Mating Behaviors and Courtship Rituals Among Reptiles
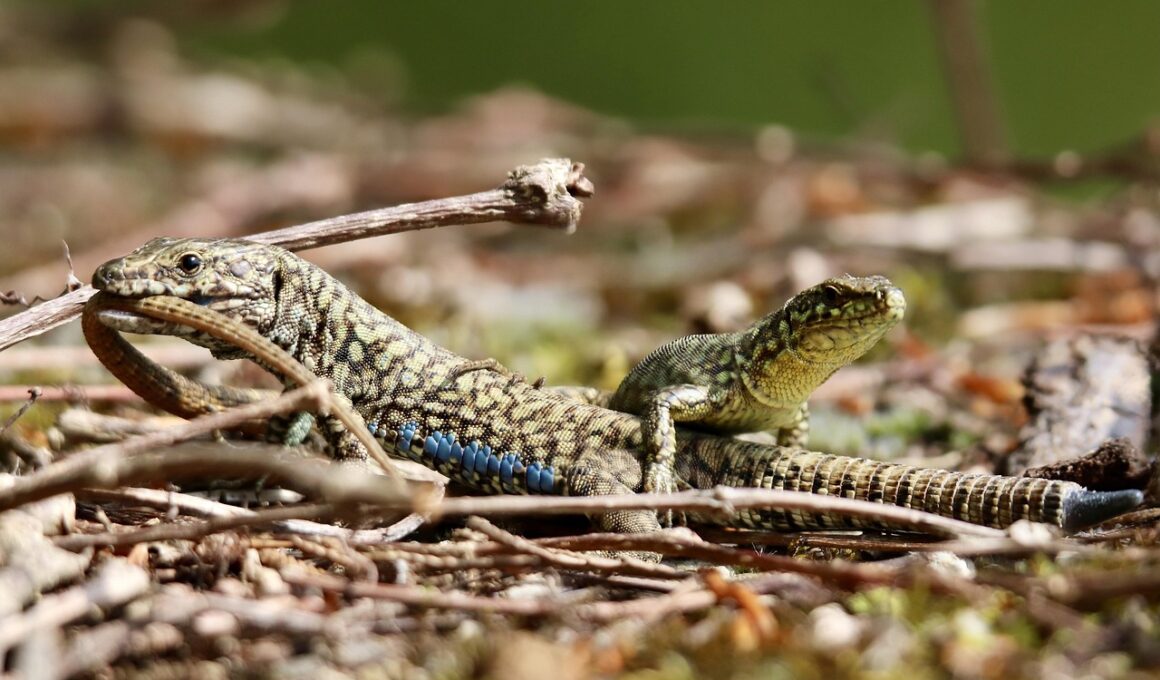
Mating behaviors and courtship rituals among reptiles are fascinating subjects to explore. These evolutionary strategies have developed over millions of years, ensuring the survival of various species. The complexities of these behaviors often involve intricate displays and rituals that differ significantly across reptile classes. For instance, many lizard species engage in colorful displays through body postures and throat inflations. These visual signals are critical in attracting potential mates and demonstrating fitness. Another common tactic is pheromone release, where reptiles use scent to convey reproductive readiness. Turtles and snakes also engage in unique competitive behaviors to secure mates, including elaborate wrestling rituals and courtship swimming. Understanding these mating rituals offers insight into their survival strategies and adaptability in the face of environmental changes. Some species even exhibit parental care, demonstrating a strong bond formed from mating. It highlights the crucial role that mating behaviors play in the reproductive cycle and the continuation of each species. As we study these fascinating behaviors, it is essential to consider the environmental and social factors influencing these mating strategies.
Visual Displays and Body Language
Visual displays and body language are critical components of reptile courtship rituals. Lizards often use vibrant colors, body postures, and head bobs to initiate mating behaviors and show readiness. For instance, male Anole lizards extend their brightly colored dewlaps to attract females. This show not only serves to capture attention but also demonstrates the male’s fitness and overall health. Similarly, iguanas perform elaborate rituals where males may display a combination of posturing and head nodding. These visual signals vary among species but serve as a universal language in the reptile kingdom. In contrast, snakes rely heavily on tactile and olfactory cues. Male snakes will often engage in “courtship” dances, where they intertwine their bodies and exhibit synchronized movements. Additionally, many reptiles utilize subtle body language, such as slow movements, to avoid alarming potential mates. This aspect of their behavior is crucial, as it sets the tone for interactions. Understanding the nuances of these displays sheds light on the evolutionary traits that enhance reproductive success and species survival. Ultimately, it reveals the sophisticated means reptiles employ to reproduce in their complex habitats.
Sound communication also plays a significant role in reptile courtship. While many think of reptiles as silent creatures, numerous species use vocalizations to attract mates. For example, some species of frogs and lizards produce unique calls or hisses during mating season to entice females. These sounds can indicate the male’s size and vitality, serving as an auditory cue for selecting the fittest mate. Acoustic signals vary greatly; some are loud and aggressive, while others are soft and inviting. The methods of producing these sounds are typically due to anatomical adaptations, such as vocal sacs in certain frog species. The diversity in sound-making capabilities among reptiles enhances the complexity of their courtship rituals and the challenges they face in crowded environments. Moreover, research continues to uncover new forms of communication, demonstrating that our understanding of reptilian social behavior is still evolving. As these fascinating studies unfold, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate adaptations reptiles have developed over time. Exploring the evolution of these calls is essential in understanding species diversity and reproductive strategies among reptiles throughout the animal kingdom.
