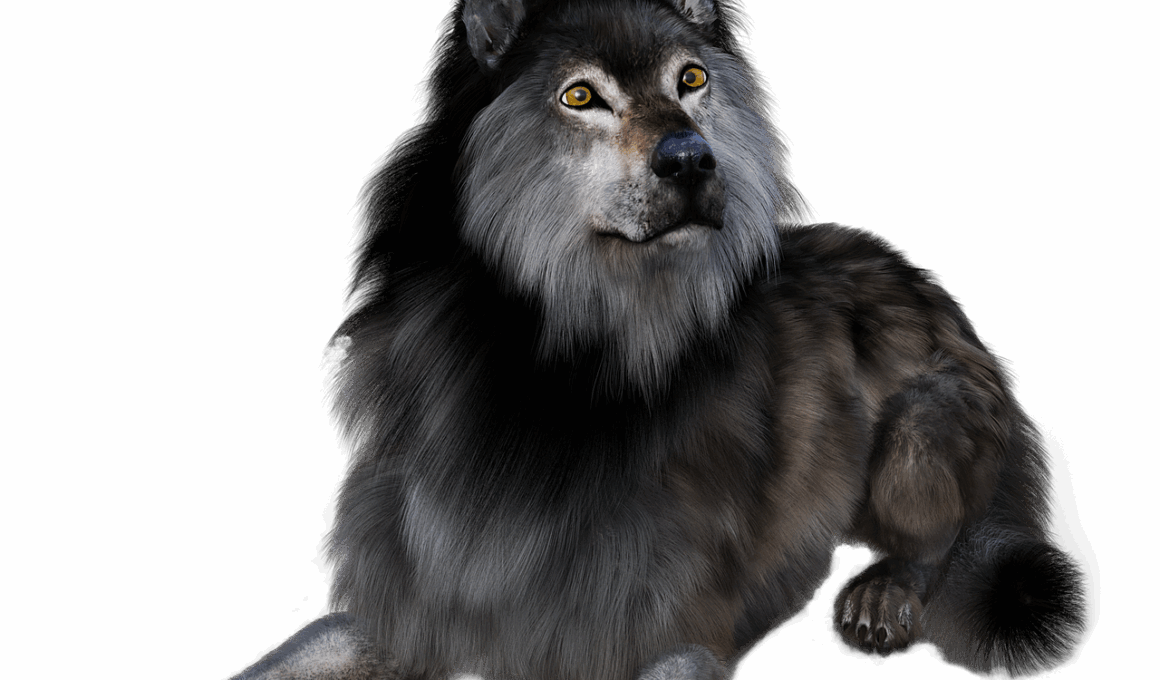
The Canidae Family: Wolves, Foxes, and Their Kin
The Canidae family, known as canines, includes a diverse group of mammals, ranging from the fierce wolves to the cunning foxes. These fascinating animals have adapted to various habitats, demonstrating a wide array of behaviors, physical traits, and social structures. The family consists of several genera, including Canis, Vulpes, and Lycaon, each showcasing unique adaptations that enable them to thrive in their environments. Canidae members are primarily carnivorous, but many species display omnivorous tendencies, consuming plants and small animals. This flexibility in diet helps them survive in changing environments and seasonal variations. Wolves, for example, are social animals forming intricate pack structures that enhance their hunting success and protect their territories. Foxes, on the other hand, are more solitary and resourceful, often using their keen senses and agility to hunt and evade larger predators. The overview of this incredible family reveals the interconnectedness of species within ecosystems, illustrating the balance of nature. Understanding the canids’ role in wildlife dynamics informs conservation efforts, promoting a healthier environment for all species involved.
Wolves are one of the most iconic members of the Canidae family, known for their complex social structures and impressive hunting strategies. They are primarily found in pack groups, which provide strength and stability in their survival efforts. Each pack has a clear hierarchy, usually led by an alpha male and female. This alpha pair mates exclusively, ensuring the continuation of their genetic line. Wolves communicate through vocalizations, body language, and scent marking, all crucial in maintaining pack unity. Their diet mainly consists of large ungulates, but they also adapt to prey on smaller animals and scavenging opportunities when necessary. Understanding wolf behavior and their ecological role is vital for ensuring their conservation in the wild. As apex predators, wolves help regulate prey populations and maintain healthy ecosystems. They play a significant role in their habitats, contributing to biodiversity and ecosystem stability. Conservation efforts assist in restoring their numbers, allowing people to appreciate their ecological importance. Supporting wolf conservation is essential, and organizations work tirelessly to educate the public about these extraordinary creatures and the challenges they face.
