Marsupial Population Monitoring Techniques
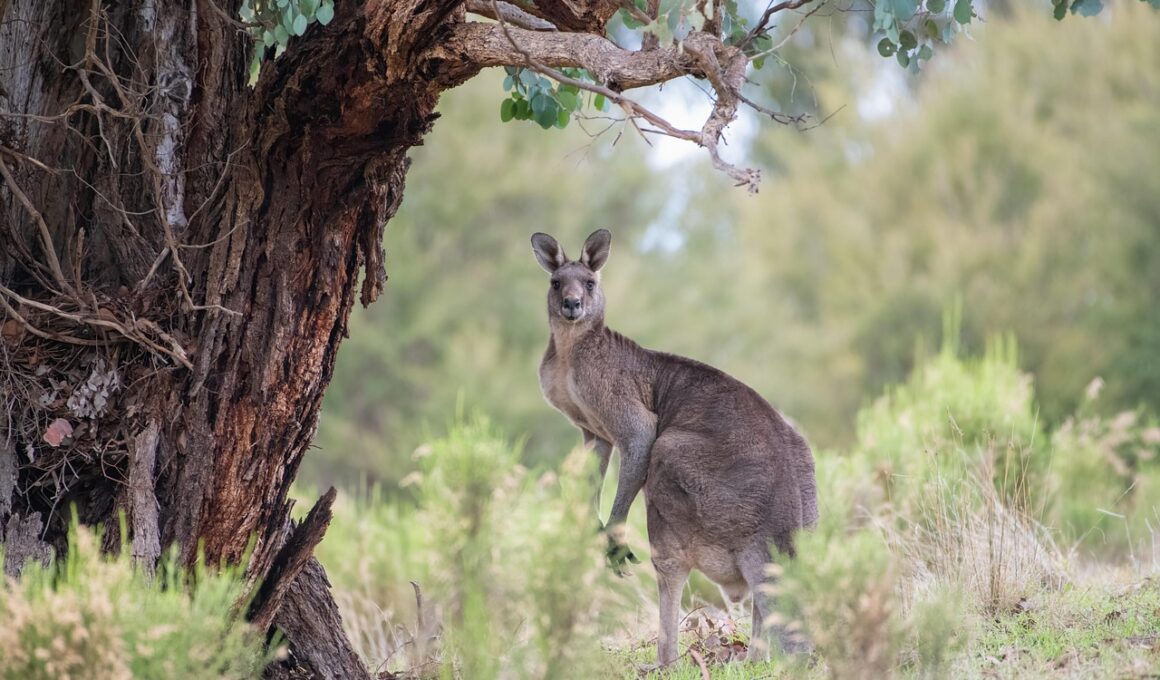
Marsupials are fascinating creatures that play significant roles in ecosystems. Monitoring their populations is crucial due to the threats these animals face. Traditional methods like counts and sightings have limitations; therefore, new techniques are essential. Effective monitoring requires a combination of methods that include direct observation, tracking, and scientific analysis. The first step involves identifying specific habitats where marsupials thrive, which can vary drastically. Understanding their behavior patterns is essential. Use of camera traps has gained popularity for capturing their activities unobtrusively. These devices provide valuable data without human interference. Sound recording devices also offer insights into marsupial communications and interactions. Remote sensing technology aids in mapping their distribution and habitat changes over time. Combining these approaches helps in developing ecological models which can predict future population dynamics. Additionally, community involvement can enhance data collection. Local volunteer programs can track sightings and contribute to broader databases. Collaboration between researchers and the public increases awareness and conservation efforts. Moreover, this collaboration fosters a sense of responsibility towards protecting marsupials. Continued research and innovation in population monitoring will help safeguard their future.
One notable aspect of monitoring these fascinating creatures comes from genetic analysis. Understanding the genetic diversity within marsupial populations can help evaluate their health. Genetic monitoring can reveal how isolated populations are adapting to environmental changes. For instance, advancements in molecular techniques allow researchers to collect and examine DNA samples from marsupials. This genetic information can guide conservation strategies effectively. Additionally, understanding migration patterns through genetic studies helps maintain genetic flow. By identifying distinct populations, it is possible to inform captive breeding programs. Such programs can enhance genetic diversity, improving the chances of species survival. Furthermore, integrating citizen science reinforces the significance of public engagement in scientific endeavors. Training locals on how to collect samples increases the volume of data available to researchers. This sustainable approach not only enhances research but also fosters community ties to biodiversity. Data collected can also inform land management practices ensuring habitat connectivity. Moreover, long-term studies that track population changes over time provide essential insights into the effectiveness of conservation initiatives. The intersection of traditional methods and modern sciencewill undoubtedly enhance the future of marsupial conservation.
The Role of Technology in Monitoring
Modern technology has revolutionized the way researchers monitor marsupial populations. Tracking devices, such as radio collars and GPS units, enable real-time data collection. These devices can track movement patterns and habitat use, yielding invaluable insights. The data collected helps in understanding their daily activities and seasonal behaviors. Such information is crucial when planning conservation efforts, as it highlights critical areas for protection. Furthermore, technology facilitates remote data collection. Drones equipped with cameras can survey large areas, providing perspectives that ground surveys cannot. This allows researchers to monitor populations without causing disruption to their natural behavior. Moreover, remote sensing provides data on habitat conditions, incorporating both morphological and climatic factors. By analyzing these elements, researchers can predict how environmental changes might affect marsupial populations. Integration of artificial intelligence in data analysis enhances the ability to identify patterns within vast datasets. This data-centric approach empowers researchers to make informed decisions, driving effective conservation outcomes. Ultimately, technology paves the way for a comprehensive understanding of marsupial dynamics, one that bridges gaps between traditional knowledge and cutting-edge science.