Mating Strategies and Genetic Diversity
Mating strategies employed by reptiles can significantly influence genetic diversity within populations. Many reptiles exhibit polygamous behaviors, where one male mates with several females. This strategy increases genetic variability, enhancing the resilience of the population against diseases, climate changes, and other environmental pressures. For instance, numerous snake species are known to engage in scramble competition, where males compete to mate with multiple females during the breeding season. This results in a diverse genetic pool, giving rise to adaptive characteristics in subsequent generations. In contrast, some species practice monogamy, which leads to stronger pair bonds but may limit genetic diversity. These mating strategies often depend on ecological contexts and species survival requirements. Moreover, hybridization can occur between closely-related species, leading to new genetic combinations that can enhance adaptability. The dynamic interactions between mating strategies and genetic variability are crucial for evolution in reptile populations. Understanding these mechanisms can provide insights into conservation strategies for vulnerable species. As habitats continue to change, conserving genetic diversity becomes increasingly important for ensuring the survival of diverse reptilian species.
Environmental factors significantly impact mating behaviors and reproductive strategies of reptiles. Changes in temperature, habitat availability, and food resources can influence the timing of mating seasons and the success of courtship rituals. For example, in areas with fluctuating climates, reptiles may adjust their reproductive cycles to maximize offspring survival. Some species, like certain tortoises, may even delay reproduction until conditions become favorable, exhibiting remarkable adaptability. Habitat destruction, climate change, and pollution have forced many reptiles to adapt their mating behaviors to ensure successful reproduction. These shifts can lead to altered courtship rituals and breeding patterns, affecting the overall reproductive success of a species. Habitat fragmentation can lead to isolated populations, resulting in reduced genetic diversity, a situation known as the “Allee effect.” As understanding grows regarding these environmental influences, conservation frameworks must consider tailored strategies for each species. Educating the public and policymakers about these adaptations is essential for developing effective conservation programs. Ultimately, recognizing the importance of environmental factors leads to a greater understanding of the holistic nature of reptile reproduction and conservation.
The Role of Temperature in Sex Determination
In many reptiles, temperature plays a critical role in determining the sex of the offspring, a phenomenon known as temperature-dependent sex determination (TSD). For instance, certain turtle and crocodile species develop into males or females based on the incubation temperature of their eggs. Warmer temperatures typically skew the sex ratio toward females, while cooler conditions tend to favor males. This fascinating mechanism raises concerns regarding climate change, as shifting temperature patterns can disproportionately affect the gender balance within populations. For example, increasing temperatures may lead to fewer males reaching maturity, ultimately risking the survival of entire species. Understanding the implications of TSD highlights the interconnection between reproductive strategies and environmental conditions that reptiles navigate. Additionally, researchers are studying the genetic factors influencing TSD, which may provide invaluable insights into how populations may adapt to changing climates. As we embark on these scientific endeavors, it’s vital to communicate the potential impacts of rising temperatures on reproductive success. Supporting conservation efforts that address the consequences of climate change on reptile reproduction is crucial to maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Reproductive behaviors of reptiles also encompass various territorial disputes and aggressive encounters. Male reptiles, particularly in species with strong sexual dimorphism, often exhibit overt aggression to establish dominance and secure mating rights. This aggression can be observed through displays, body posturing, and sometimes physical confrontations. For example, male iguanas often engage in head-bobbing displays to assert their dominance over rival males. Although aggression is paramount, certain species, like tortoises, use head-butting as a ritualistic form of competition to minimize injury during fights. These behaviors underscore the importance of social hierarchy and territorial claims in reproductive success. Additionally, observing these competitive interactions contributes to understanding evolutionary adaptations among reptiles. Researchers are keen to study the balance between aggression and cooperation in these behaviors, as they reveal diverse social strategies. Exploring these dynamics leads to insights into the ecological influences shaping behavioral developments. Moreover, expanding knowledge about the interactions between mating behaviors and aggression provides critical information for wildlife management programs. Improving our understanding of reptilian social interactions can prove vital for their ongoing conservation.
Conclusion on Courtship and Mating
In conclusion, mating behaviors and courtship rituals among reptiles showcase the complexity inherent in the animal kingdom. From visual displays, vocal communications, to environmental adaptations, reptiles exhibit diverse strategies tailored to ensure successful reproduction. Each species has honed its unique rituals through evolutionary processes influenced by ecological conditions, competition, and environmental changes. Understanding these nuanced behaviors is crucial for conservation and management efforts, especially as many reptile populations face threats from habitat destruction and climate change. The interplay between mating strategies and genetic diversity offers valuable insights into the resilience of populations amidst environmental pressures. Moreover, recognizing the role of temperature in sex determination highlights the need for proactive conservation strategies in light of shifting climates. Ultimately, by deepening our understanding of reptilian reproduction, we can better advocate for preserving their habitats. Educating the public about the importance of these behaviors will contribute to a greater appreciation for reptiles and the role they play in ecosystems. As we advance research in this area, fostering awareness will help safeguard the future of diverse reptilian species.