Impact of Climate Change on Mammal Populations
Climate change has become one of the most pressing issues for conservationists and researchers alike. The effects of rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns have significantly impacted mammal populations worldwide. As habitats shift and seasonal cycles alter, many species face challenges in food availability, reproductive success, and habitat suitability. Consequently, it becomes crucial to identify the species at risk and develop targeted research projects. Such studies are aimed at understanding patterns in mammalian population declines across various ecosystems. Conservation efforts must be rooted in a solid understanding of these dynamics, allowing for better management strategies. Researchers are employing various methods, including field studies, remote sensing, and genetic analysis, to gather data on mammals affected by climate change. These insights will help create predictive models for future scenarios. In certain cases, species are migrating to higher altitudes or latitudes in search of suitable climates, which may lead to conflicts with human activities. If these trends continue, biological diversity will decline and lead to ecosystem imbalances. Protecting critical habitats and corridors is paramount for the survival of many vulnerable species in the face of climate change.
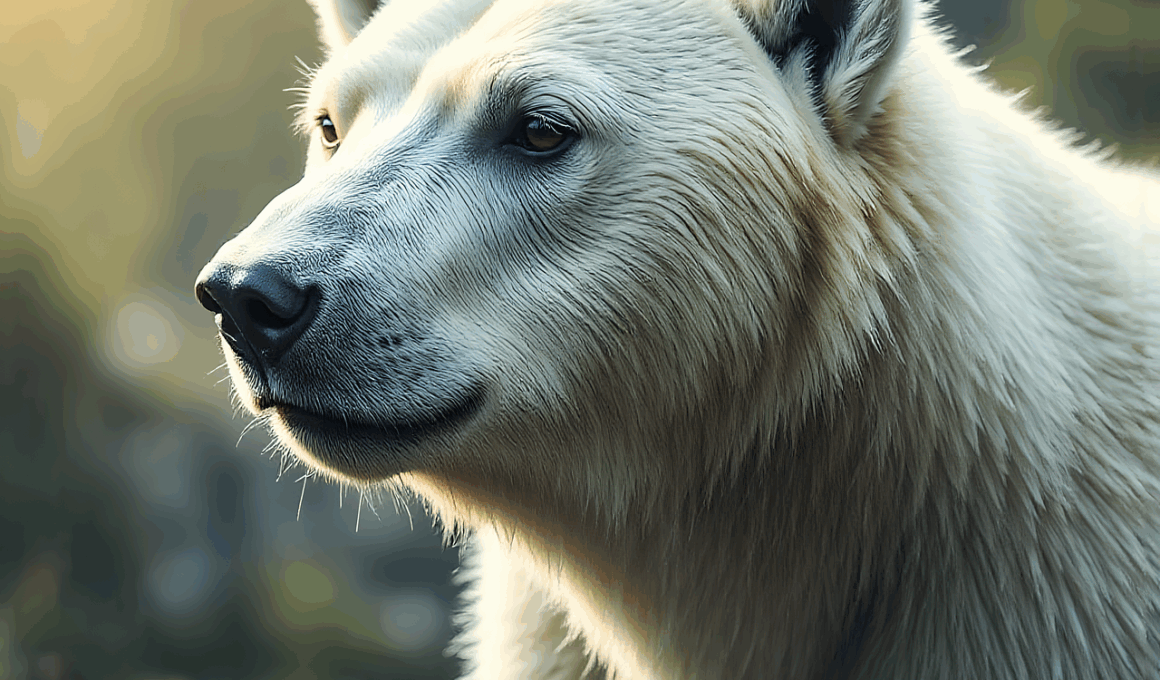
The effects of climate change on mammals extend far beyond just temperature and precipitation. Habitat fragmentation often worsens the impacts due to human activities, such as agriculture and urban development. Mammals, which require large territories for foraging and breeding, are particularly vulnerable to these changes. Many species are finding it increasingly difficult to adapt or can no longer migrate to suitable habitats. For instance, polar bears rely on sea ice as their platform for hunting seals, their primary food source. With climate warming melting sea ice at a rapid pace, their populations have begun to decline dramatically. Furthermore, increased human-wildlife conflict poses another threat, as animals are forced closer to populated areas. This can lead to dangerous encounters and increased mortality rates. To mitigate these problems, scientists are focusing on collaborative efforts involving local communities. Sustainable land-use practices can help reduce habitat destruction, while awareness campaigns can improve human perceptions of wildlife. Continuous monitoring and research are essential to track changes in populations and guide appropriate conservation actions. More investment and support for such initiatives will be critical in addressing these ongoing challenges. Conservation strategies should be flexible and adaptive to ongoing changes in ecosystems.
Project Examples and Collaborations
Numerous mammal research projects are currently being conducted to understand the effects of climate change. These projects range from local initiatives to international collaborations aimed at conserving different species. For example, a significant project in the Amazon rainforest evaluates how temperature increases alter the distribution of various mammal species, especially those endemic to specific regions. The findings from such projects are essential for informing policymakers about critical habitats that need protection. Additionally, large-scale tracking studies on migratory species like caribou are being undertaken to monitor how their ranges change over time. These studies utilize innovative technologies like GPS collars to gather accurate data on movement patterns. They also explore food availability and interactions with other species affected by climate change. By analyzing these data, researchers can develop effective strategies to manage habitats and mitigate risks. Collaborative research efforts, involving governments and non-profits, enhance the impact of individual projects, ensuring that findings are widely shared and acted upon. Engaging the public in such projects also raises awareness about the importance of conservation. Ultimately, these initiatives strive to protect biodiversity amidst changing environmental conditions, aiming to sustain populations of mammals for generations to come.
