Threats from Boat Strikes and Human Activities
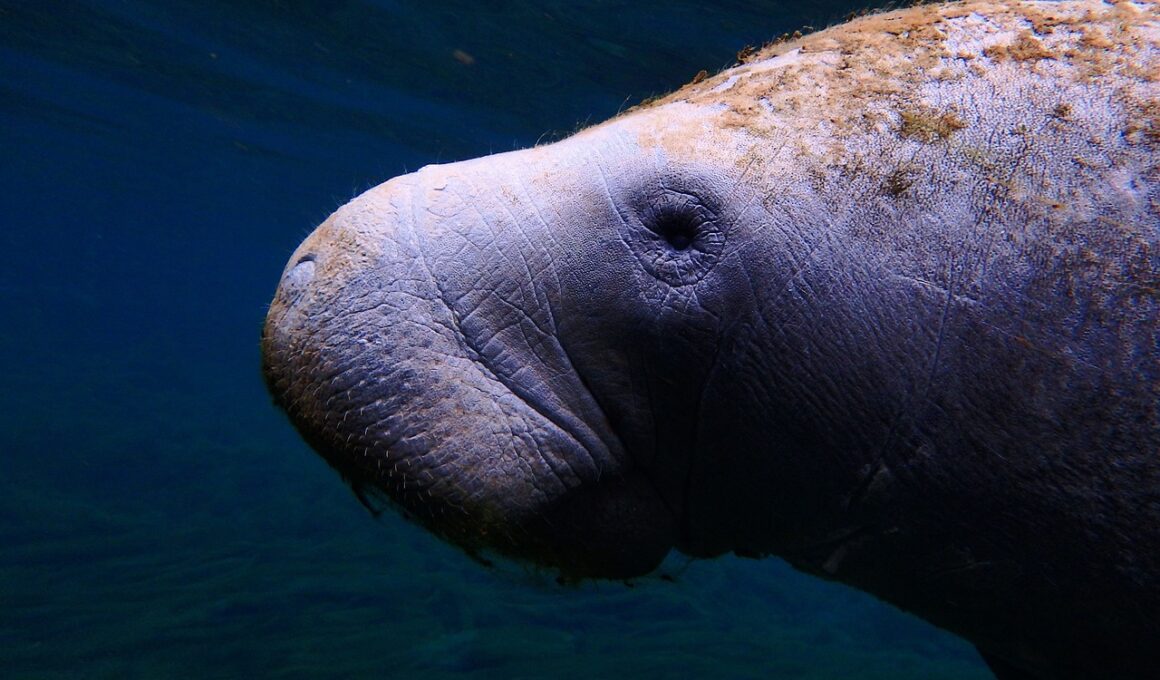
Sirenian mammals, specifically manatees and dugongs, face significant threats from boat strikes and human activities, jeopardizing their populations. Boat strikes lead to injuries and fatalities among these vulnerable animals. The increasing number of recreational and commercial vessels exacerbates this risk. In regions where manatees are prevalent, awareness should be raised concerning speed limits in designated areas. Strict adherence to such regulations is crucial for their survival. Furthermore, habitat degradation due to coastal development and pollution worsens the plight of Sirenians. The loss of seagrass beds, a primary food source for dugongs, directly impacts their health and well-being. Additionally, human-induced climate change, leading to altered water temperatures, further complicates their habitat viability. Educating the public on safe boating practices and active participation in conservation efforts is paramount. Boat operators must exercise caution, especially in areas known for high Sirenian populations. Organizations are collaborating with local governments to implement protective measures, ensuring that these gentle giants receive the attention they urgently require for conservation. Hence, understanding the critical threats posed by human activities is essential to protect Sirenians effectively.
Impact of Habitat Loss on Sirenians
The habitat loss significantly impacts Sirenians, particularly due to human activities. Coastal development, industrialization, and urban sprawl all contribute to the destruction of vital seagrass habitats, upon which manatees and dugongs depend for their survival. When seagrass meadows diminish, these mammals struggle to find adequate nutrition, leading to malnourishment and a decline in reproductive success. In addition, pollution from agricultural runoff and industrial waste deteriorates water quality, further threatening the delicate ecosystems that support these species. Moreover, increased boat traffic not only raises the potential for deadly strikes but also disturbs their natural behaviors, including feeding and breeding. Conservation efforts must prioritize the protection and restoration of these habitats to mitigate the impacts of human activities. Community involvement is also essential, encouraging local stakeholders to respect natural environments actively. Rehabilitation programs for affected areas have shown promise in enhancing seagrass growth, thus fostering the resilience of future Sirenian populations. Policymakers must implement regulations that safeguard crucial habitats and promote sustainable practices within coastal industries to maintain these sensitive marine environments. Increased global awareness surrounding these issues is vital for enhancing conservation outcomes.
Boat strikes are among the most immediate threats faced by Sirenians. These mammals often inhabit shallow coastal waters, where they are more prone to collisions with boats. Many boat operators are unaware of the presence of these animals in busy waterways, resulting in tragic and avoidable fatalities. High-speed boats, particularly, pose a significant danger, leading to severe injuries or death upon impact. Thus, effective speed regulations in Sirenian habitats must be enforced and publicized. Education campaigns can help prepare boaters to recognize signs of manatee and dugong presence, reducing strike incidents. Additionally, partnerships with marine organizations can support outreach efforts to emphasize the importance of wildlife protection. The role of technology, such as boat alarms and tracking systems, is also worth exploring to enhance safety. Conservation groups advocate for the implementation of designated manatee zones, where speed limits are enforced, and wildlife monitoring occurs consistently. These measures can significantly reduce the incidence of boat-related injuries, but compliance depends on shared community responsibility. Without proper intervention, the ongoing threats from boat strikes can severely disrupt future Sirenian populations, making proactive measures essential for their continued existence.