Field surveys remain fundamental in marsupial population studies, despite technological advancements. These surveys can involve direct counts, transect walks, or systematic trapping programs. Field methods provide invaluable grounding knowledge while complementing technological approaches. Well-designed surveys help ascertain population sizes and distribution patterns. Emphasizing standardized methodologies is crucial to ensure data consistency. Long-term datasets acquired through repeated surveys are vital for assessing trends and identifying threats. Researchers often enlist trained volunteers to broaden survey efforts, which can amplify their findings. A diverse range of community volunteers brings additional insights and perspectives to data collection processes. Collaborations between various institutions can enhance knowledge-sharing, thus improving methodologies over time. Moreover, incorporating local ecological knowledge into surveys can yield unexpected results, as locals often have insights into behavior patterns unnoticed by observers. Regular training ensures volunteers are prepared and knowledgeable, maintaining the study’s integrity. Furthermore, ensuring ethical practices and minimizing animal stress during surveys is paramount. This involves understanding animal welfare principles in field methodology. Ultimately, effective population monitoring of marsupials thrives on a blend of technology and traditional field techniques, promoting robust conservation practices.
Importance of Data Interpretation
Data interpretation plays a pivotal role in marsupial population monitoring. Collecting data is only the first step; subsequent analysis can drive meaningful conservation strategies. Employing statistical models allows researchers to draw insights related to population dynamics. Notably, employing tools like occupancy modeling provides an understanding of detection rates in various habitats. They can estimate abundance and evaluate how environmental changes impact populations. Importantly, understanding the context of data is crucial for accurate interpretation. Researchers must consider local ecological variables, geographic regions, and historical data to avoid misrepresentation. Visualization techniques, such as mapping or graphs, can significantly aid in conveying findings clearly to stakeholders. Additionally, effective communication of results to the public enhances awareness of marsupial conservation issues. Engaging with policymakers is equally crucial, as data empowers effective decision-making regarding the management of lands and resources. Collaborative efforts with indigenous communities and local organizations can make these findings more relevant. Sharing insights at conferences promotes discussions among conservationists and researchers alike. Such dialogues foster innovative ideas and collaborations that could further enhance conservation outcomes for marsupials. Therefore, robust data interpretation is the backbone of successful marsupial population monitoring.
Valuing the role of education in conservation is paramount for marsupial population monitoring. Raising awareness about the significance of these unique creatures can motivate conservation efforts. Initiatives such as community workshops and school programs foster understanding amongst younger generations. Education empowers individuals to recognize the threats faced by marsupials, including habitat loss and climate change. By encouraging active participation in conservation, individuals become better stewards of their environment. Schools can incorporate field trips to habitats, providing practical experiences that enhance understanding. Engaging storytelling methods can captivate children’s attention regarding marsupial life and their ecosystems. Additionally, promoting citizen science projects amplifies community participation, allowing locals to track marsupial sightings. This inclusiveness ensures that monitoring efforts are comprehensive, helping build larger datasets. Sharing success stories regarding marsupial recovery also instills a sense of hope and encourages further action. Moreover, offering formal training to volunteers increases the skills and efficacy of fieldwork. Collaboration with local universities can bolster educational outreach programs. By integrating knowledge with action, communities can significantly impact the future of marsupials. Continued advocacy for education and outreach will solidify support for conservation initiatives.
Conclusion on Marsupial Conservation
In conclusion, monitoring marsupial populations through various techniques is vital to their conservation. The collaborative integration of technology, field surveys, and community involvement fosters a comprehensive understanding of these unique animals. It paves the way for informed decision-making regarding landscape management and conservation priorities. Through ongoing research and data sharing, new interventions can emerge that protect marsupials from the threats they face. Long-term partnerships with local communities lead to stewardship, ensuring that conservation becomes a shared responsibility. Education plays an indispensable role in this process, inspiring future generations to value biodiversity. As we advance our technological capabilities, merging them with traditional knowledge further enriches marsupial understanding. Ultimately, every effort that promotes awareness and conservation lays the groundwork for sustainable ecosystems. Fostering a collective commitment to preserving marsupials, biodiversity in general, contributes to ecological balance. Future monitoring strategies will continue to evolve, contributing significantly to the success of conservation efforts. Ensuring the survival of marsupials not only maintains ecological integrity but enriches cultural landscapes as well. Thus, through dedication and strategic monitoring, we can secure a brighter future for marsupials and their habitats.
As we look ahead, the impact of policy changes on marsupials cannot be overlooked. Legislation focusing on wildlife protection directly influences monitoring efforts. Policies that prioritize habitat preservation create more opportunities for these creatures to thrive. Conversely, insufficient regulations can exacerbate issues like habitat fragmentation and poaching. Researchers and advocates must work collaboratively with governments to establish protective measures for marsupials. Comprehensive land-use planning is vital for balancing development and wildlife conservation. Sustainable practices in agriculture, forestry, and urban planning can significantly reduce human-wildlife conflicts. By integrating marsupial needs into policy frameworks, we promote coexistence. Furthermore, engaging the public in advocacy campaigns enhances political pressure on decision-makers. Public awareness should highlight the importance of maintaining biodiversity. Additionally, long-term funding allocation towards conservation initiatives is crucial. Securing financial resources allows for uninterrupted monitoring efforts and research. Partnerships between governmental and non-governmental organizations can leverage funding for project implementation. With continued advocacy, research, and collaboration, we can pave the way for a sustainable future for marsupials. The collective voice for these incredible creatures will ensure their place in our ecosystems for generations to come.