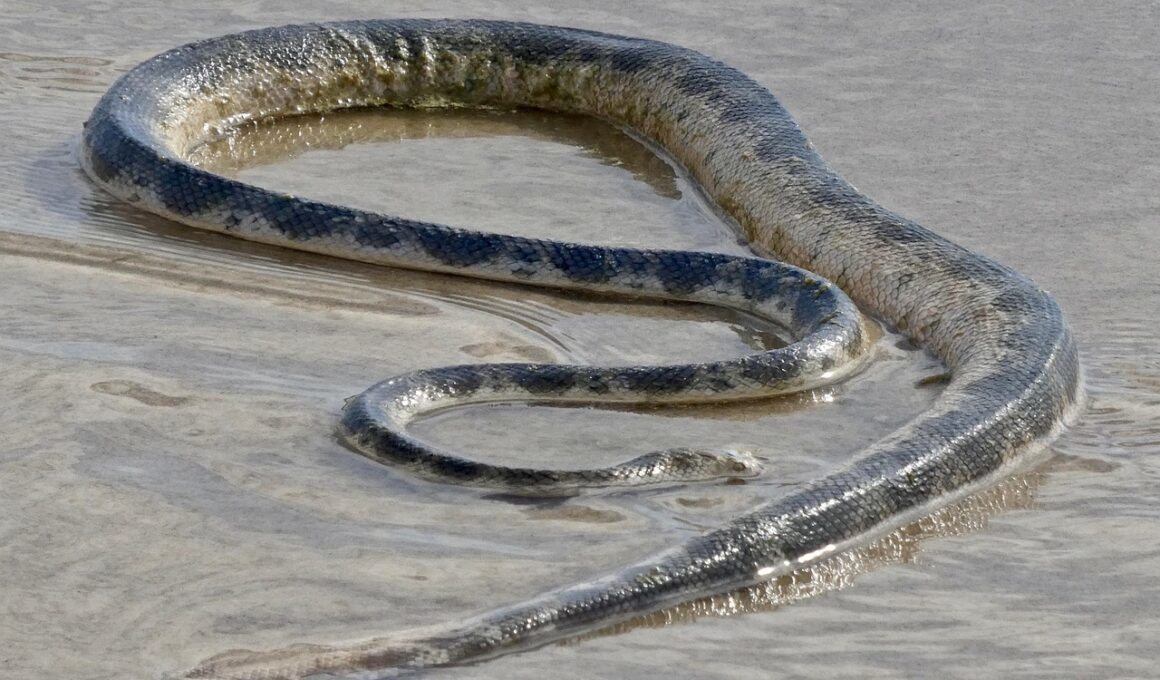
The Fascinating World of Sea Snakes: An Introduction
Sea snakes are a remarkable group of reptiles that live in marine environments. They belong to the family of Elapidae, which also includes cobras and mambas. These fascinating creatures are uniquely adapted to life in the ocean. Their flattened bodies and paddle-like tails enable them to glide gracefully through water. Sea snakes can be found in warm coastal waters across the Indo-Pacific region. They primarily inhabit shallow waters where they can easily find prey such as fish and eels. Unlike terrestrial snakes, sea snakes are entirely aquatic, meaning they spend their entire lives in the ocean. Breathing through their nostrils, which are positioned on top of their heads, allows them to remain submerged while taking in air. Most have a highly potent venom used for paralyzing prey, making them formidable hunters. Despite their dangerous reputation, sea snakes are generally not aggressive towards humans. They usually prefer to retreat when confronted. This unique aspect of their behavior makes them an interesting topic of study for marine biologists and environmentalists alike.
Adaptations for an Aquatic Life
The adaptations of sea snakes for survival in the ocean are truly astounding. Their scales are smooth and flattened, enhancing their hydrodynamic performance. These scales prevent drag as they navigate through the water. In addition, sea snakes have specialized lungs that can hold air for long periods. This allows them to dive deep and stay submerged for extended durations when hunting. Sea snakes are also known for their ability to tolerate saltwater, thanks to specialized glands that excrete excess salt. This adaptation allows them to maintain hydration while living in a saline environment. Their eyesight is well adapted for underwater visibility, enabling them to hunt effectively in murky waters. Furthermore, sea snakes are excellent swimmers, often using their side-to-side motion to propel themselves swiftly. This efficient movement aids in escaping predators and capturing fast-moving prey. Their coloration varies significantly, with some species displaying striking patterns for camouflage, while others possess vibrant hues to deter potential threats. Overall, these adaptations play a crucial role in their survival and success in the marine ecosystem.
Sea snakes exhibit varied reproductive strategies, including ovoviviparity and oviparity. Ovoviviparous species give birth to live young, providing better survival chances in open waters. In contrast, oviparous sea snakes lay eggs in coastal areas. The choice of reproduction method largely depends on environmental conditions and species-specific traits. Females typically seek shelter to protect their eggs from predators. The gestation period for many species can last several months, with young snakes emerging fully formed and capable of swimming immediately. This rapid independence is crucial for survival in predatory marine habitats. Sea snake young often resemble adults, yet they possess distinct markings that may help them evade predators. Various factors affect reproductive success, including prey availability and environmental stability. Habitat degradation and climate change pose significant risks to sea snake populations. Consequently, researchers are investigating the impact of human activities on their breeding habits. Conservation efforts are necessary to ensure the sustainability of these unique creatures. In doing so, we can preserve not only their fascinating lives but also the integrity of marine ecosystems that rely on their presence.
