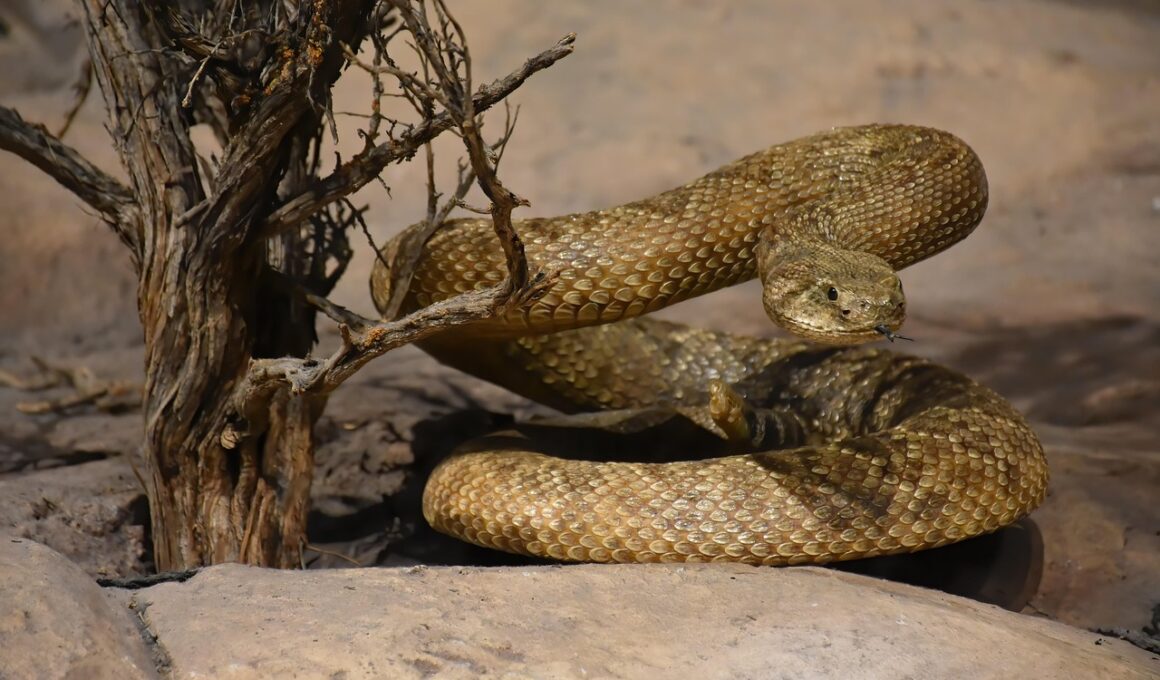
Predator-Prey Dynamics Among Desert Reptiles
Understanding predator-prey dynamics among desert reptiles is crucial for comprehending their ecological roles. In arid environments, reptiles exhibit unique behaviors adapted to harsh conditions and limited resources. Predator-prey relationships play a critical role in shaping the population dynamics of these organisms. Reptiles often hunt during specific times, optimizing their foraging efficiency while minimizing exposure to extreme temperatures. Their adaptations include effective camouflage, quick bursts of speed, and enhanced sensory perception. For example, the Gila monster is known to be both predator and prey, showcasing the balance in ecosystem interactions. Additionally, many desert reptiles have developed specific hunting strategies. Some utilize ambush techniques, while others actively forage. Such strategies affect prey spatiotemporal distribution and predator success rates. Additionally, reproductive strategies impact predator-prey dynamics; the life cycles of reptiles often coincide with prey availability. The interplay between growth rates, reproductive output, and predation pressure determines population stability and diversity among desert reptile species. In essence, predator-prey dynamics drive ecological processes, influencing not only individual species but entire ecosystems. This interplay is further complicated by environmental changes and human impacts, demanding ongoing research into these relationships.
Predator-prey interactions are fascinating examples of survival strategies. Advancing our understanding requires studying various aspects of behavioral ecology. For instance, research has shown that temperature influences metabolic rates, affecting energy expenditure during hunting. This is critical in deserts, where daytime temperatures can dramatically affect activity patterns. Additionally, reptile predators often rely on stealth and surprise to take down prey. Species like the eastern diamondback rattlesnake demonstrate ambushed hunting techniques, using their keen senses to detect movement. Furthermore, some prey species have evolved counter-strategies; for example, horned lizards can produce blood from their eyes to deter potential predators. Notably, complex social interactions can develop among predator and prey species, influencing overall community dynamics. For example, communal hunting not only improves prey capture success but alters competition among predators. In this high-stakes environment, adaptability directly correlates with survival rates, demonstrating the importance of behavioral flexibility. Moreover, seasonal changes can lead to shifts in predator-prey dynamics, affecting the composition and health of reptile populations. Ongoing field studies and controlled experiments are crucial for unraveling these complex interactions to gain insights into desert ecosystem functioning.
