes inhabit regions ranging from grasslands to dense forest areas. Their adaptability enables them to thrive in varied climates, yet they prefer habitats with abundant prey. The range of dholes extends across a variety of countries, including India, Nepal, Bhutan, China, and Southeast Asian nations. Unfortunately, their distribution is not as widespread as it once was, as their populations are often fragmented due to human activity and habitat changes. These dogs make their dens in natural cavities, utilizing abandoned burrows or rock formations to secure their young. The characteristics of their habitats, such as the availability of water and prey, directly influence the structure of their packs. While they are most commonly found in forested regions, dholes adapt well to different environmental conditions, demonstrating their resilience. They are primarily active during dawn and dusk, which coincides with higher prey visibility. Protecting their habitat is vital for sustaining the best conditions for their survival. Conservation efforts focused on preserving the ecosystems they inhabit play a significant role in ensuring the longevity of dholes.
Dholes are a unique aspect of wildlife, contributing significantly to the biodiversity in their ecosystems. Their social behavior is fascinating, as they display a high level of cooperation while hunting and caring for their young. The pack dynamics are similar to those of wolves, involving complex interactions that promote teamwork. Dholes are particularly known for their impressive hunting techniques, often employing a strategy where they chase down prey over long distances, with members taking turns to wear out the target. Their diet primarily consists of medium to large ungulates, including species like sambar deer and wild boar. However, they are also opportunistic feeders, consuming smaller animals and scavenge when necessary. The ability of dholes to adapt to diverse feeding habits helps them withstand various environmental challenges. Reproduction in dholes usually takes place once a year, with litters averaging about five to six pups. The parental care received is remarkable, as all pack members contribute to the upbringing of the young. This collaborative breeding strategy increases the survival rate of pups, ensuring the next generation of these wild dogs can thrive. Monitoring their population is crucial for effective conservation management.
Conservation Status and Challenges
The conservation status of dholes remains a pressing concern due to various threats they face in their natural habitat. Classified as endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), their populations have significantly decreased over the past few decades. Habitat destruction caused by deforestation and agricultural expansion has resulted in severe fragmentation of their living spaces. Additionally, dholes face intense competition from more dominant carnivores, such as tigers and leopards, further complicating their survival. The human-wildlife conflict often leads to retaliatory killings, particularly when dholes prey on livestock. This conflict undermines the essential role dholes play in maintaining ecological balance, leading to a decline in their numbers. Conservation initiatives are critical, focusing on habitat restoration and legal protections to safeguard their populations. Awareness programs aimed at local communities play a vital role in minimizing human-wildlife conflict and fostering coexistence. Protecting crucial habitats ensures the survival of these remarkable animals while promoting biodiversity. Collaboration among governments, NGOs, and local communities is necessary to secure the future of dholes in the wild.
Education and awareness about dholes are integral parts of their conservation story. Efforts are being made to engage local communities in understanding the ecological importance of these wild dogs, emphasizing their role in maintaining healthy ecosystems. Educational programs often highlight the balance between predator and prey dynamics, showcasing how dholes help control herbivore populations. The involvement of local people in conservation projects encourages sustainable practices and denounces harmful actions against wildlife. Moreover, wildlife tourism that features dholes and other exotic species can provide economic incentives for communities to actively participate in conservation efforts. Responsible tourism brings funding that supports habitat preservation and creates jobs, reinforcing the need for protecting these unique animals. Research and monitoring are ongoing aspects of conservation work aiming to better understand dholes’ behavior, ecology, and genetics. Collaborations with universities and wildlife organizations enhance knowledge about these elusive creatures. The sharing of experiences and success stories can inspire people worldwide to appreciate and protect wildlife. By promoting a shared sense of responsibility towards conserving dholes, we can build a future where humans and wildlife coexist harmoniously.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, the continuation of studies on dholes is essential not just for their survival but for overall ecosystem health. Recognizing their role in their habitats and advocating for their protection is necessary for future conservation efforts. Given the challenges they face, we must reinforce the importance of ongoing research, public education, and community involvement. Long-term strategies need to focus on sustainable land practices, enhancing biodiversity, and preserving genetic diversity within dholes’ populations. As complexities regarding climate change increase, understanding how they adapt could shed light on broader conservation efforts. Collaborative international efforts to conserve dholes can yield significant results, paving the way for thriving wildlife in various regions. Their unique social structures offer an opportunity to study complex mammalian social behaviors and ecological interactions. With dedicated efforts in place, there’s hope for reversing the trends of decline. Conservation success stories inspire further action and reveal how coexisting with wildlife can be mutually beneficial. Dholes represent an integral piece of the puzzle in wildlife ecosystems, and their conservation remains crucial to safeguarding our planet’s rich biodiversity.
Overall, dholes embody a remarkable example of a species faced with adversity but also an opportunity for conservation success. Their captivating social dynamics and impressive hunting strategies present opportunities for research in ethology and ecology. By developing comprehensive conservation plans that account for their intricate social structures and behaviors, efforts can be tailored to meet the specific needs of this species. Involving a wider audience in their preservation ensures a collective responsibility to protect these wild dogs. The future for dholes can be bright if communities unite their voices for wildlife and support sustainable practices. As with many wildlife conservation initiatives, the key lies not only in legal protections but also in fostering positive relationships between humans and nature. Encouraging awareness through diverse platforms will increase public interest and commitment. By investing in education and engaging with local communities, we can ensure that dholes and their habitats receive the attention they deserve. Continuing to study and protect dholes ensures that future generations can enjoy witnessing these magnificent animals roaming freely in the wild.
Understanding and advocating for the conservation of dholes entails recognizing their unique ecological role and the beauty of their behaviors. As wildlife enthusiasts and conservationists, our responsibility is to share the urgency of protecting this endangered species and the ecosystems where they thrive. Raising awareness about their plight will foster empathy and support for conservation actions. Efforts to monitor populations and habitats of dholes contribute to informed management strategies that can lead to more sustainable results. The journey towards preserving dholes reveals the interconnectedness of all living beings and the shared responsibility of inhabiting this planet. Mobilizing support for wildlife in need can lead to meaningful change. The natural world depends on the survival of species like dholes, making their conservation more urgent than ever. Through commitment, collaboration, and education, we can ensure that the legacy of dholes continues in the wild. Each small action contributes to a bigger mission of wildlife preservation. The journey towards a sustainable future for dholes and other wildlife species is a shared endeavor, one that holds promise for all living beings.