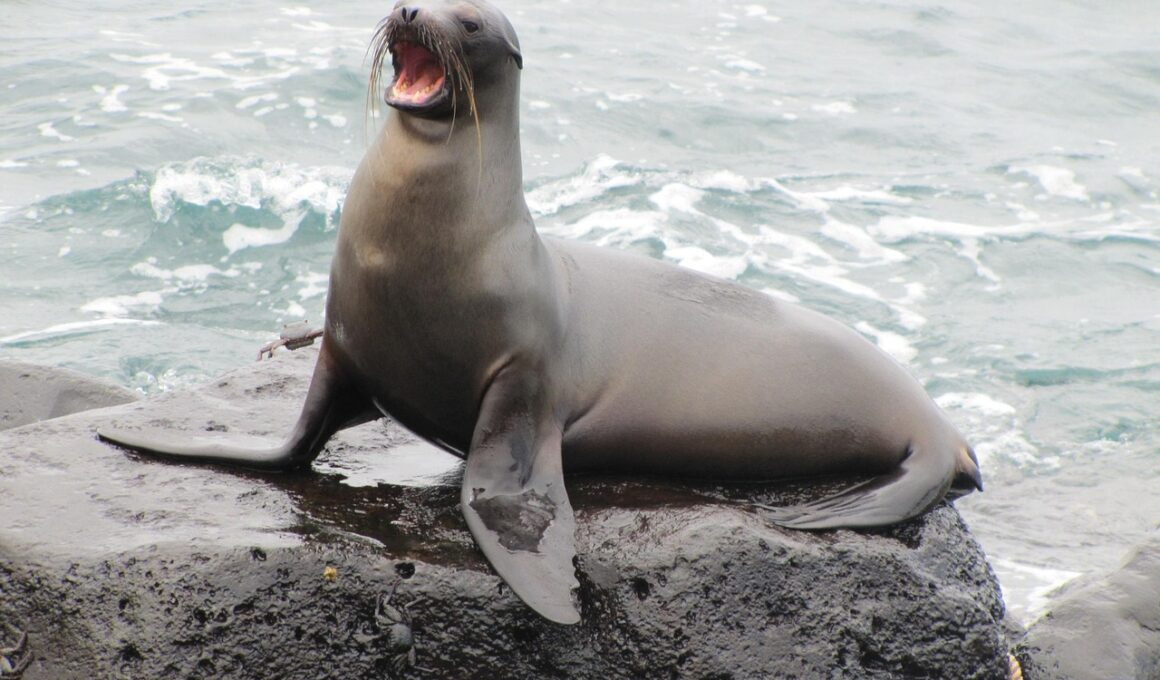
How Sea Lions Use Their Vibrissae for Sensory Detection
Sea lions are exceptional animals known for their intelligence and adaptability in aquatic environments. One of the remarkable adaptations they possess is their vibrissae, which are sensitive whisker-like structures that aid in sensory detection. Found on their snouts, these vibrissae play a crucial role in navigating through their surroundings, especially in murky waters. As the sea lions swim, the vibrissae detect changes in water currents and vibrations produced by nearby prey. This adaptation enhances their hunting skills, allowing them to find food more efficiently. Furthermore, vibrissae can sense minute changes in pressure, providing sea lions with the ability to locate objects even in low visibility conditions. This is particularly useful when hunting fish or other marine organisms that may not be easily spotted. Moreover, sea lions also utilize their vibrissae for social interactions and communication with one another. Through tactile stimulation, they can convey messages and establish social bonds within their groups. Thus, vibrissae are integral to the life of sea lions, encompassing navigation, hunting, and socialization within their environment.
Vibrissae consist of a specialized structure that is embedded in the skin and connected to a network of nerve endings. These structures are highly sensitive and can detect even the slightest movements in the water around them. When a sea lion swims, its vibrissae act like antennae, providing a continuous stream of sensory information. This capability is crucial for detecting prey, as many fish and other marine creatures can create subtle disturbances in the water. In addition to locating food, vibrissae help sea lions avoid obstacles in their environment. Along with their acute vision, this sensory adaptation allows them to thrive in various marine environments. Differences in vibrissae length and density can also be observed among different sea lion species, suggesting that these adaptations have evolved to suit specific ecological niches. For some species, longer and denser vibrissae may enhance their ability to navigate through murky waters or hunt particular prey types. The evolutionary significance of vibrissae demonstrates the intricate relationship between sensory adaptation and survival in marine mammal species. Understanding these adaptations can help researchers gain insights into animal behavior and ecology.
In addition to their role in hunting and navigation, sea lions’ vibrissae may also play a part in their interactions with their environment and each other. For example, during social encounters, sea lions often engage in behaviors that involve physical contact, such as rubbing against one another. This tactile interaction may serve various functions, including social bonding and establishing hierarchical structures within groups. Vibrissae can enhance this tactile communication by providing detailed information about physical proximity and movement. Furthermore, the ability to detect vibrations through their whiskers allows sea lions to remain alert to their surroundings, helping them avoid potential predators. In the case of pups, the sensation provided by their mothers’ vibrissae can guide their movements and encourage them to stay close during the early stages of life. Overall, vibrissae contribute significantly to both the social dynamics and the survival strategies of sea lions in the wild. Their adaptability showcases how evolutionary processes shape sensory systems, enabling species to thrive in complex environments. The understanding of such adaptations contributes to the broader knowledge of animal behavior and ecological interactions.