Impact of Environmental Changes
Environmental changes pose significant challenges to the predator-prey interactions among desert reptiles. Climate change, habitat destruction, and pollution are just a few struggles each ecosystem faces today. These factors can alter prey availability, affect breeding cycles, and disrupt existing predator-prey dynamics. For example, fluctuations in temperature and precipitation patterns impact vegetation growth, subsequently affecting herbivore populations. Reptile predators rely heavily on these herbivores for sustenance, meaning any change in food supply can have a cascading effect. Additionally, droughts reduce the availability of water sources, forcing reptiles to adapt their hunting and foraging behaviors. In many cases, this creates increased competition among predator species struggling to find food. Another critical aspect is that increased human activity often leads to habitat fragmentation. This disrupts traditional paths and hunting grounds for desert reptiles, further complicating their survival. In some instances, invasive species might become established, resulting in higher predation pressure on native reptiles. Such conditions necessitate ongoing adaptation and resilience among these species. Therefore, understanding how environmental changes influence predator-prey dynamics is fundamental to conserving these reptiles and their habitats.
Conservation efforts are imperative not only for reptiles but also for maintaining overall desert biodiversity. Protecting these ecosystems involves addressing the various factors influencing predator-prey dynamics. Restricting habitat destruction by promoting sustainable land use practices is vital for long-term ecosystem health. Additionally, creating wildlife corridors could help facilitate movement between fragmented habitats. Such initiatives would enhance genetic diversity and resilience, improving species survival rates in changing conditions. Education plays a crucial role in conservation as well, ensuring local communities recognize the importance of preserving reptile populations. Engaging citizens in responsible land stewardship can foster a sense of responsibility towards the desert environment. Moreover, integrating traditional ecological knowledge with modern conservation approaches can benefit local efforts. Researchers must collaborate with communities to devise strategies reflecting the unique challenges posed by each ecosystem. Furthermore, legal frameworks supporting the protection of endangered reptiles contribute to overall population recovery. Monitoring populations and conducting regular assessments are essential in gauging conservation success. Ultimately, protecting predator-prey dynamics in desert ecosystems ensures the survival of diverse species, paving the way for healthy, functioning habitats that can endure environmental challenges.
Field Studies and Research
Field studies play a critical role in enhancing our comprehension of desert reptile predator-prey dynamics. In situ observations allow researchers to collect invaluable data about behaviors and interactions in natural environments. For instance, studying the foraging patterns of desert lizards allows for insights into how they navigate their arid habitats. These observations help clarify factors influencing predator success and prey evasion strategies. Furthermore, employing tracking technologies such as radio transmitters enables scientists to monitor movements over time, revealing essential patterns linked to seasonal changes and resource availability. Laboratory experiments complement field studies, allowing researchers to hone in on specific variables impacting predator-prey interactions. Testing under controlled conditions sheds light on how environmental factors like temperature and humidity affect hunting efficiency. Additionally, dietary studies reveal which prey items are most crucial for sustaining predator populations, facilitating better understanding of these relationships. Integrating traditional ecological knowledge with scientific research provides a more holistic perspective on desert ecosystems. By encompassing broader contexts, scientists can develop more robust conservation strategies, ensuring the delicate balance between predator and prey continues amidst changing environmental conditions.
Moreover, the implications of predator-prey dynamics extend beyond the immediate interactions between species. They significantly impact the broader ecosystem health and biodiversity levels. For instance, apex predators maintain balance by controlling prey populations, preventing any one species from overpopulating. This regulatory function ultimately supports a rich diversity of life, ensuring ecological resilience against disturbances. Additionally, the interactions between various reptile species can facilitate energy flow and nutrient cycling within these habitats. As reptiles prey upon their smaller counterparts, they contribute to the transfer of energy through trophic levels. Moreover, the presence of a variety of predator types can help stabilize ecosystems, leading to healthier populations overall. By contrast, the decline of key predator species often results in ecological imbalances, emphasizing the importance of conservation. Efforts aimed at preserving these species must consider their integral role in the larger ecological framework. Thus, ongoing conversations around desert conservation must recognize the interconnectedness of all species within these fragile systems. Ultimately, a holistic approach will prove beneficial in addressing the challenges desert reptiles face today, allowing for sustainable ecosystems that thrive.
Looking Forward: Research and Conservation
Addressing future research needs and conservation strategies are essential in protecting desert reptile predator-prey dynamics. Increased funding for ecological studies will facilitate deeper insights into the complexities of these interactions. Moreover, collaboration between governmental organizations, universities, and conservation groups can enhance research efforts, integrating diverse expertise and resources. Developing long-term ecological monitoring programs is crucial for assessing population trends and responses to environmental changes. By tracking specific species over time, scientists can identify potential threats and facilitate timely conservation measures. Furthermore, promoting public awareness campaigns can help educate communities about the significance of desert reptiles in maintaining ecological balance. Engaging local populations in conservation initiatives fosters community stewardship and collaboration, amplifying the impact of these efforts. Additionally, research on the effectiveness of specific conservation interventions will inform best practices tailored to desert ecosystems. As technologies continue to evolve, utilizing tools such as remote sensing and genetic analysis might offer new insights into monitoring and managing desert reptile populations. Ultimately, working together towards sustainable practices and ongoing research will be essential for ensuring future generations can enjoy the rich biodiversity that desert reptiles provide.