Foxes: Adaptable and Cunning
Foxes, particularly the red fox (Vulpes vulpes), are well-known for their cunning nature and adaptability. They inhabit a wide range of environments, from urban areas to wilderness settings, showcasing their remarkable ability to thrive in various conditions. This adaptability is largely due to their opportunistic feeding habits, allowing them to consume a varied diet consisting of small mammals, fruits, and even carrion. Their acute senses—excellent hearing, keen eyesight, and a keen sense of smell—aid them in locating food and avoiding danger. Foxes are known for their solitary behavior, often hunting and foraging alone, which allows them to maneuver stealthily. A highlight of their behavior includes their characteristic “fox trot,” a unique way of moving that aids them in navigating their environment silently. The cleverness of foxes has also ingrained them deeply into various cultures and folklore, symbolizing cunning and intelligence. They remind us of nature’s resilience and the intricate balance of life. Understanding the importance of foxes in ecosystem dynamics encourages us to appreciate and protect these enchanting animals, as well as their habitats.
The Canidae family showcases remarkable diversity not only in species but also in their reproductive strategies. For instance, many species like wolves and coyotes exhibit monogamous traits, forming lasting pair bonds. This behaviour ensures better parental care and increased survival rates of the pups. Other species, however, demonstrate more flexibility, with some fox species participating in polygamous breeding systems. Canidae pups are often born in litters and rely heavily on their parents for warmth, protection, and nutrition during their vulnerable early stages. Their development phase is critical, as they learn essential survival skills from their parents. The nurturing role of the mother, along with social interactions among siblings, shapes their abilities and behaviors. This strong emphasis on familial bonds highlights the importance of social structures within the family. Furthermore, understanding these reproductive strategies provides insight into the survival and adaptability of canids within their respective environments. Conservationists emphasize protecting breeding territories and family units to ensure the health and sustainability of canid populations, allowing future generations of these captivating animals to flourish.
The Ecological Impact of Canids
Canids play an integral role in regulating ecosystems, maintaining balance through their predatory behaviors. As apex predators, wolves influence the populations of herbivores, which directly affects vegetation dynamics. This cascading effect leads to improved biodiversity, as various plant species flourish without overgrazing by large prey populations. Similarly, other canids, including foxes and coyotes, help control smaller prey populations, such as rodents, which can thrive unchecked without natural predation. Their predation significantly impacts the populations of numerous small mammals and birds, ensuring a healthy ecological balance within their habitats. Canids also contribute to nutrient cycling; when they hunt or scavenge, they leave behind remains that enrich the soil, promoting healthier ecosystems. Understanding these ecological relationships is essential for wildlife management and conservation efforts. Protecting and promoting canid populations will enhance not only their survival but also the overall health of their ecosystems. As human activities increasingly encroach upon natural habitats, highlighting the ecological significance of canids offers insights into maintaining biodiversity and the delicate balance of life.
Additionally, canid conservation faces various challenges, including habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict, and climate change. Urbanization and agricultural expansion dramatically reduce the natural habitats available for these species, forcing them into closer proximity with human populations, often leading to conflicts. Wolves, in particular, may be viewed as threats to livestock, leading to retaliatory killings. Education and awareness initiatives are crucial in promoting coexistence strategies, helping humans understand canids’ ecological roles. Providing compensation for livestock losses, implementing non-lethal deterrents, and creating wildlife corridors are effective strategies to mitigate conflicts. Climate change further complicates their survival, altering habitats and affecting prey availability. Wildlife conservation organizations work diligently to address these challenges through research, advocacy, and community engagement. By investing in canid conservation, we contribute to preserving these magnificent animals and ensuring the stability of the ecosystems they inhabit. Collaborative efforts can foster understanding and respect between humans and wildlife, allowing future generations to appreciate and coexist with these exceptional creatures.
Conclusion: Protecting the Canids
In conclusion, understanding the Canidae family, including wolves, foxes, and their kin, reveals much about our natural world and wildlife ecosystems. These animals exemplify nature’s resilience and adaptability, each species holding a unique role within its environment. Their behaviors, social structures, and ecological contributions highlight the importance of preserving their populations and habitats. By fostering a better understanding of these captivating creatures, we promote wildlife conservation and the necessity for coexistence. Supporting endeavors to protect canids ensures that these extraordinary animals will continue to thrive in their natural habitats. Raising awareness, educating communities, and advocating for effective conservation policies are essential steps in securing the future of these wondrous beings. Together, we can showcase the balance of nature and the interconnectedness of all life forms. Engaging in efforts to conserve canids allows us to appreciate their vital roles in our ecosystems and the beauty of biodiversity. Future generations must also celebrate the incredible diversity found in the Canidae family, ensuring that wolves, foxes, and their relatives continue to inspire admiration in all who encounter them.