In the realm of neurotoxic venom, sea snakes hold a prominent position. Their venom is among the most potent in the animal kingdom, designed primarily for subduing prey. It contains neurotoxins capable of causing paralysis in small fish, allowing the snake to consume its meal without struggle. Interestingly, not all sea snake bites are fatal to humans. Thankfully, these creatures are generally docile unless threatened or provoked. Known for their reluctance to attack, they often retreat from potential threats, including divers. However, accidents can occur. It is crucial to respect their space and avoid disturbance. The symptoms of a sea snake bite can range from swelling and pain to serious neurological manifestations. Medical attention must be sought immediately if bitten. Anti-venom is available for specific bites, although its use requires expert medical intervention. Understanding these fascinating creatures and their venomous capabilities is essential for safety and conservation efforts. Education on how to interact safely with sea snakes contributes to a harmonious relationship between humanity and marine wildlife. The need to conserve their habitats is more vital than ever, as their survival is intertwined with our ocean’s health.
Diet and Feeding Habits
Sea snakes are carnivorous, primarily feeding on various types of fish and occasionally crustaceans. Their hunting techniques can vary from species to species, but they generally rely on stealth and agility. Many sea snakes are ambush predators, waiting patiently for the right moment to strike. Some utilize a hunting strategy that involves blending into their surroundings, while others chase down prey in open water. Their venom serves as a crucial tool in capturing food, allowing them to immobilize fast-moving fish. The feeding habits of sea snakes are vital to the marine ecosystem, as they help maintain population control of different fish species. Their presence balances the underwater food web. Typically, sea snakes hunt during the day, although some species may exhibit nocturnal behavior. Feeding frequency can vary, depending on the snake’s size and metabolic needs. After consuming a meal, sea snakes can go for several days without eating again. This ability helps them survive in environments where food availability fluctuates. Understanding their dietary habits sheds light on their ecological role and the importance of conserving their habitats for the future.
Despite their importance in marine ecosystems, sea snakes face numerous threats in today’s rapidly changing environment. Overfishing, pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change are significant factors impacting their populations. Many species are caught unintentionally in fishing nets, resulting in drowning or injury. Additionally, habitat degradation has transformed their natural environments, affecting their hunting and breeding. Climate change further exacerbates these issues by altering water temperatures and salinity levels, endangering the delicate balance of marine life. Conservation efforts are vital to addressing these threats. Governments and organizations are increasingly recognizing the importance of protecting aquatic habitats. Strategies such as establishing marine protected areas and promoting sustainable fishing practices are critical for preserving sea snakes and their ecosystems. Public education is also essential in fostering awareness of these creatures and their plight. By informing communities and individuals about the challenges sea snakes face, we can encourage protective measures and responsible behaviors. Collaborative efforts between researchers, conservationists, and local communities can spearhead initiatives that guarantee the survival of these fascinating creatures and ensure the health of our oceans.
Importance of Sea Snake Conservation
Conserving sea snakes goes beyond simply protecting a single species; it plays a fundamental role in preserving ecological balance within marine environments. These reptiles serve as indicators of ocean health. Changes in sea snake populations can signify shifts in marine biodiversity. By studying their populations and behaviors, scientists can gather vital information that informs conservation initiatives. Additionally, preserving sea snakes helps protect their prey species, further supporting the food web. Activists and researchers advocate for stronger regulations regarding marine life protection. Collaborative efforts among various stakeholders can lead to significant advancements in conservation strategies. Engaging local communities can foster support for creating marine reserves, ensuring a safe haven for sea snakes and other marine organisms. Furthermore, public initiatives can raise awareness about environmental stewardship, encouraging people to engage in actions that benefit the ocean. Supporting environmentally friendly policies and sustainable practices can foster a healthier ecosystem for all marine life. As the awareness of sea snakes grows, so does the potential for conservation. These fascinating creatures are indeed a critical component of a vibrant and healthy marine ecosystem.
In conclusion, sea snakes are extraordinary creatures that deserve our attention and protection. Their unique adaptations for aquatic life, intriguing behaviors, and ecological significance highlight their importance within marine ecosystems. Understanding their biology and the challenges they face due to human activities is essential for developing effective conservation strategies. By ensuring their survival, we preserve not only their intriguing existence but also the health of our oceans. Education and awareness play pivotal roles in conservation efforts. By engaging the public through campaigns and informational resources, we can uplift the status of sea snakes and promote their protection. It is essential for researchers, conservationists, and local communities to collaborate and organize initiatives aimed at safeguarding these reptiles. As the awareness of sea snakes spreads, so too does the hope for their conservation. Together, we can build a future where sea snakes thrive in a balanced marine ecosystem. By prioritizing their protection, we also contribute to the overall health and sustainability of our oceans. Let us work towards a world that celebrates the beauty and importance of all marine life, including the fascinating sea snake.