Human Pollution and its Effects
Human pollution significantly affects Sirenians and their habitats. Polluted waters can harm the delicate ecosystems in which these animals thrive. Nutrient runoff from agriculture leads to algal blooms, decreasing oxygen levels in the water and harming seagrass beds. Enhanced algal growth can smother crucial habitats, leaving less food available for Sirenians. Additionally, heavy metal contamination from industrial sources can enter the food chain, further endangering these mammals’ health. Emerging studies also indicate that microplastics could adversely impact marine life through ingestion and entanglement. Consequently, the effects of pollution extend beyond immediate visibility, threatening Sirenian populations’ long-term viability. Effective waste management practices are crucial to combat these pollution issues, highlighting the importance of responsible chemical applications in agriculture. Community engagement in clean-up efforts and advocacy for better industrial regulations are steps that can yield positive results. Increasing public awareness about the connections between pollution and marine health is essential. Strong partnerships between conservation organizations and governmental bodies can lead to developing policies aimed at minimizing human impacts. In this way, targeted actions can significantly contribute to restoring the quality of Sirenian habitats and ensuring a healthier future for these endangered species.
Climate change poses additional threats to Sirenians and their habitats. Rising sea levels caused by melting ice caps can inundate coastal areas, reducing the available habitat for manatees and dugongs. As seagrass habitats become submerged or lost, these animals face challenges in locating adequate food sources. Furthermore, shifts in water temperature can disrupt critical breeding and feeding patterns. Changing ocean conditions can also exacerbate existing pollution issues, making previously suitable habitats untenable. Hence, it is crucial to understand how climate change interacts with existing threats. Conservation strategies must incorporate climate change projections, tailoring efforts to ensure the resilience of marine ecosystems. Restoration projects focusing on seagrass habitats can be vital components of adaptive management plans. Additionally, collaboration with climate scientists can enhance understanding of potential impacts on Sirenian populations. Advocacy for sustainable practices in agriculture and industry must remain at the forefront of discussions around climate action. The impact of climate change, while global, calls for local actions that can influence outcomes positively. Recognizing the interplay of marine health and climate awareness will allow communities to align conservation efforts with broader sustainability goals.
Advocacy and Conservation Efforts
Advocacy plays a crucial role in protecting Sirenian populations from various threats arising from human activities. Numerous organizations are dedicated to raising awareness about the challenges these mammals face, actively promoting conservation initiatives. By engaging local communities, these organizations can cultivate supportive environments for the protection of marine wildlife. Educational programs targeting schools and the general public are essential to highlight the importance of Sirenians and their ecosystems. Volunteers can engage in beach clean-ups, habitat restoration projects, and other activities that directly benefit these marine habitats. Legislative advocacy is paramount in promoting stringent regulations on boat operations and marine pollution. Collaborations with governmental bodies can lead to the enforcement of protective measures, ensuring safer environments for Sirenians. Programs that track Sirenian populations allow scientists to gather data essential for informed conservation decisions. Engaging the tourism sector in conservation efforts can help promote responsible wildlife viewing, providing economic incentives for protecting these animals. Ultimately, comprehensive advocacy efforts that unite communities, organizations, and policymakers can lead to sustainable practices and enhanced awareness. A collective approach promises a brighter future for Sirenians in the face of growing challenges.
Maintaining the balance between conservation and human activities is essential for the survival of Sirenians. As boat strikes and pollution continue to pose threats, proactive measures are necessary for ensuring their protection. Existing challenges are complex, and effective solutions must incorporate the interests of various stakeholders, including local communities and industries. Policymakers must consider the needs of Sirenians while crafting legislation that accommodates economic growth. Collaboration between conservation organizations and governments is critical in this regard, providing a platform for dialogue and shared responsibility. The integration of traditional knowledge from local communities can enhance conservation strategies, ensuring that local practices align with scientific insights. Public awareness campaigns should emphasize how individual actions contribute to collective conservation efforts. This can include advocating for eco-friendly boating practices and responsible waste disposal. By fostering a culture of stewardship, communities can feel invested in the survival of these mammals. As challenges evolve, adaptable strategies will be crucial for meeting the needs of Sirenians. Conclusively, maintaining an ongoing commitment to conservation will play a pivotal role in safeguarding Sirenians for future generations.
Ultimately, the survival of Sirenians is directly linked to collaborative conservation efforts that address the multiple threats posed by human activities. As boat strikes, habitat degradation, and pollution intertwine into complex challenges, dedicating resources toward awareness, education, and advocacy becomes crucial. The integration of scientific research with community stewardship will underline the importance of sustainable marine practices. Furthermore, employing innovative technology to monitor these populations can enable timely interventions where necessary. Partnerships with local, regional, and national organizations strengthen the conservation work needed to protect Sirenians. The global support for conservation initiatives is equally vital, advocating for their protection on wider platforms. Combining effective management strategies with a strong focus on public engagement will create a pathway toward recovery for these vulnerable species. Strengthening laws and regulations that safeguard their habitats is essential to counteract growing threats. The quest for sustainable modes of interaction with marine environments must be prioritized. Engaging stakeholders, policymakers, and the public will help foster a collective understanding of the need for urgent action in preserving these mammals. Ultimately, protecting Sirenians benefits marine biodiversity, contributing to healthier ecosystems for future generations.