The Role of Vibrissae in Foraging Strategies
For sea lions, foraging is an essential aspect of survival in their aquatic habitats. The vibrissae’s sensitivity allows them to detect and respond to prey movements, facilitating effective hunting strategies. They often rely on their acute sense of vibrissae feedback to identify the location of schools of fish, even when visibility is limited. As sea lions dive underwater, they position themselves strategically, using their vibrissae to pick up the slightest vibrations caused by their prey. This adaptation significantly increases their success rate while foraging in diverse underwater environments, where prey can be elusive. Moreover, sea lions are known to employ a variety of foraging techniques, such as cooperative hunting and using tools, showcasing their intelligence. They often work together in groups, enhancing their hunting efficiencies. During these cooperative efforts, the vibrissae help individuals stay coordinated, as each sea lion uses its sensory information to avoid collisions and optimize capture strategies. This sophisticated use of vibrissae not only improves individual foraging success but also strengthens group dynamics, highlighting the importance of social learning and coordination in their hunting practices.
The significance of vibrissae extends to their contribution to the overall health of sea lion populations. By improving hunting efficiency, vibrissae reduce energy expenditure, enabling sea lions to adapt better to changing environmental conditions and prey availability. As climate change alters marine ecosystems, these adaptations may help some species better cope with reduced fish stocks or shifts in their habitats. Furthermore, maintaining healthy sea lion populations is crucial for balancing marine ecosystems, as they serve as apex predators. Their role in controlling prey populations contributes to the overall health of marine environments. Thus, the vibrissae are not merely a specialized set of sensory organs, but a vital component influencing ecological dynamics. Efforts to protect sea lion habitats, mitigate human impacts, and ensure sustainable marine resource use must consider the role of these remarkable structures as they navigate the changing marine landscape. The interdependence between sea lions and their environment emphasizes the need for ecological conservation measures aimed at preserving their populations and the biodiversity within their ecosystems.
Conservation of Sea Lions and Their Adaptations
The conservation of sea lions and their unique adaptations is essential for the preservation of marine ecosystems. As apex predators, sea lions play a crucial role in regulating marine life and ensuring the balance of aquatic food webs. Unfortunately, habitat loss, climate change, and human interference threaten their populations and diminish their numbers dramatically. To safeguard these remarkable creatures, it is imperative to implement effective conservation strategies that address the challenges they face. Awareness campaigns, marine protected areas, and legislation aimed at reducing pollution and human disturbances can significantly enhance the chances of survival for sea lions. Additionally, research into their behavioral and physiological adaptations, such as vibrissae sensitivity, may inform better conservation practices. For example, understanding their foraging behaviors can help establish fishing regulations that prevent overfishing and protect critical feeding grounds. Encouraging responsible ecotourism and public engagement are also vital in raising awareness about the importance of sea lion protection in maintaining healthy ecosystems. By prioritizing the conservation of these intelligent marine mammals, we contribute not only to their survival but also to the well-being of our planet’s marine biodiversity.
Ultimately, the vibrissae of sea lions exemplify the marvelous adaptations evolved by marine mammals to thrive in their environments. These whisker-like structures empower sea lions to navigate, forage, and communicate, showcasing the intricate relationship between anatomy and ecology. As we continue to explore the complexities of marine ecosystems, it is crucial to recognize the vital roles that sea lions play and the adaptations that support their existence. Every adaptation, including the vibrissae, contributes to the overall health and resilience of marine biodiversity, making it essential to understand and protect it. The lessons learned from studying sea lions can be applied more broadly to conservation efforts targeting various marine species. By preserving and promoting the health of marine habitats, we can foster stronger ecosystems that support diverse life forms. In conclusion, appreciating the functions of sea lions’ vibrissae provides insight into the fascinating world of marine mammals and their adaptations. Protecting their habitats will ensure that future generations can witness these incredible creatures thrive in their natural environments, maintaining the ecological balance of our oceans.
In summary, sea lions are fascinating creatures with remarkable sensory adaptations primarily driven by their vibrissae. These whisker-like structures significantly enhance their ability to detect prey, navigate through murky waters, and communicate effectively. Understanding the role of vibrissae is essential for appreciating the complexities of sea lion behavior and ecology. Through ongoing research aimed at uncovering these adaptations, we can deepen our knowledge of marine life and preserve the health of ocean ecosystems. It is vital that conservation efforts continue to focus on the protection of these unique animals and their habitats. By ensuring that sea lions have the necessary resources and safe environments, we can support their remarkable adaptations and promote their survival in the face of various anthropogenic threats. Public awareness and community involvement will play crucial roles in fostering a culture of marine conservation. Ultimately, it is our responsibility to ensure that future generations inherit a world where sea lions and other marine species thrive harmoniously in their ecosystems. In doing so, we can celebrate the beauty and diversity of life in our oceans while safeguarding the health of our planet.