Mammals are not only affected on an individual level but also within their populations. Social structures may shift due to climate-induced pressures, resulting in potential conflict during breeding seasons. For example, changes in the availability of resources can lead to increased competition among individuals. This competition could impact reproductive success and juvenile survival rates, ultimately reducing population numbers. In species with complex social structures, such alterations could disrupt group dynamics, affecting the overall fitness of the population. These changes can also influence mating patterns and gene flow among populations. When resources become scarce, stress levels rise, which can affect overall health and immunity. Notably, thermal stress is an emerging concern for many mammals, particularly those in more vulnerable habitats. Strategies aimed at minimizing these effects must consider specific species’ biology and behavior. Understanding how climate change influences social structures in mammals is a vital avenue for future research. The cumulative impacts of these pressures may lead to significant declines if not adequately addressed. Researchers are encouraged to consider these social implications alongside ecological factors to enrich conservation planning. Collaboration among scientists and stakeholders remains critical to develop adaptive strategies that can keep pace with changing environmental conditions.
The Role of Genetics in Adaptation
Genetic diversity is essential for populations to adapt to climate change. Research shows that genetic variations bestow resilience in species, enabling them to withstand alterations in their environment. Evaluating genetic diversity in mammal populations can provide insights into their ability to adapt to changing climates. For instance, studies on genetic markers have helped uncover how certain mammals possess traits that enhance their survival in varying conditions. Understanding these genetic traits can inform conservation strategies aimed at protecting and enhancing the adaptability of vulnerable populations. Genetic research aids in identifying key populations for conservation efforts, ensuring that genetic diversity is maintained in the face of environmental changes. Additionally, assisted gene flow or translocation efforts may sometimes be considered, particularly in endangered species close to extinction. These approaches require a precise understanding of the genetic makeup of the populations involved to be effective. Continuous monitoring of genetic variations can identify shifts in diversity as conditions change, underscoring the importance of integrating genetics into conservation research. Prioritizing projects with a genetic focus will be vital for the future of many mammal populations as they respond to the challenges posed by climate change.
Community engagement and education play a significant role in the success of mammal conservation initiatives. Raising awareness about the impacts of climate change on mammals encourages local communities to participate in conservation efforts. Communities that understand the value of wildlife are more likely to support protective measures, contributing to conservation success. Educational programs can foster a sense of stewardship toward local wildlife, emphasizing the role of mammals in maintaining ecosystem balance. Projects centered around citizen science invite laypeople to collect data, which can augment researchers’ findings. These initiatives empower communities, providing them with tools to observe and report changes in wildlife populations firsthand. Collaborations with schools and local organizations can facilitate the transfer of knowledge and spark interest in environmental sciences. Involving young people in conservation efforts can inspire a new generation of ecologists, ultimately shaping future conservation strategies. A well-informed public is a crucial ally in the battle against biodiversity loss fueled by climate change. Transforming communities into active participants in conservation initiatives can yield significant benefits for mammal populations. Engaging people from all walks of life in these projects will build resilience against the ongoing impacts of climate change.
Future Directions in Mammal Research
The future of mammal conservation research hinges on interdisciplinary approaches that incorporate various fields of study. Integrating ecology, genetics, and sociology will yield a thorough understanding of mammals’ complexities as they navigate climate change. Emerging technologies, such as machine learning and remote sensing, will revolutionize the capacity to gather and analyze data. Effective deployment of these advanced tools can enhance predictive modeling of species distributions under changing climates. Researchers should continue exploring how anthropogenic pressures and climate change interact to inform more precise conservation strategies. Collaborative partnerships between research institutions, governments, and local stakeholders remain essential for advancing knowledge and effectiveness in conservation efforts. Future projects must be adaptable, addressing rapid environmental changes to ensure mammal populations’ perseverance. Continuous assessments of threats and responses will be necessary to adjust strategies as new information becomes available. Funding for innovative research endeavors is crucial to overcoming the challenges posed by climate change. Through combined efforts and dedication, the scientific community can pave the way for more sustainable outcomes for mammals facing uncertain futures. Collaborative efforts will be the cornerstone of successful conservation initiatives as we move forward.
In conclusion, climate change represents one of the most profound threats to mammal populations globally, impacting their survival and biodiversity. The need for urgent action and effective research strategies is critical for addressing these challenges. Collaborative efforts between researchers, conservationists, and the public can lead to positive outcomes when developing innovative solutions. Integrating various research methods, including genetics and community engagement, enhances the understanding and protection of mammal populations. The stakes are high, and without decisive action, many species may face extinction within the next few decades due to climate change. Constant monitoring, adapting to new information, and adjusting strategies are essential to alleviating these pressures. Moreover, the importance of education and community involvement cannot be overstated. Fostering an informed and engaged public is vital for conservation success, as communities become advocates for local mammal populations. As we strive to protect our planet’s biodiversity, we must ensure that conservation actions are grounded in scientific research and community support. Only then can we hope to mitigate the impacts of climate change and secure a future for our mammalian friends across different ecosystems.